Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Treatments, Outcomes, & Measures
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: A treat-to-target (TTT) approach results in superior outcomes compared to conventional care in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, TTT strategies are still not widely adopted in clinical practice and many patients never reach the target of remission. We compared achievement of remission in two early RA cohorts, examining whether a TTT strategy implemented in a randomized controlled trial (RCT) led to superior outcomes compared to a TTT approach implemented in an observational study.
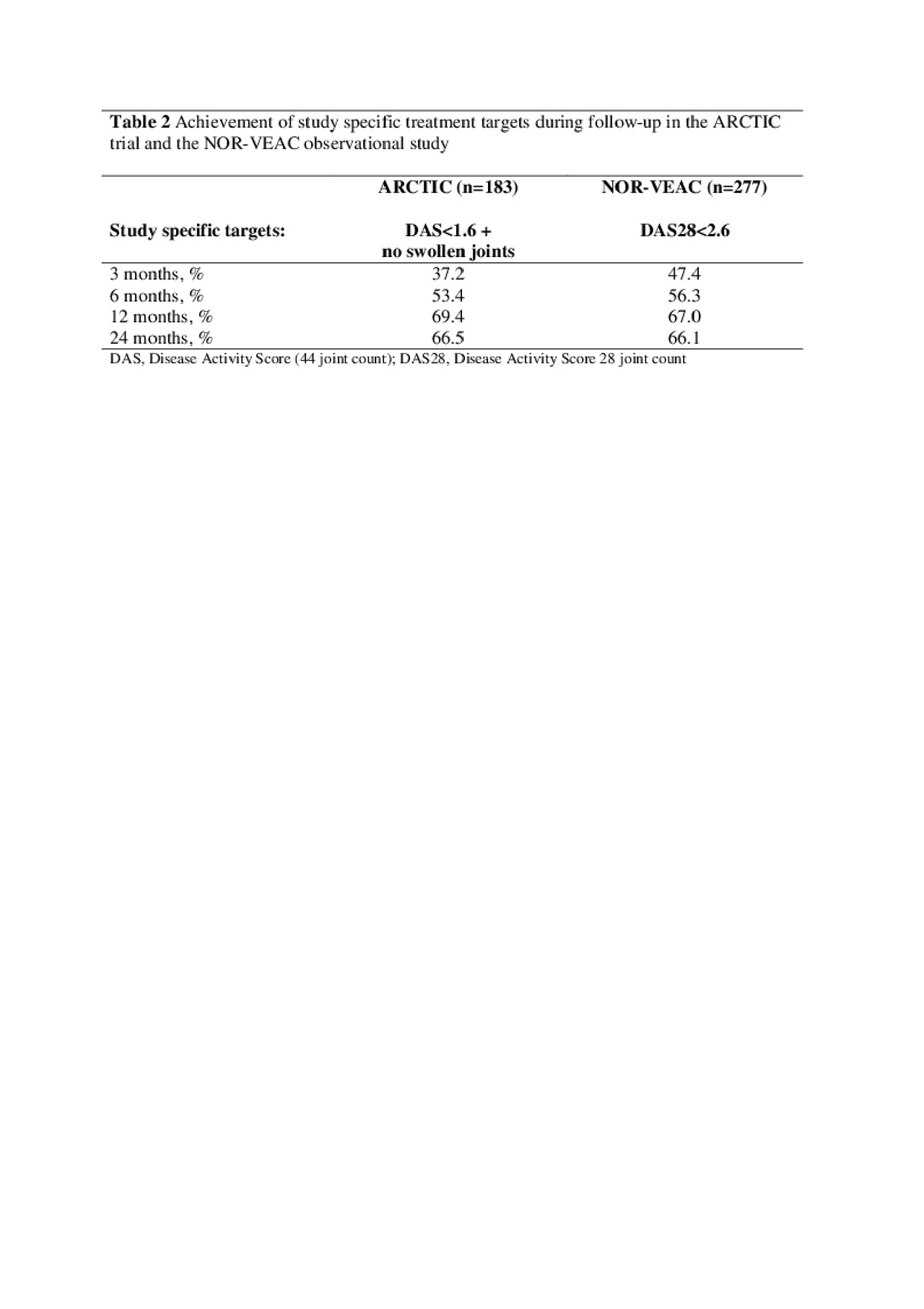
Methods: Data were provided by two Norwegian multicenter studies, the ARCTIC trial and the NOR-VEAC observational study. Both studies included DMARD-naïve RA-patients in the period 2010-2016 and implemented a TTT strategy. All patients fulfilled the 2010 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for RA. The target in the ARCTIC trial was stringent remission defined as a Disease Activity Score (DAS44) < 1.6 plus no swollen joints, while the target in the NOR-VEAC study was the less stringent DAS28 remission (DAS28< 2.6). In the current study we assessed: 1) achievement of the study specific treatment targets and 2) achievement of a stringent remission defined by the ACR/ EULAR Boolean criteria during follow-up over 24 months. We assessed achievement of the study specific targets using descriptive analyses and compared achievement of ACR/EULAR Boolean remission using logistic regression with inverse probability of censoring weights to account for missing data. For the comparative analyses we balanced the two cohorts on baseline covariates using propensity score weights.
Results: We included 183 patients from the ARCTIC trial and 277 patients from the NOR-VEAC study. After baseline balancing with propensity score weights, patients in the two cohorts were similar with regard to age, sex, ACPA positivity and disease activity (Table 1). Patients in both cohorts started with methotrexate (MTX) monotherapy. At 12 months, more patients in the NOR-VEAC study than in the ARCTIC trial were still treated with MTX monotherapy (79% vs. 67%), while more patients in ARCTIC had switched to another synthetic DMARD regimen or started a biologic DMARD. At 24 months, 25% of patients in both cohorts had switched to a biologic DMARD, while 17% of patients in the ARCTIC trial and 9% of patients in the NOR-VEAC study had switched to another synthetic DMARD regimen. More than half of patients in each cohort had reached the study specific targets at 6 months, and this increased to more than 2/3 in both cohorts at 12 and 24 months (Table 2). The odds of reaching ACR/EULAR Boolean remission during follow-up were higher in the ARCTIC trial compared to the NOR-VEAC study, with statistically significant differences at 3 months (OR 1.73; 95% CI 1.03-2.89), 12 months (OR 1.97, 95% CI 1.21-3.20) and 24 months (OR 1.82; 95% CI 1.05 – 3.16; Table 3).
Conclusion: Our results suggest that TTT is feasible and successful in clinical practice, similar to clinical trials. The odds of reaching the stringent ACR/EULAR Boolean remission during follow-up was higher in the ARCTIC trial than in the NOR-VEAC observational study, suggesting that targeting a more stringent remission improves the outcome of a TTT strategy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Norvang V, Brinkmann G, Yoshida K, Lillegraven S, Aga A, Sexton J, Tedeschi S, Uhlig T, Kvien T, Mjaavatten M, Solomon D, Haavardsholm E, Lyu H. Achievement of Remission in Two Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Cohorts Implementing Different Treat-To-Target Strategies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achievement-of-remission-in-two-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-cohorts-implementing-different-treat-to-target-strategies/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achievement-of-remission-in-two-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-cohorts-implementing-different-treat-to-target-strategies/