Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Bechet’s disease (BD) is a vasculitis characterized by oral aphtae, genital ulcers, skin lesions, uveitis and with less frequent involvement of the neurological, vascular and gastrointestinal tract. Amyloidosis is an uncommon but highly morbid complication of BD. This study is aimed to investigate frequency, clinicodemographic features and disease course of amyloidosis in Behcet’s Disease.
Methods: Patients with vasculitis diagnosis have been recording at Hacettepe University Vasculitis Center (HUVAC) database since October 2014. Enrolled 451 Adult BD patients were searched in terms of clinically and histopathologically amyloidosis. Demographics, clinical features and treatment characteristics of patients were re-evaluated.
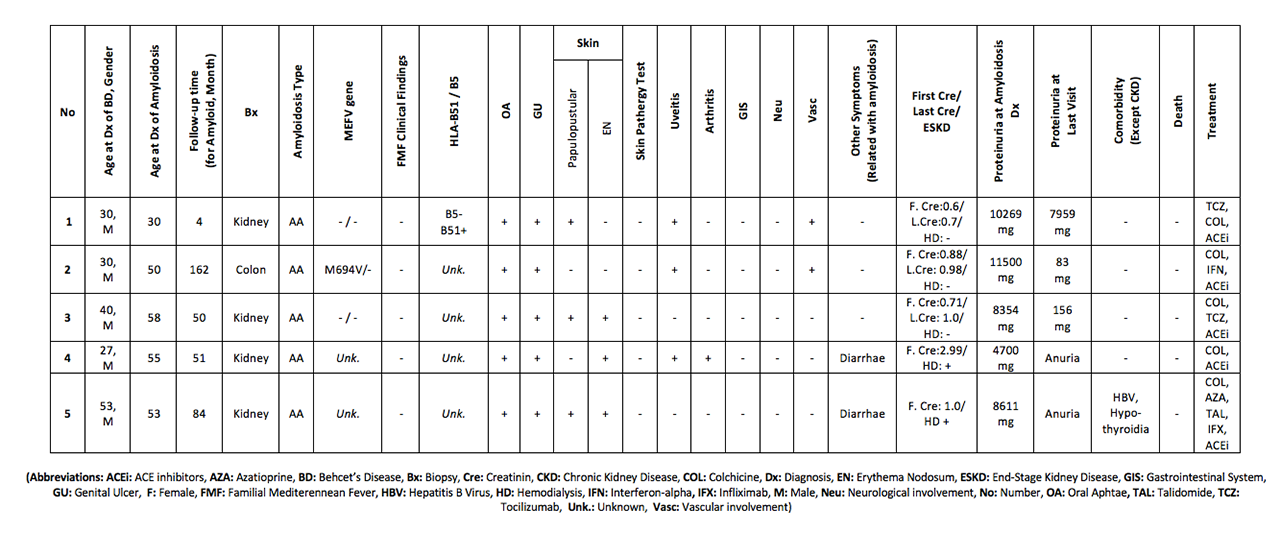
Results: Two hundred thirty seven (52.5%) patients were male and 211 (46.8%) of all patients had only mucocutaneous disease. Mean age at BD diagnosis was 30.9 ±8.2 years. Five patients (1.1%) had biopsy-proven AA-type amyloidosis diagnosis (Table). All BD-amyloidosis patients were male and presented with nephrotic-range proteinuria. Diarrhea was observed in two patients. There was no clinical evidence about familial mediterranean fever (FMF) and other rheumatic or infectious etiology for development of amyloidosis in any patient. All of five patients had genital ulceration. During follow-up time after amyloidosis diagnosis (median 51 month), end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) were developed in two patients (No: 4 and 5) and no death was observed. Interferon alpha and Tocilizumab were emerging drugs used in these patients. Proteinuria almost completely regressed in two patients (No: 2 and 3).
Conclusion: BD is one of the rare causes of the AA amyloidosis. Furthermore amyloidosis in BD is an important but it is relatively rare. Therefore other possible etiologies (e.g. FMF) should be excluded. Amyloidosis could result in life-threatening disease course. Amyloidosis-related symptoms and findings (e.g. proteinuria) may be treatable according to data from our cohort and literature. Definite predictors for development of ESRD are unknown in amyloidosis of BD. However early recognition of these patients and awareness of clinicians about this rare complication is quite important.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bolek E, Erul E, Yardımcı G, Kilic L, Akdoğan A, Karadag O. Amyloidosis in Behcet’s Disease: Experience of a Vasculitis Centre at Silk Road [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/amyloidosis-in-behcets-disease-experience-of-a-vasculitis-centre-at-silk-road/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/amyloidosis-in-behcets-disease-experience-of-a-vasculitis-centre-at-silk-road/