Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is an inflammatory disease that commonly treated with TNF inhibitors for controlling active inflammation. To predict treatment response to TNF inhibitors upon clinical disease activity, differentially expressed genes were screened and AIF-1 was identified and validated in serum protein level in our previous study.
To elucidate the mechanism of how systemically elevated allograft inflammatory factor-1(AIF-1) could affect refractoriness of TNF inhibitors in AS, we focused on the change of CD4+ helper T cells and monocytes induced by AIF-1. The effect of AIF-1 on the response to TNF inhibitors was also investigated.
Methods: Flow cytometry including intracellular staining, ELISA, and whole transcriptome analysis using RNA sequencing were performed in whole PBMCs, CD4+ T cells, and CD14+ monocytes after stimulating by AIF-1 in vitro. Healthy volunteers and AS patients provided peripheral blood. The effect of TNF inhibitors (adalimumab, etanercept) and tofacitinib were also examined in AIF-1 induced inflammatory response.
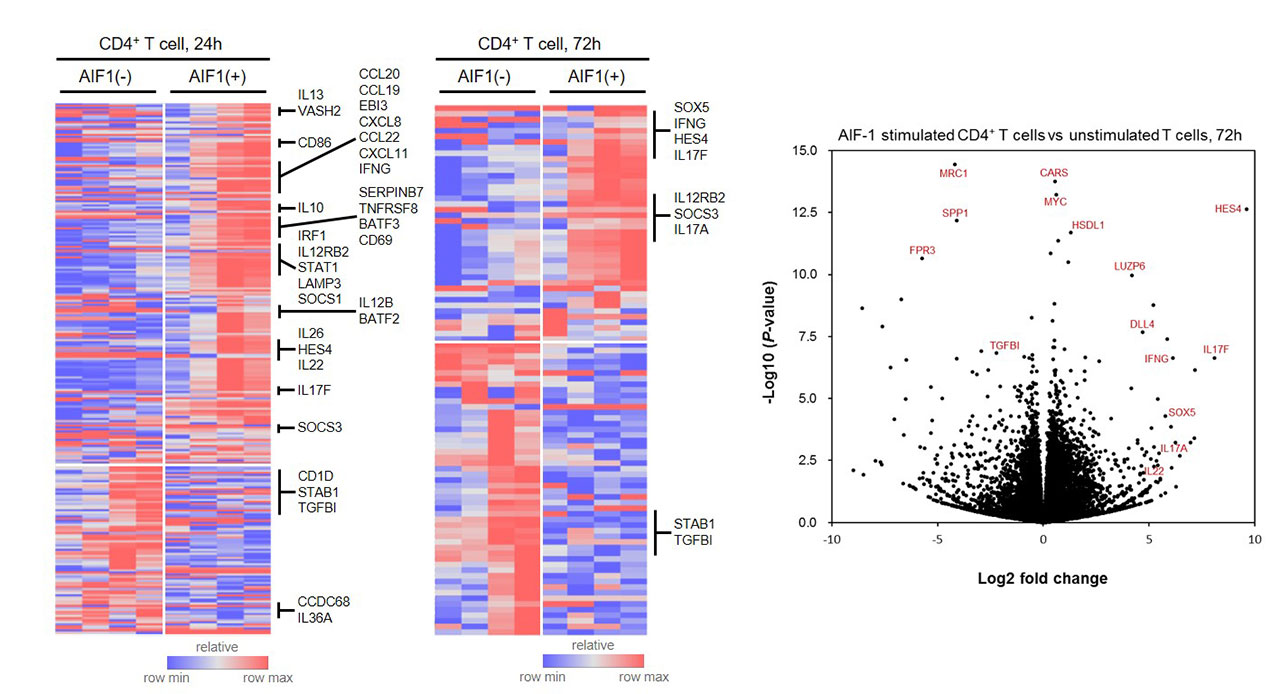
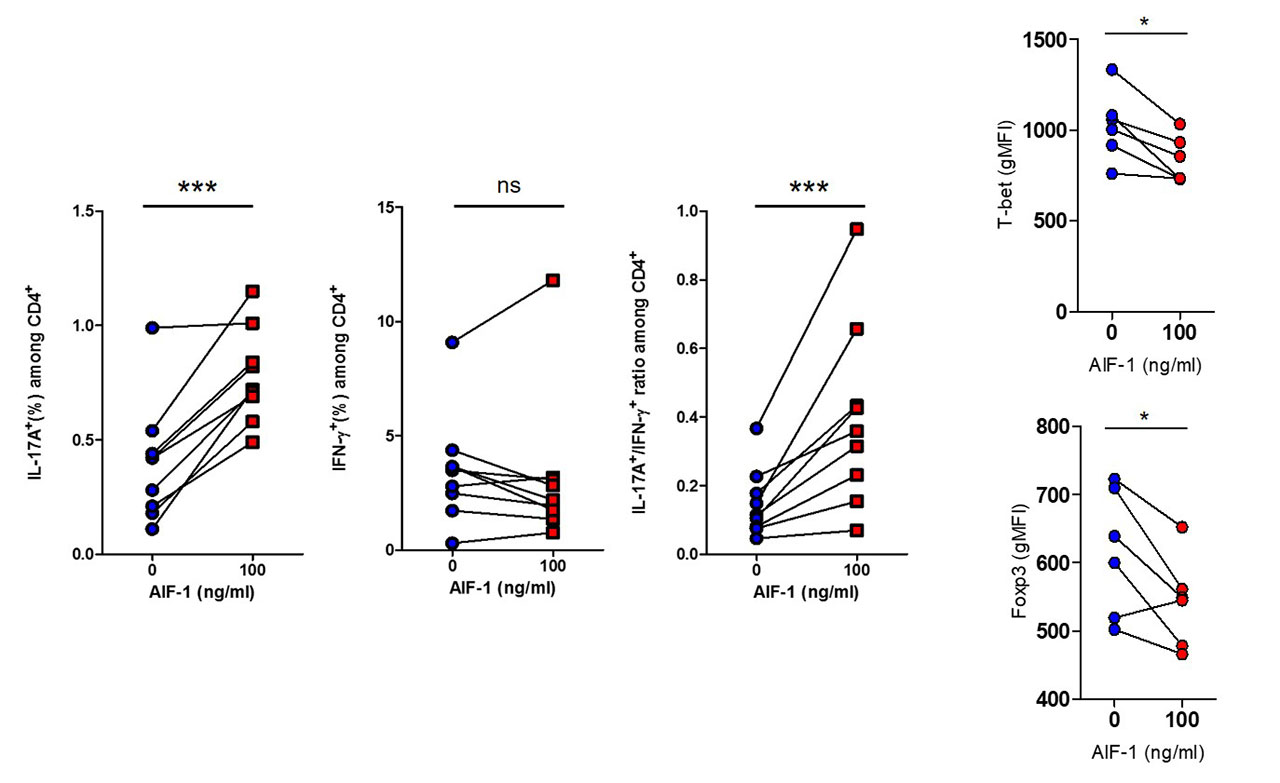
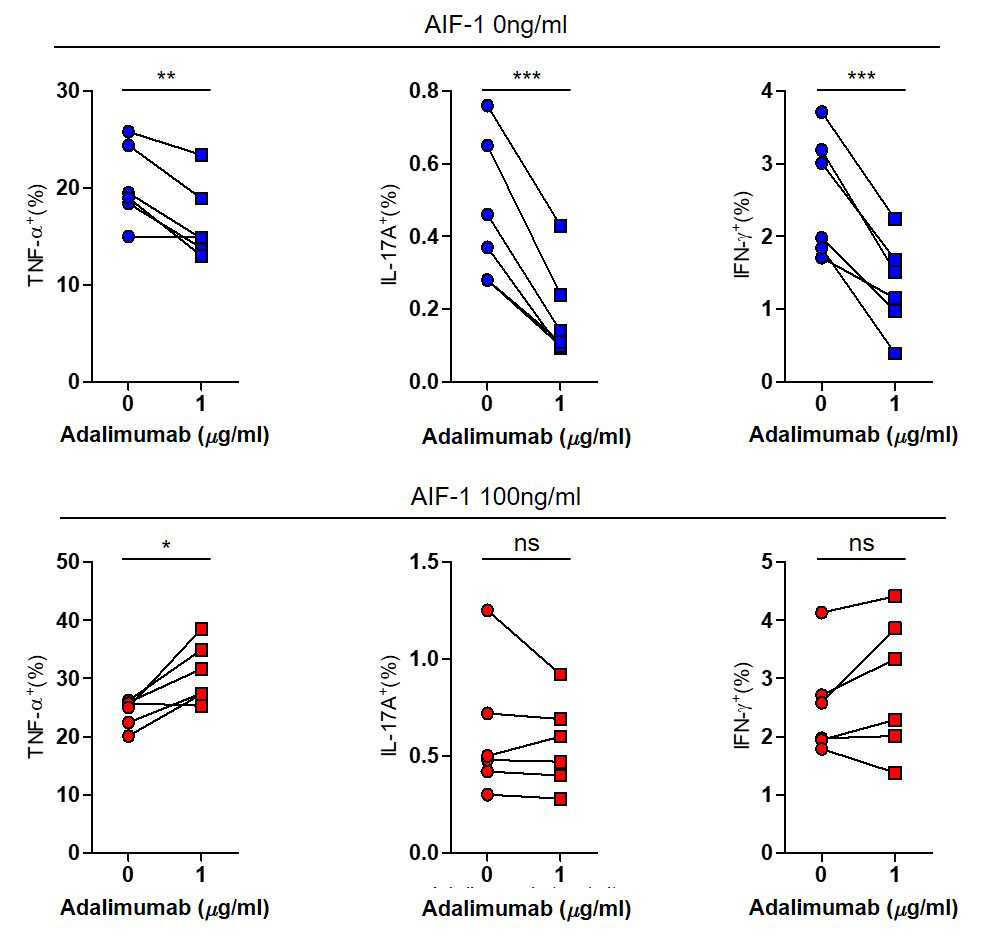
Results: AIF-1 aggravated inflammatory response via both directly increased TNF secretion from CD4+ T cells and monocytes (TNF dependent) and IL-17 associated pathways (TNF independent). This effect resulted in shifting of CD4+ T cell repertoire toward T helper 17 (Th17) rather than T helper 1 (Th1)(Figure 1). For the monocyte aspect, AIF-1 activated monocytes and increased surface expression of IL-17 receptor. In addition, TNF inhibition lost its positive effect of decreasing Th17 in the AIF-1 high environment. Whole transcriptome analysis showed that increased differentiation of Th17 cells by AIF-1 stimulation was prominent in both isolated CD4+ T cell and monocytes.
Conclusion: AIF-1 aggravated Th17 response of AS and contribute to poor response to TNF inhibitors. Use of IL-17 blockade could be an effective alternative therapy in AS patients who has high AIF-1 level.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lee J, Lee E, Choi J, Song Y, Shin E, Lee E. Allograft Inflammatory factor-1 Drives Th17 Like Pathologic Signature and Predict Poor Response to TNF Inhibitor in Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/allograft-inflammatory-factor-1-drives-th17-like-pathologic-signature-and-predict-poor-response-to-tnf-inhibitor-in-ankylosing-spondylitis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/allograft-inflammatory-factor-1-drives-th17-like-pathologic-signature-and-predict-poor-response-to-tnf-inhibitor-in-ankylosing-spondylitis/