Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: ALPN-101 is an Fc fusion protein of a human inducible T cell costimulator ligand (ICOSL) variant immunoglobulin domain (vIgDTM) designed to inhibit simultaneously the CD28 and ICOS costimulatory pathways. CD28 and ICOS each play a role in T cell activation and adaptive immunity which can contribute to autoimmune disease when dysregulated. ALPN-101 has previously been shown to have potent immunosuppressive activity in various in vitro and in vivo models of disease, including acute graft versus host disease, inflammatory arthritis, and multiple sclerosis. We report here in vitro assays using PBMC from healthy donors vs. patients to analyze human T cell and B cell activation and suppression of antibodies and inflammatory mediators thought to contribute to the pathogenesis of Sjögren’s syndrome (SjS) and other connective tissue diseases. Additionally, the efficacy of ALPN-101 was confirmed in vivo in mouse immunization models, and in a mouse model of SjS.
Methods: Primary cell assays were performed with healthy donor and SjS patient PBMC stimulated with K562 cells expressing CD80, CD86, ICOSL, and anti-CD3 (OKT3) to evaluate the potency of ALPN-101 to suppress cytokine production. The activity of dual pathway inhibition by ALPN-101 was compared to the CD28-only inhibitor abatacept (CTLA-4-Fc) and to the ICOS pathway inhibitor prezalumab (AMG-557; anti-ICOSL, Creative Biolabs). ALPN-101 was compared to abatacept in vivo in standard mouse immunization models (KLH, sheep RBC), and in a model of SjS involving anti-PD-L1 antibody-mediated acceleration of sialadenitis in NOD mice.
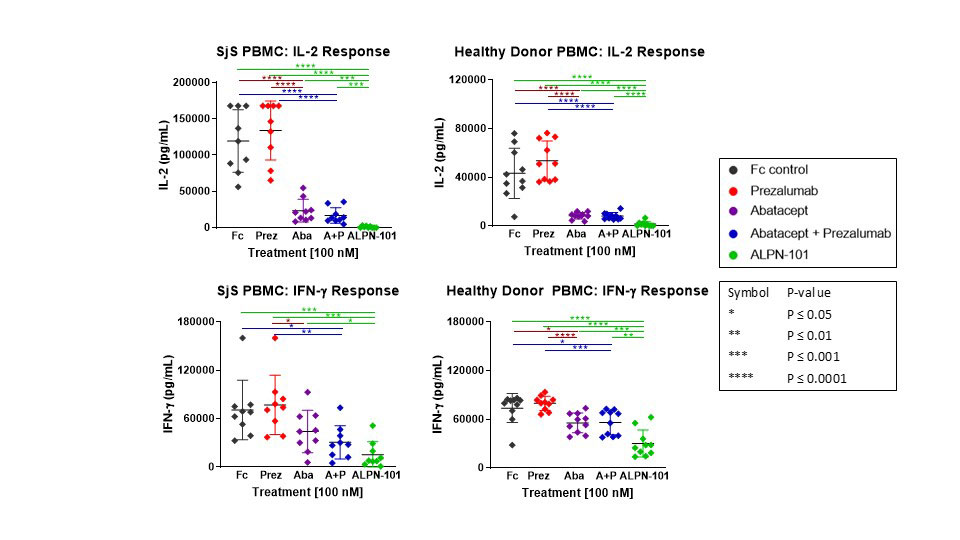
Results: Compared to abatacept, prezalumab, or combination abatacept + prezalumab, ALPN-101 demonstrated superior suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokine (i.e. TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-6, IL-17A, GM-CSF, etc.) release from stimulated healthy or SjS patient PBMCs (Fig. 1). ALPN-101 treatment inhibited antibody production in vivo in mouse immunization models, and suppressed proliferation and antibody production in human B cell/T cell co-cultures. In anti-PD-L1-treated NOD mice, ALPN-101 suppressed sialadenitis with activity superior to abatacept (Fig. 2); analyses of SjS-related autoantibodies are underway.
Conclusion: The efficacy of dual CD28/ICOS antagonist ALPN-101 is superior to CD28 or ICOS costimulatory pathway inhibitors, administered individually or in combination, in human in vitro and/or mouse in vivo translational studies. A Phase 1 clinical trial with ALPN-101 in healthy volunteers is underway, in preparation for future trials in multiple autoimmune diseases.
In vitro stimulation of healthy donor and Sjogren’s syndrome -SjS- patient PBMC with artificial APC [fixed K562 expressing cell surface OKT3 -anti-CD3-/CD80/ CD86/ICOSL-] at a 20:1 ratio. Test articles were added at 100 nM and supernatants were collected and assayed for cytokine concentrations after a 48 hr incubation. ALPN-101 demonstrated statistically significant superiority to prezalumab, abatacept, or a combination of prezalumab+abatacept for the majority of donors and analytes tested.
Six-week old female NOD/ShiLtJ mice were treated IP with a blocking anti-mouse PD-L1 antibody -to induce inflammation in the salivary glands, as described in Zhou et al., 2016, Sci. Rep. 6:39105- along with Fc control, abatacept, or ALPN-101 test articles on days 0, 2, 4, and 6. On Day 8, submandibular glands -SMG- were collected, sectioned, and stained with H&E and scored for inflammation on a scale of 0-3.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dillon S, Evans L, Lewis K, Bort S, Rickel E, Yang J, Wolfson M, Susmilch K, Mudri S, Levin S, Bhandari J, Ahmed-Qadri F, Rixon M, Hillson J, Peng S, Swiderek K. ALPN-101, a First-in-Class Dual ICOS/CD28 Antagonist, Suppresses Key Effector Mechanisms Associated with Sjögren’s Syndrome [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/alpn-101-a-first-in-class-dual-icos-cd28-antagonist-suppresses-key-effector-mechanisms-associated-with-sjogrens-syndrome/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/alpn-101-a-first-in-class-dual-icos-cd28-antagonist-suppresses-key-effector-mechanisms-associated-with-sjogrens-syndrome/