Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Pre-existing structural damage in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) has been suggested to impact therapeutic improvements in disease activity and functional outcomes.1,2 Here we evaluate whether pre-existing structural damage in patients with active PsA limits functional improvements from treatment with certolizumab pegol (CZP) over 4 years. CZP is an Fc-free, PEGylated, tumor necrosis factor inhibitor that has shown long-term efficacy and safety in patients with PsA.3
Methods: Patients enrolled in RAPID-PsA (NCT01087788) with active PsA (≥3 tender joints; ≥3 swollen joints; ESR ≥28 mm/hour and/or CRP >upper limit of normal) who had failed treatment with ≥1 DMARD were randomized 1:1:1 to CZP 200 mg every 2 weeks (wks; Q2W), CZP 400 mg every 4 wks (Q4W) or placebo. Both CZP treatment arms received a loading dose of CZP 400 mg at Wks 0, 2, and 4, followed by the randomized dose regimen to Wk 216.3 Current analyses are based on data pooled across active treatment arms. Radiographs taken at baseline and Wks 12, 24, 48, 96, 168 and 216/withdrawal were read using the van der Heijde modified Total Sharp Score (mTSS) for PsA (scores based on average of two readers). Patients were grouped according to baseline mTSS quartiles (Q1–Q4). Disease activity was assessed using Disease Activity Index for Psoriatic Arthritis (DAPSA; high disease activity [HDA]: >28; moderate [MoDA]: >14–≤28; low [LDA]: >4–≤14; remission: ≤4). Physical function was assessed using the Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI; ≤0.5 defined as no adverse impact on physical function).4 The association of HAQ-DI, both change from baseline and achievement of ≤0.5, and concurrent DAPSA status was compared between the baseline mTSS groups using descriptive statistics.
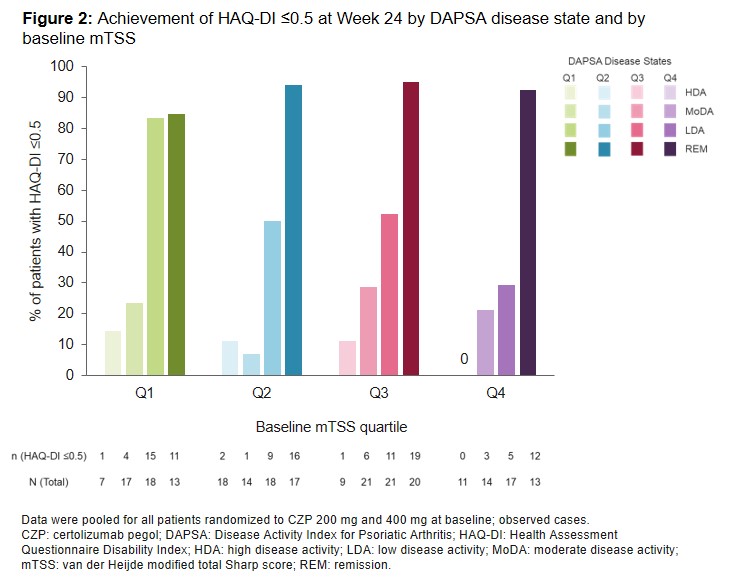
Results: Of 409 patients randomized, 407 were assessed for mTSS. As expected, at baseline, HAQ-DI scores were numerically higher in patients in mTSS Q3 and Q4 than Q1 (Table). With CZP treatment, across all mTSS quartiles, the proportion of patients in DAPSA remission increased over time (Figure 1). Across all mTSS quartiles (Q1–Q4), at least 80% of patients who achieved DAPSA remission also achieved HAQ-DI ≤0.5 (no adverse impact on physical function) at Wk 24 of CZP treatment. Over 80% of patients in mTSS Q1 who achieved either DAPSA remission or LDA also achieved HAQ-DI ≤0.5 at Wk 24. However, for mTSS Q2–Q4, >90% of patients in DAPSA remission achieved HAQ-DI ≤0.5 as compared with only ~30–50% of patients with DAPSA LDA (Figure 2).
Conclusion: These data indicate that patients achieving a high level of disease control (DAPSA remission) over 4 years of treatment with CZP are likely to achieve a normative state in terms of physical function, regardless of pre-existing radiographic damage. However, a state of DAPSA LDA may not result in normalization of function in patients with pre-existing radiographic damage. This supports the rationale of aiming for remission in PsA.
References
1. Bond SJ. ARD 2007;66:370–6; 2. Torre Alonso JC. Rheumatology 1991;30:245–50; 3. van der Heijde D. RMD Open 2018;4:e000582; 4. Strand V. ART 2018;20:269.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Coates L, van der Heijde D, Kristensen L, Tillett W, Eells J, Nurminen T, Deodhar A. Achievement of Remission Is Associated with Improvement in Functionality in Certolizumab Pegol-Treated Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis, Irrespective of Pre-Existing Radiographic Structural Damage [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achievement-of-remission-is-associated-with-improvement-in-functionality-in-certolizumab-pegol-treated-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-irrespective-of-pre-existing-radiographic-structural-damage/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achievement-of-remission-is-associated-with-improvement-in-functionality-in-certolizumab-pegol-treated-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-irrespective-of-pre-existing-radiographic-structural-damage/