Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: Measures Of Healthcare Quality Poster I: Testing, Screening, & Treating
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Gout is the most common inflammatory arthritis, affecting about 4% of the adult population in the United States. Management is often costly, with estimates around one billion dollars in yearly spending. The American College of Rheumatology recommends serum uric acid level (sUA) less than 6 mg/dL for the appropriate management of gout and prevention of recurrences. Despite the gout-related burden on the general patient population and its impact on the health-care system, guideline-directed management of patients with gout remains inconsistent among general practitioners. The degree to which general practitioners at the Miami VA adhere to guideline-directed management of veterans with gout is unknown – understanding discrepancies in care of veterans with gout can allow us to formulate and implement quality improvement projects to address these deficiencies and standardize care.
Methods: Retrospective chart review of veterans seen at the Miami VA primary care outpatient clinics was performed by searching ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes (274 and M10, respectively) between the years of 2017 to 2018. Patients not seen by a general practitioner within the last year were excluded. The dose of uric acid lowering drugs, as well the value and date of the last serum uric acid level were recorded. Descriptive analysis of these data points was conducted.
Results:
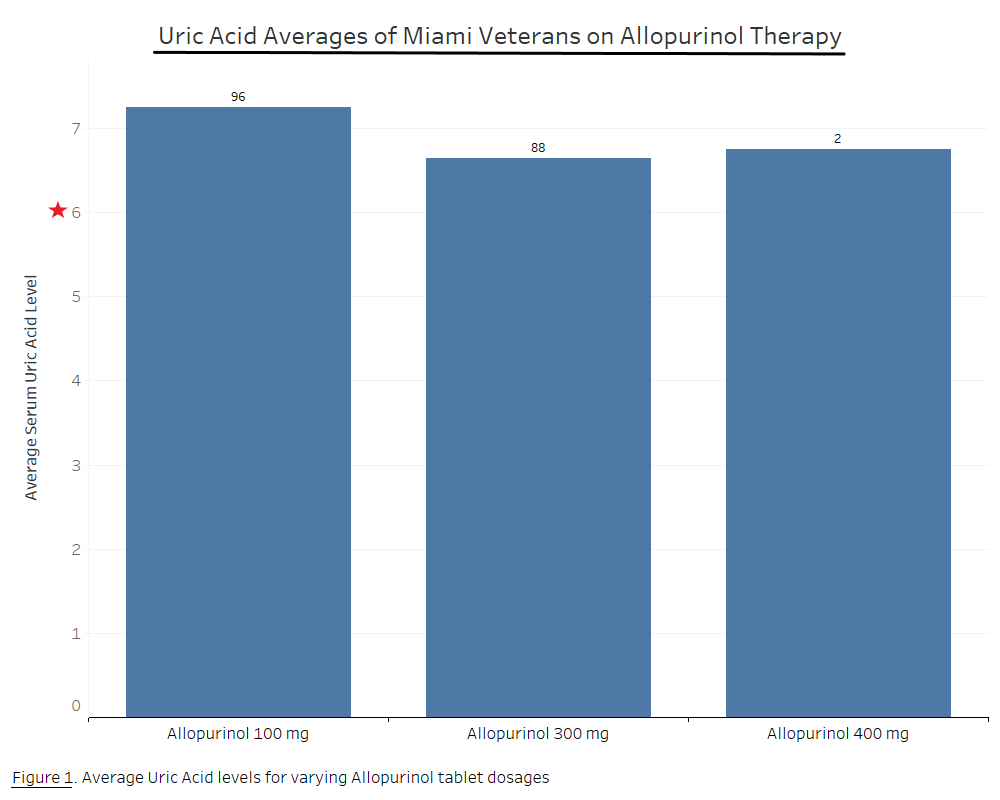
We identified 398 veterans with an ICD-9 or 10 diagnosis of gout managed by primary care providers, out of which 186 veterans were prescribed allopurinol. Of the 186 veterans prescribed allopurinol, 96 veterans were on 100 mg daily dosing, 88 veterans on 300 mg daily dosing, and 2 veterans on 400 mg daily dosing. The average sUA of veterans on the 100 mg dosing was 7.24 mg/dL, the average sUA level on the 300 mg dosing was 6.64 mg/dL, and the average sUA on the 400 mg dosing was 6.75 mg/dL.
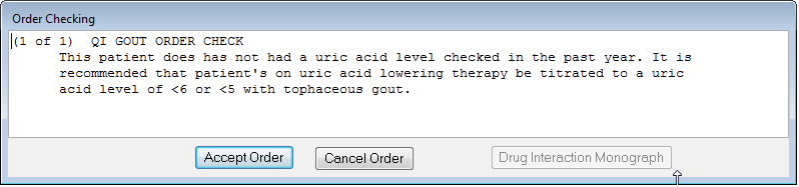
Among the 398 veterans with a diagnosis of gout, 171 of them had sUA checked in the past year, with an average sUA value of 6.94 mg/dL, irrespective if they were on allopurinol therapy. Of the 186 patients on allopurinol, 36% (67 patients) had no sUA level obtained over a one-year span to assess uric acid lowering response.
Conclusion: Our results reveal that adherence to guideline-directed management of veterans with gout is lacking. We found that a large number of veterans with gout did not have a follow-up sUA level over a one-year span, while among veterans whose sUA levels were recorded, the average sUA level failed to meet the guideline-accepted sUA level of less than 6 mg/dL, irrespective of allopurinol dosage. In an effort to improve standardization of care for the management of gout among our patients, several quality improvement measures were developed. First, an electronic alert in the VA electronic medical record was created to prompt primary care providers to order a repeat sUA when attempting to place a refill for urate lowering medications if this was not ordered within the year. The goal for sUA level is also displayed via the alert system. An order set has also been developed to assist providers in initiating uric acid lowering agents that includes sUA checks at appropriate intervals. We hope that implementation of these quality improvement measures will lead to improved management of veterans with gout.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Corbitt K, Lopez I, Dillon D. Adherence to Guideline Directed Management of Gout Among VA Providers [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/adherence-to-guideline-directed-management-of-gout-among-va-providers/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/adherence-to-guideline-directed-management-of-gout-among-va-providers/