Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Minimal disease activity (MDA) is associated with clinically meaningful improvements in disease activity and patient (pt)-reported outcomes among pts with PsA.1 However, it is challenging for pts with PsA to achieve MDA, and even fewer achieve very low disease activity (VLDA).2
This retrospective study evaluated the achievement of MDA/VLDA and factors associated with MDA/VLDA achievement among pts with PsA initiating biologic/targeted synthetic DMARDs (b/tsDMARDs) between 03/2013 and 10/2023 in the CorEvitas PsA/SpA Registry.
Methods: Eligible pts had a follow-up visit 6 months (range: 5–9 months) post-treatment initiation (index) and sufficient criteria to compute MDA/VLDA at index and follow-up. Pts in MDA and VLDA at the index date were excluded from MDA and VLDA cohorts, respectively, while the VLDA cohort included pts in MDA at index.
Baseline characteristics were described at index using descriptive statistics. Achievement of MDA (≥5/7 criteria met)/VLDA (7/7 criteria met) were assessed at the 6-month follow-up visit. Relative risks (RR) of achieving MDA/VLDA were estimated using Poisson regression models; predictors of MDA/VLDA achievement were identified using adjusted multivariable models. MDA/VLDA achievement and predictors were stratified by b/tsDMARD experience at index.
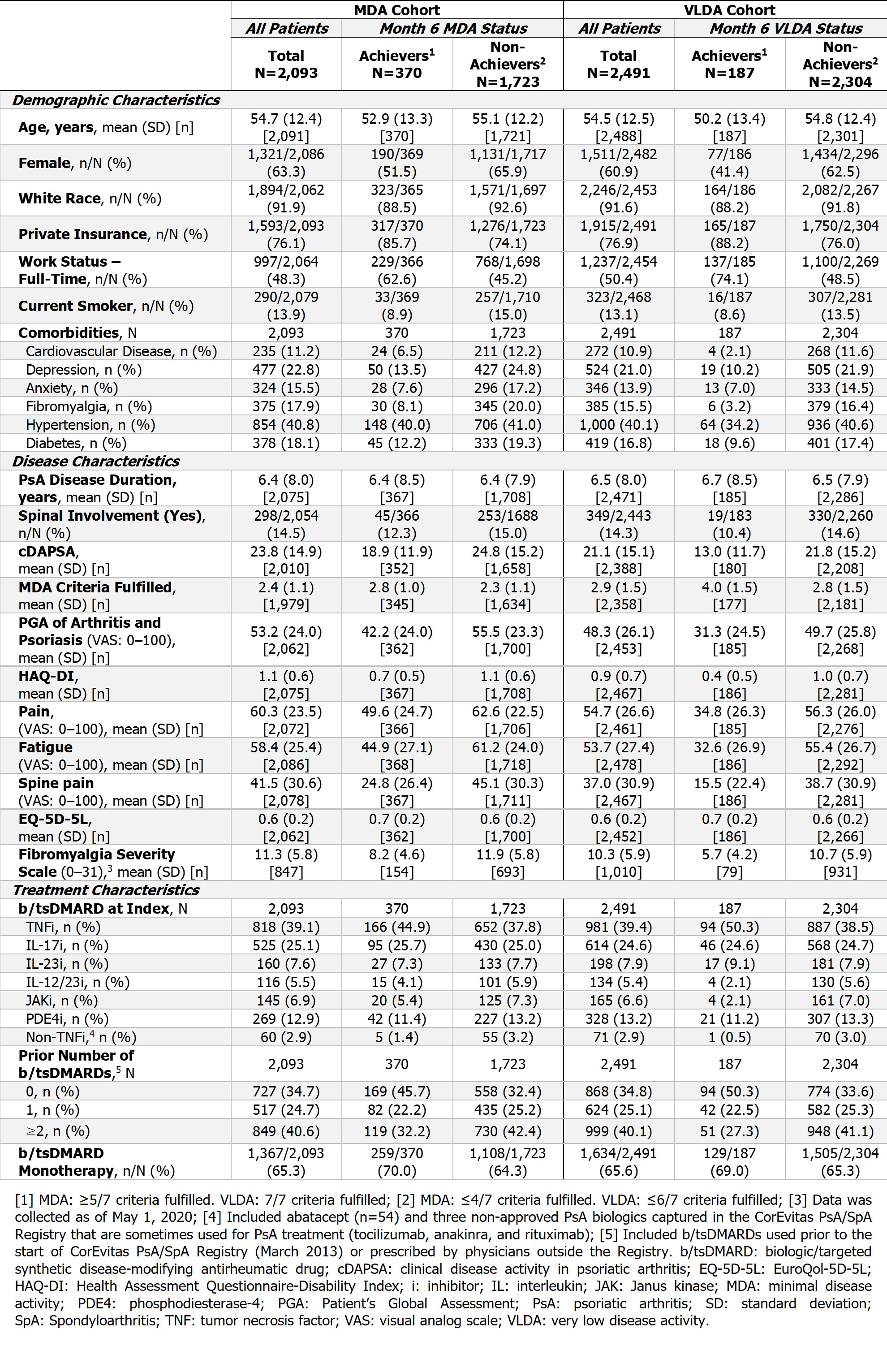
Results: There were 2,093 and 2,491 pts in the cohorts used to assess achievement of MDA and VLDA, respectively. In both cohorts, approximately 35% of pts were b/tsDMARD-naïve (MDA cohort: n=727; VLDA cohort: n=868) and 65% were b/tsDMARD-experienced (MDA cohort: n=1,366; VLDA cohort: n=1,623) at index. Baseline characteristics are summarized in the Table.
After 6 months, 18% (n=370/2,093) of pts in the MDA cohort achieved MDA; 23% (n=169/727) in the b/tsDMARD-naïve and 15% (n=201/1,366) b/tsDMARD-experienced subgroups. In the VLDA cohort, 8% (n=187/2,491) of pts achieved VLDA after 6 months; 11% (n=94/868) in the b/tsDMARD-naïve and 6% (n=93/1,623) b/tsDMARD-experienced subgroups.
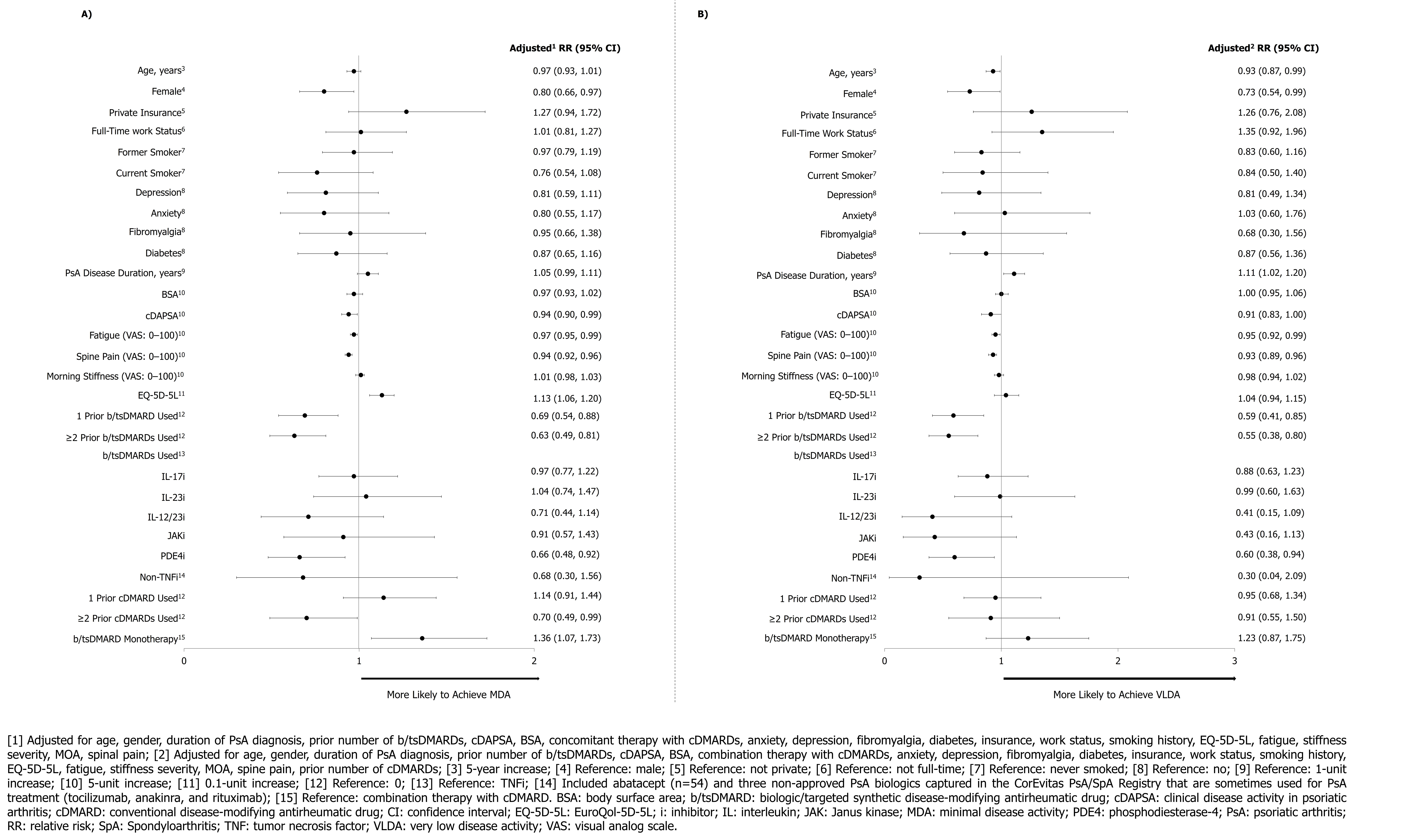
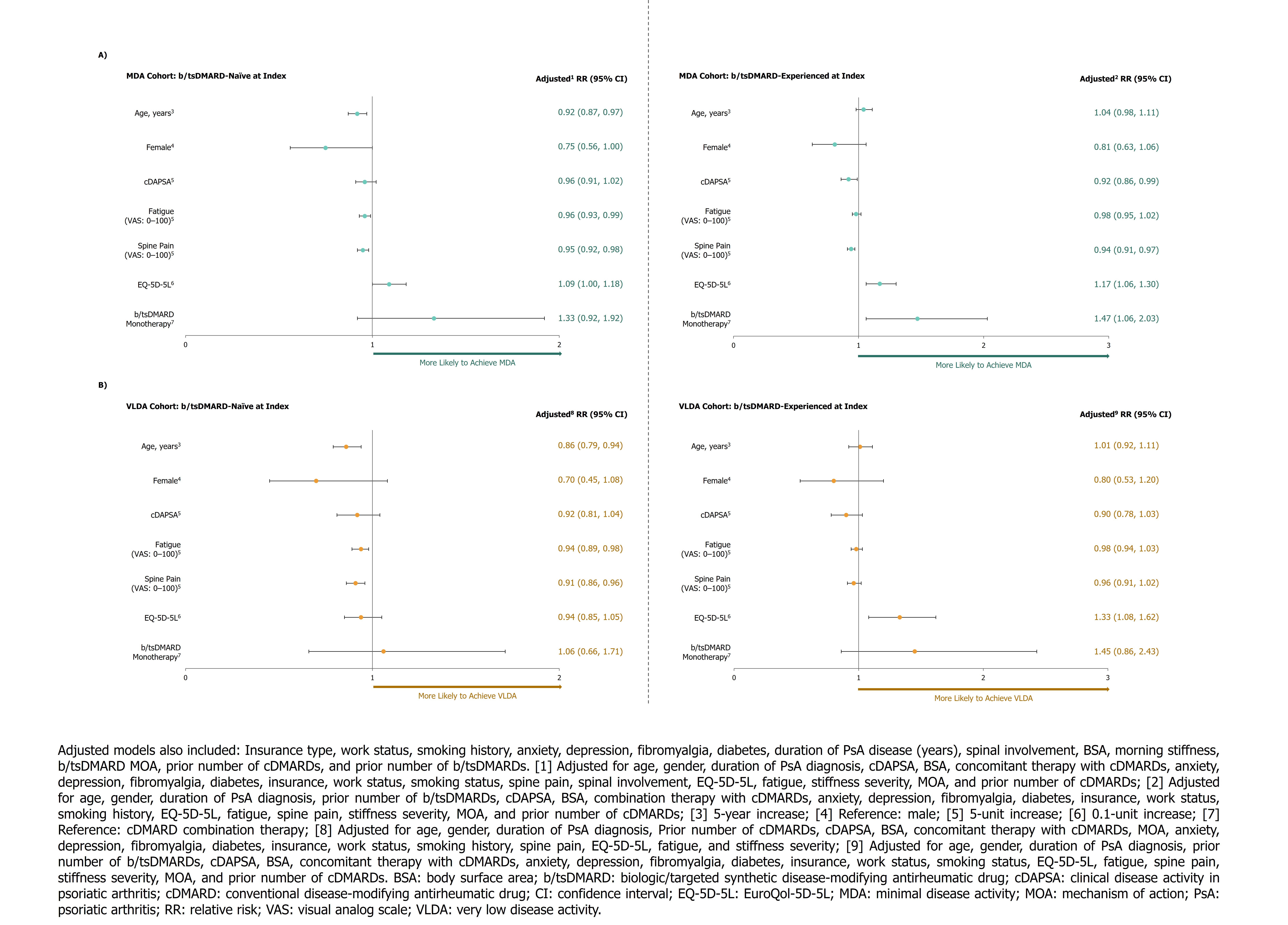
Multivariable-adjusted analysis showed that female sex, higher baseline clinical Disease Activity Index in Psoriatic Arthritis (cDAPSA) score (5-unit increase), fatigue, spine pain, and prior b/tsDMARD experience were associated with a decreased probability of achieving MDA/VLDA (Figure 1). Pts with a higher baseline EuroQol-5D-5L (EQ-5D-5L) score (0.1-unit increase) were 13% more likely to achieve MDA (Figure 1). Pts treated with b/tsDMARD monotherapy were 36% more likely to achieve MDA compared with conventional DMARDs and b/tsDMARDs combination therapy (Figure 1). Factors associated with MDA/VLDA achievement were generally similar regardless of b/tsDMARD experience at index (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Relatively few pts achieved MDA/VLDA after 6 months of b/tsDMARD treatment. Pts with worse baseline disease activity and pt-reported outcomes were less likely, while pts with higher baseline EQ-5D-5L score (denoting greater baseline quality of life) and those on b/tsDMARD monotherapy, were more likely to achieve MDA/VLDA after 6 months of treatment. These data highlight unmet needs in PsA management.
References:
1. Ogdie A. Arthritis Rheumatol 2021;73 Suppl 9:1–4259; 2. Ortolan A. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2023;62:152237.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ogdie A, Song C, Middaugh N, Marchese M, Eliot M, Low R, Mease P. Achievement of Minimal and Very Low Disease Activity Among Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis Initiating Biologic or Targeted Synthetic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in the CorEvitas PsA/SpA Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achievement-of-minimal-and-very-low-disease-activity-among-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-initiating-biologic-or-targeted-synthetic-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-in-the-corevitas-psa-spa-re/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achievement-of-minimal-and-very-low-disease-activity-among-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-initiating-biologic-or-targeted-synthetic-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs-in-the-corevitas-psa-spa-re/