Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Post-COVID interstitial lung disease (post-COVID ILD) is a critical sequelae yet the role of immunomodulatory therapies remains unclear. We explored to characterize post-COVID ILD in patients with rituximab-treated immune mediated inflammatory diseases (IMID), and using adjunctive biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) as treatment.
Methods: In the NTUH-RTX cohort, we included IMID patients with COVID-19 infection during September 2022 and January 2024, received adjunctive bDMARDs in addition to tocilizumab (TCZ) for post-COVID ILD. Patients with repeat COVID-19 infection > 60 days apart were calculated as separate events. The demographics, serum markers and medical outcomes were systematically reviewed from the electronic health records.
In this analysis, the patients were categorized based on the mechanism of adjunctive bDMARDs received for post-COVID ILD: adjunctive abatacept (ABA), adjunctive belimumab (BEL) and TCZ-only. We defined the significant ferritin response as serum ferritin recovery over 80% or normalization after bDMARDs initiation. Outcomes included significant ferritin response, all-cause mortality, subsequent hospitalization and oxygen independence (within 90 days). Associations with outcomes were explored using Chi-square test or Mann-Whitney U-test. The Kaplan-Meier method with log-rank test was adopted for analysis. All analyses were conducted via R software.
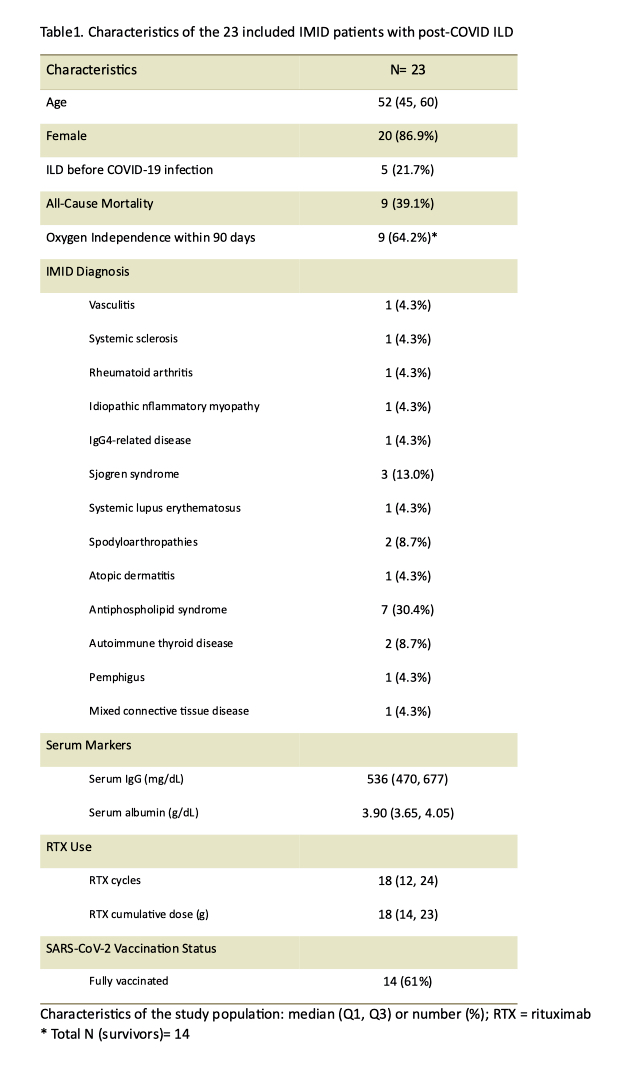
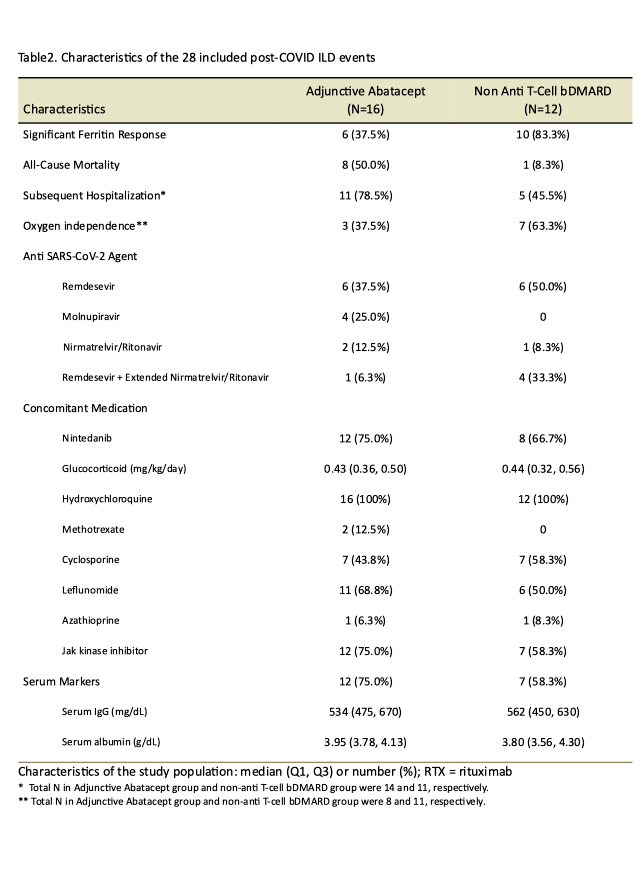
Results: A total of 28 post-COVID ILD events in 23 IMID patients were included. Table 1 and 2 summarized the characteristics. The median age was 52 and 21.7% had ILD before COVID-19 infection. Five patients had repeat COVID-19 infection. All-cause mortality was 39.1%. 64.2% of the survivors achieved oxygen independence within 90 days. Among the 28 included post-COVID ILD events, 16 (57.1%) in ABA group, 5 (17.9%) in BEL group and 7 (25.0%) in TCZ-only group. All events utilizing combinational extended antiviral regimen survived (Fig 1A).
Stratified with ABA exposure, no between-group difference regarding demographics, concomitant medications or serum markers yet numerically less combinational extended antiviral regimen users in the ABA group. Poor serum ferritin recovery (p=0.041), higher all-cause mortality (p=0.054), and numerically higher subsequent hospitalization (p=0.087) while less oxygen independence were seen in the ABA group (Fig 1B-D).
In comparing BEL vs. ABA group, higher serum ferritin significant responses (p=0.053) were seen in the BEL group. No mortality detected in the BEL group (Fig 1E-F). No differences regarding subsequent hospitalizations for the survivors in ABA and BEL groups.
Conclusion: This study highlights new evidence of belimumab use in IMID patients. Adjunctive belimumab for refractory post-COVID ILD exerts favorable ferritin recovery and survival. Combinational extended antiviral regimen potentially reduces mortality in post-COVID ILD. Further studies are needed to assess the clinical implications of this study, investigate the role of B-cell activating factor (BAFF) signaling in COVID-19 ILD especially for patients under chronic B cell depletion, and if belimumab’s anti-atherogenic potential attenuate post-COVID hyperinflammation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lai P, Lu C, Hsieh S. Adjunctive Belimumab Exerts Favorable Ferritin Recovery and Survival for Post-COVID Interstitial Lung Disease in Patients with Immune Mediated Inflammatory Diseases Treated with Rituximab: A Case Series [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/adjunctive-belimumab-exerts-favorable-ferritin-recovery-and-survival-for-post-covid-interstitial-lung-disease-in-patients-with-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases-treated-with-rituximab-a-case-seri/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/adjunctive-belimumab-exerts-favorable-ferritin-recovery-and-survival-for-post-covid-interstitial-lung-disease-in-patients-with-immune-mediated-inflammatory-diseases-treated-with-rituximab-a-case-seri/