Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Previous reports of dysphagia in patients with inflammatory myopathy (IM) have been focused on detection, intervention and rehabilitation. However, whether dysphagia with abnormal videofluoroscopy swallow study (VFSS) findings is in relation to clinical manifestations and treatment response is not known. We hypothesized that clinical entities in IM patients with dysphagia would be distinct from non-dysphagia patients and abnormal VFSS finding could be a predictor of prognosis.
Methods: Total 236 patients with IM were reviewed in this study. Of them, the patients with dysphagia were evaluated with clinical functional scale, VFS scale, new VFSS scale, and American Speech-Language-Hearing Association National Outcome Measurement System swallowing scale. VFSS score was categorized into oral, pharyngeal and esophageal phase based on modified Logemann’s methods. Association between VFSS scale and serum creatinine kinase (CK), clinical findings, or treatment response were analyzed.
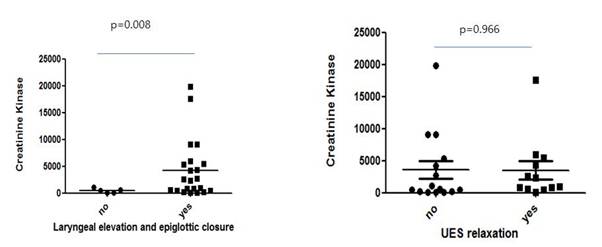
Results: Among 236 IM patients, 28 patients had IM related dysphagia (26 with dermatomyositis, 1 polymyositis and 1 inclusion body myositis). Ten male and 18 female with mean age of 42.7 were included. Dysphagia was a presenting symptom in 5 patients (17.9%) and rest of patients developed dysphagia in average 221 days later. The VFSS results showed more prevalent abnormalities in pharyngeal phase than oral phase (n=26 vs. n=9). Baseline CK level was higher in delayed laryngeal elevation and epiglottic closure (LEEC) patients than in normal LEEC patients (473.8 ± 415.6 mg/dl vs 3931.7 ± 5532.3 mg/dl, p=0.008) (Figure). There was no correlation in total VFSS score with baseline CK level. Intravenous immunoglobulin were significantly more prescribed in delayed LEEC patients than in normal LEEC patients (OR=10.7, p=0.047). Frequency of pulmonary involvement and malignancy were significantly different between patients with dysphagia and patients without dysphagia (7.1% vs 40.4%, p<0.001, 35.7% vs 9.6%, p=0001, respectively) (Table 1).
Conclusion: Abnormal VFSS findings in IM Patients with dysphagia were more prominent in pharyngeal phases than oral phases. Delayed LEEC was associated with higher baseline CK level and use of intravenous immunoglobulin. IM patients with dysphagia showed lower pulmonary involvement and higher malignancy. These results indicate that dysphagia in IM is not only a localized symptom or disabling condition, but also a predictor of prognosis
Table 1. Comparison of clinical characteristics between IM patients with dysphagia versus without dysphagia.
|
Baseline characteristics |
Dysphagia (n=28) |
Nondysphagia (n=208) |
p-value |
|
Male/female (n, %) |
10/18 (35.7/64.3) |
47/161 (22.6/77.4) |
0.157 |
|
Age (mean ± SD) |
42.7 ± 21.6 |
46.3 ± 14.5 |
0.244 |
|
DM/PM/IBM (n, %) |
26/1/1 (92.9/3.6/3.6) |
156/51/1 (75.0/24.5/0.5) |
0.013 |
|
Creatinine kinase |
3869.8 ± 5916.3 |
1546.3 ± 3529.9 |
0.004 |
|
Interstitial lung disease (n, %) |
2 (7.1) |
84 (40.4) |
<0.001 |
|
Malignancy (n, %) |
10 (35.7) |
20 (9.6) |
0.001 |
Disclosure:
H. W. Kim,
None;
H. Kim,
None;
S. H. Chang,
None;
H. J. Oh,
None;
M. J. Yoon,
None;
B. S. Ku,
None;
B. M. Oh,
None;
E. Y. Lee,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/abnormal-videofluoroscopy-swallow-study-finding-in-inflammatory-myopathy-patient-with-dysphagia-as-predictor-of-prognosis/