Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: 4M086 ACR Abstract: RA–DX, Manifestations, & Outcomes II: DX & Prognosis I (1858–1863)
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies (ACPAs) are highly specific for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) but lack sensitivity. We evaluated autoantibodies to protein-arginine deiminase 4 (anti-PAD4) in distinguishing ACPA negative RA from other ACPA negative rheumatic diseases, either alone or in combination with rheumatoid factor (RF) isotypes.
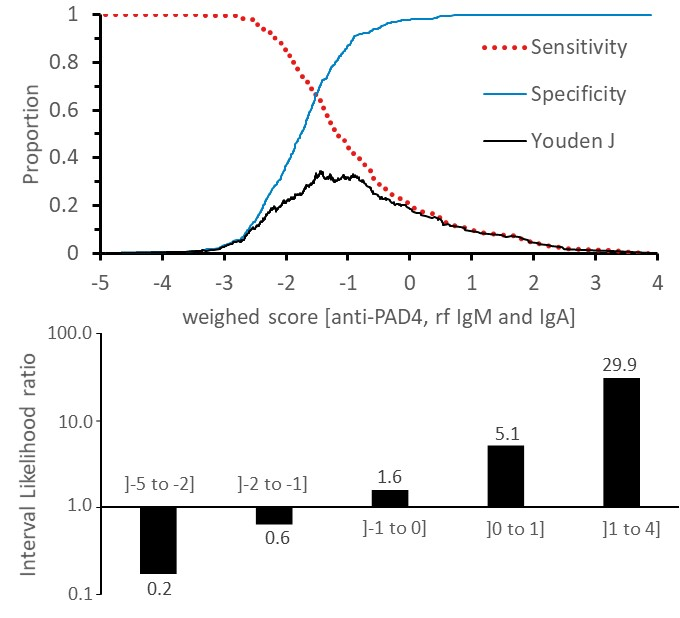
Methods: ACPA negative subjects (n = 1011, 205 RA and 806 non-RA [193 normal healthy individuals, NHV]) were selected from a cohort of 622 RA (34% ACPA negative, all fulfilling the 1987 or 2010 ACR criteria), and 830 non-RA (97% ACPA negative) consented subjects. ACPA status and IgM/IgA RF titers were measured using fluoroenzyme immunoassays (Thermofisher, Upsala Sweden). Anti-PAD4 titers were measured using a novel particle-based multi-analyte technology (research use only, Inova Diagnostics, San Diego, CA). ACPA negative subjects were grouped into a training set of 554 subjects (157 RA, and 397 non-RA [172 NHV]), and a subsequent independent validation set of 457 consecutive subjects (48 RA and 409 non-RA [21 NHV]). From the training set, a weighted scoring system cumulating log normalized anti-PAD4/RF isotypes titer estimates from multivariate logistic regression was calculated to distinguish ACPA negative RA from ACPA negative non-RA, and was applied to subsequent validation set. Diagnostic performances were estimated using area under the receiver operating curve (AUC), sensitivity, and specificity.
Results: Overall, anti-PAD4 (>1000 Units) was 19% sensitive and 95% specific in distinguishing ACPA negative RA from ACPA negative non-RA subjects (AUC = 0.65±0.02). AUCs for IgM and IgA RF isotypes were 0.67±0.02 and 0.51±0.02, respectively. From training set, multivariate logistic regression estimates for anti-PAD4 (0.36±0.11), and IgM/IgA RF isotypes (0.66±0.11 and -0.65±0.14, respectively) antibody systems were significantly and independently associated with RA (p <0.001; intercept = -2.59±0.66), and weighted cumulative score was 37% sensitive and 90% specific (cutoff >-0.4) (AUC = 0.72±0.02, Figure). In subsequent validation set, the training set based weighted cumulative score distinguished ACPA negative RA and ACPA negative non-RA groups with 35% sensitivity and 95% specificity (AUC = 0.68±0.02). Specificities in distinguishing ACPA negative RA from other ACPA negative rheumatic diseases was 92% for systemic lupus erythematosus (327/354), 97% for Sjogren’s syndrome (59/61), 95% for fibromyalgia (80/84), and 91% for NHV. Positivity rate of the weighted cumulative score was 30% among RA diagnosed for less than 2 years and rose to 50% among RA diagnosed for more than 10 years.
Conclusion: These preliminary data establish the feasibility of combining anti-PAD4 with RF isotypes to distinguish ACPA negative RA from other ACPA negative rheumatic diseases.
Disclosure: T. Dervieux, exagen, 3; L. Martinez Prat, None; J. Conklin, Exagen Diagnostics Inc., 3; C. Ibarra, Exagen Diagnostics, 1, 3; M. Mahler, Inova Diagnostics, 3; M. E. Weinblatt, None; J. Kremer, None.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dervieux T, Martinez Prat L, Conklin J, Ibarra C, Mahler M, Weinblatt ME, Kremer J. An Assay Panel Combining Anti-Protein Arginine Deiminase 4 with Rheumatoid Factor Isotypes Distinguishes Anti-Citrullinated Peptide Antibody Negative Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-assay-panel-combining-anti-protein-arginine-deiminase-4-with-rheumatoid-factor-isotypes-distinguishes-anti-citrullinated-peptide-antibody-negative-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-assay-panel-combining-anti-protein-arginine-deiminase-4-with-rheumatoid-factor-isotypes-distinguishes-anti-citrullinated-peptide-antibody-negative-rheumatoid-arthritis/