Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with inflammatory/autoimmune rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (I-RMDs) were excluded from SARS-CoV-2 vaccination development programs. Therefore, concerns regarding the safety and effectiveness of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in this population arose. Previous reports capturing a wide range of I-RMDs have been reassuring [1], but more granular data on specific conditions is desirable.
We aim to describe adverse events (AEs) in the most common inflammatory joint diseases (IJD), namely rheumatoid arthritis (RA), axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), other peripheral spondyloarthritis (pSpA), and gout/other crystal arthritis (CA), in comparison with a group of patients with non-inflammatory rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (NI-RMDs).
Methods: Physician-reported registry of RMDs patients vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2. From 5 February 2021 to 3 March 2022, data were collected on demographics, vaccination, RMD diagnosis, immunomodulatory/immunosuppressive treatments and both early AEs and AEs of special interest. Data were analyzed descriptively.
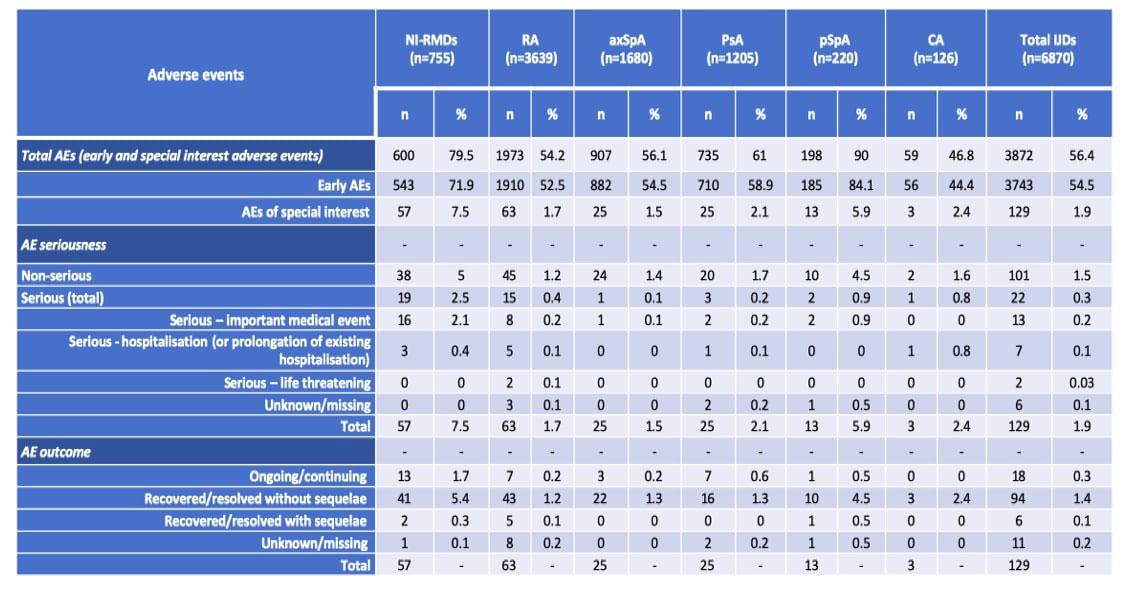
Results: A total of 7625 patients from 31 different countries were included: 6870 with IJD (63.9% female, mean age 58.8 years), namely 3639 with RA, 1680 with axSpA, 1205 with PsA, 220 with pSpA and 126 with CA, and 755 with NI-RMDs (83.2% female, mean age 68.5 years). Main results are presented on Table 1. Most patients received a full scheme of vaccination (IJD: n=5964, 86.8%; NI-RMDs: n=612, 81.1%), and the most commonly administered vaccine was Pfizer/BioNTech (first dose: IJD n=4385, 63.8%; NI-RMDs n=534, 70.7%). AEs were observed less frequently in IJD than in NI-RMDs, including early AEs (vaccine reaction) (IJDs: n=3743, 54.5%; NI-RMDs: n=543, 71.9%) and AEs of special interest (IJDs: n=129, 1.9%; NI-RMDs: n=57, 7.5%). The pSpA group was an exception, presenting a higher rate of early AEs (n=185, 84.1%) and AEs of special interest (n=13, 5.9%). The overall rate of serious AEs was very low (IJD: n=22, 0.3%; NI-RMDs: n=19, 2.5%), and similar across IJDs. The serious AE included events of arrythmia, coronary heart disease, syncopes, arterial hypertension, telogen effluvium, eczema/rash, erythema nodosum, gengivitis, abdominal pain, lymphadenopathy, dyspnoea, pharyngitis exacerbation of asthma, thoracic pain, pulmonary embolism, herpes zoster and shingles. The registry being mainly dedicated to inflammatory RMDs, there was probably a bias favoring registration pf patients with mechanical RMDs having had AE. No deaths were reported and most patients recovered from the AE without sequelae.
Conclusion: Serious AEs were infrequently reported in patients with RA, PsA, axSpA, pSpA and CA. The safety profile of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in patients with IJDs is reassuring.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Martins Fernandes A, Gomez-Puerta J, Sarmiento-Monroy J, Lawson-Tovey S, Hyrich K, Gossec L, Carmona L, Strangfeld A, Mateus E, Rodrigues A, Hachulla E, Mosca M, Durez P, Raffeiner B, Roux N, Eric V, Brocq O, Zepa J, Bulina I, Strakova E, Mlynarikova V, Šteňová E, Soubrier M, Mariette X, Machado P. Adverse Events in Patients with Inflammatory Joint Diseases: Results from the EULAR Coronavirus Vaccine (COVAX) Physician-reported Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/adverse-events-in-patients-with-inflammatory-joint-diseases-results-from-the-eular-coronavirus-vaccine-covax-physician-reported-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/adverse-events-in-patients-with-inflammatory-joint-diseases-results-from-the-eular-coronavirus-vaccine-covax-physician-reported-registry/