Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: Abstracts: Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-5:30PM
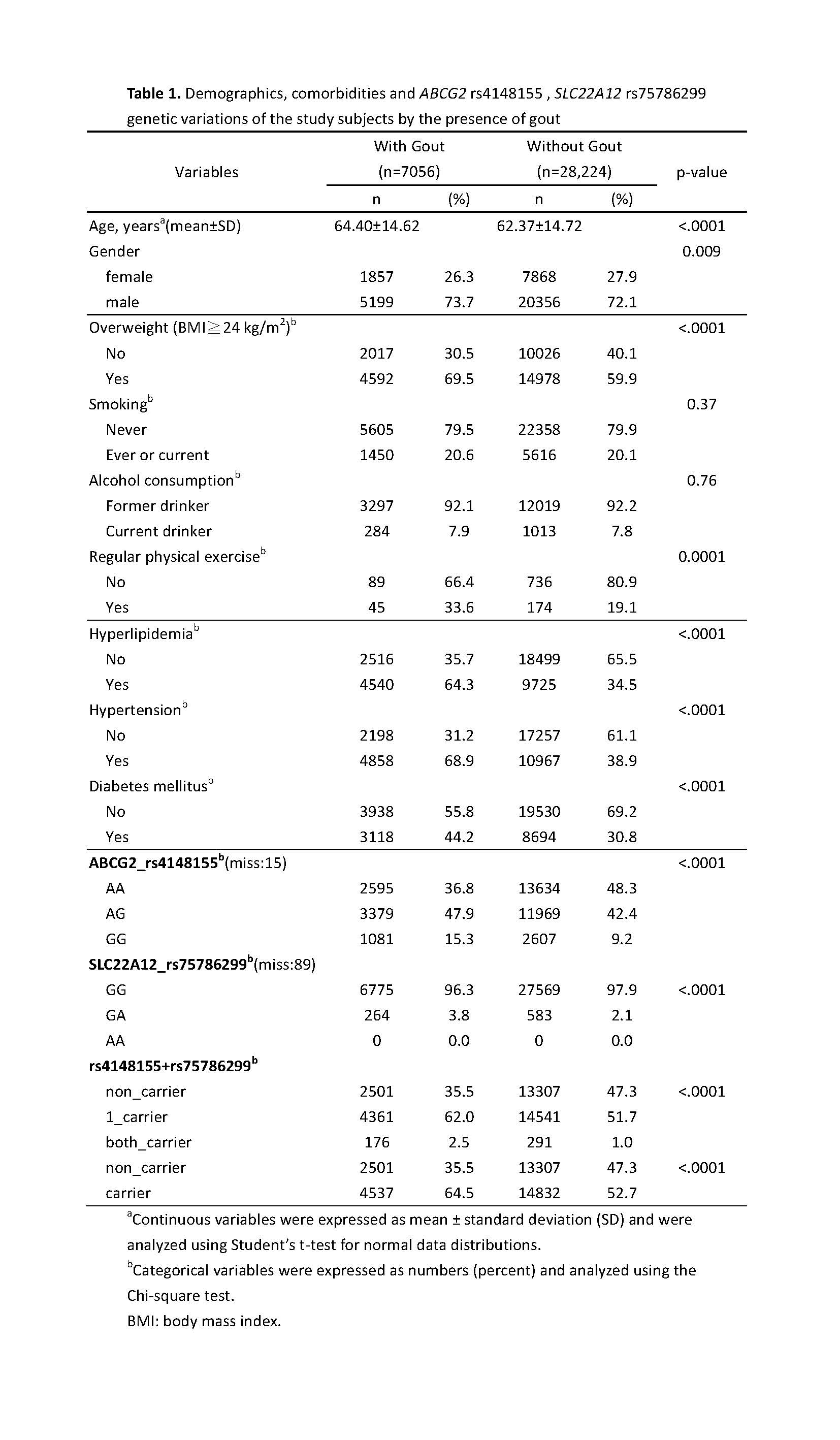
Background/Purpose: This study aimed to investigate the interaction between the ABCG2 rs4148155 and SLC22A12 rs75786299 variants and their association with incident gout and nephrolithiasis in the Taiwanese population to better understand the genetic loci regulating hyperuricemia and their contribution to nephrolithiasis development.
Methods: This retrospective case-control study involved 35,280 adults from the Taiwan Precise Medicine Initiative (TPMI) database. We examined the prevalence of gout and ultrasound confirmed nephrolithiasis as the primary and secondary outcome. Univariable and multivariable logistic regression models were used to explore the associations between genetic variants, serum uric acid levels, incident gout, and nephrolithiasis.
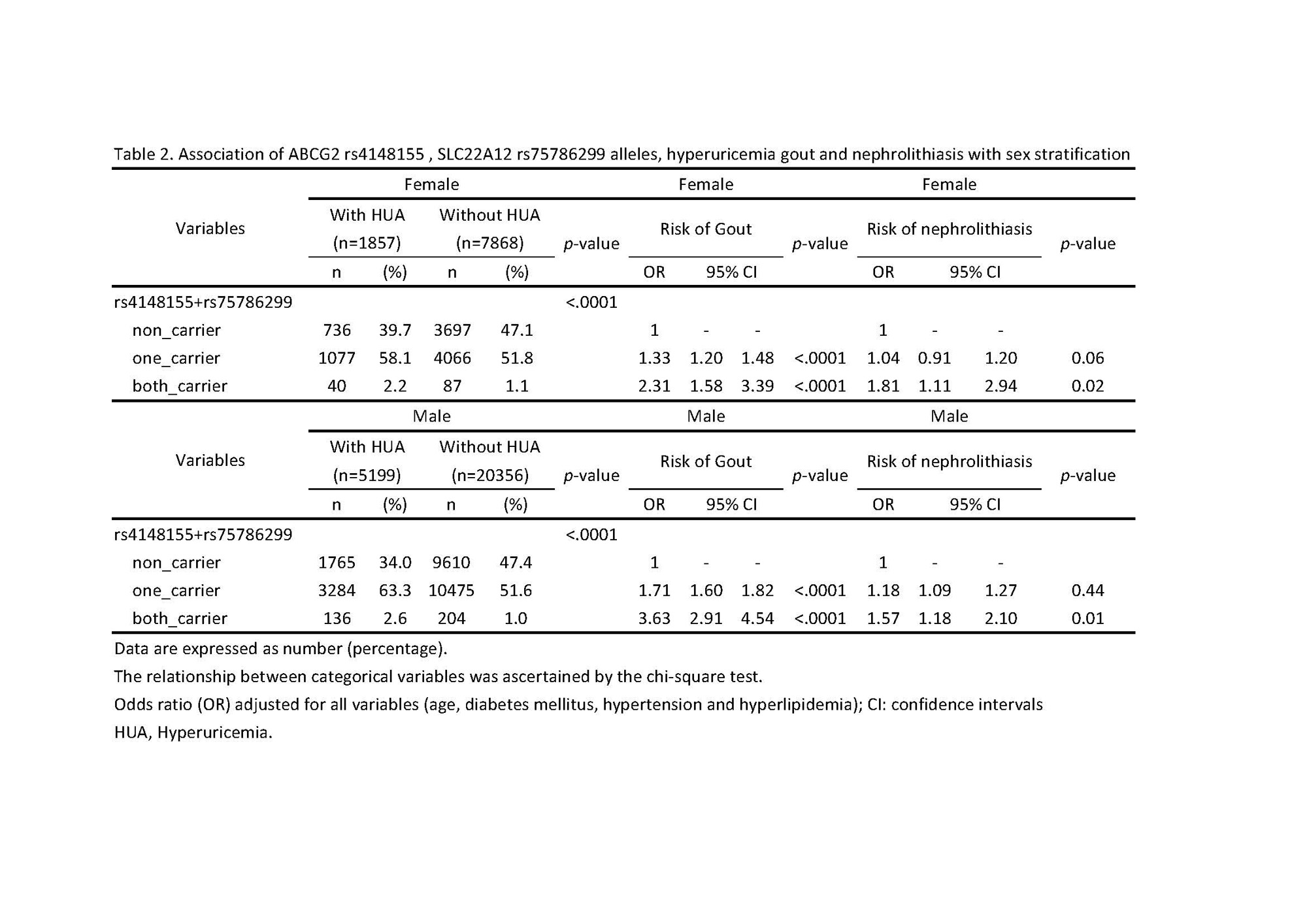
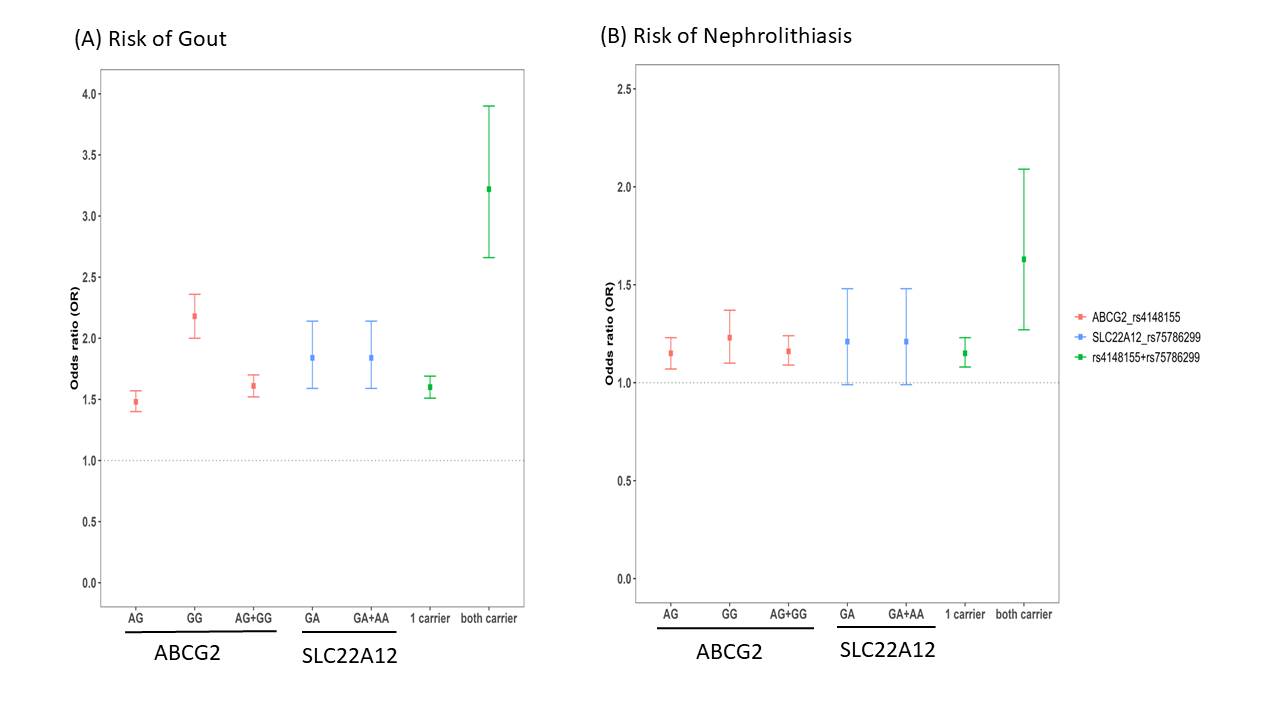
Results: The frequencies of the rs4148155 G allele and the rs75786299 A allele was 33% and 2.4%, respectively. Among participants, 7,056 were gout, and 4,110 had nephrolithiasis. Multivariable odds ratios (ORs) for gout were 1.65 (1.56-1.75) and 3.59 (2.92-4.41) among one and two carriers, respectively (p=0.01 and p< 0.001). For nephrolithiasis, the multivariable ORs were 1.09 (1.02-1.17) and 1.40 (1.09-1.81) for one and two carriers, respectively (p=0.01 and p=0.009). Sex-stratified analysis revealed an additive risk of gout and nephrolithiasis among carriers of these genetic variants, regardless of gender. Independent risk factors for nephrolithiasis included higher age, male gender, and the presence of gout, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia.
Conclusion: The study highlights a significant association between the rs4148155 (G) and rs75786299 (A) alleles and the development of gout and nephrolithiasis, indicating an additive risk among carriers. These findings support precision healthcare approaches for individuals with these genetic variants to target hyperuricemia, gout, and systemic comorbidities, ultimately preventing nephrolithiasis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lin C, Chen I, Huang W, Chen Y, Lin C, Chen Y. Additive Association of ABCG2 rs4148155 and SLC22A12 rs75786299 Polymorphisms with Hyperuricemia, Gout and Nephrolithiasis, a Hospital-Based, Case-Control Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/additive-association-of-abcg2-rs4148155-and-slc22a12-rs75786299-polymorphisms-with-hyperuricemia-gout-and-nephrolithiasis-a-hospital-based-case-control-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/additive-association-of-abcg2-rs4148155-and-slc22a12-rs75786299-polymorphisms-with-hyperuricemia-gout-and-nephrolithiasis-a-hospital-based-case-control-study/