Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Vascular inflammation and damage are implicated in the pathogenesis of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM), particularly dermatomyositis (DM). High and low density lipoprotein (HDL, LDL) particles strongly influence the vascular endothelium, but little data has characterized these particles in IIM patients. The current work evaluates standard cholesterol levels as well as the particle number and size of HDL, LDL and very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) in IIM patients compared to healthy controls.
Methods: In a cross sectional analysis of 87 patients with IIM and 47 healthy controls (HC), we measured the quantitative lipoprotein profile by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR). Cardiovascular risk factors and medications were obtained by questionnaire/chart review, and inflammatory markers and autoantibodies (ab) were measured by standard methods. Myositis disease activity was assessed using physician global 100 mm visual analogue scales (VAS) and CPK levels.
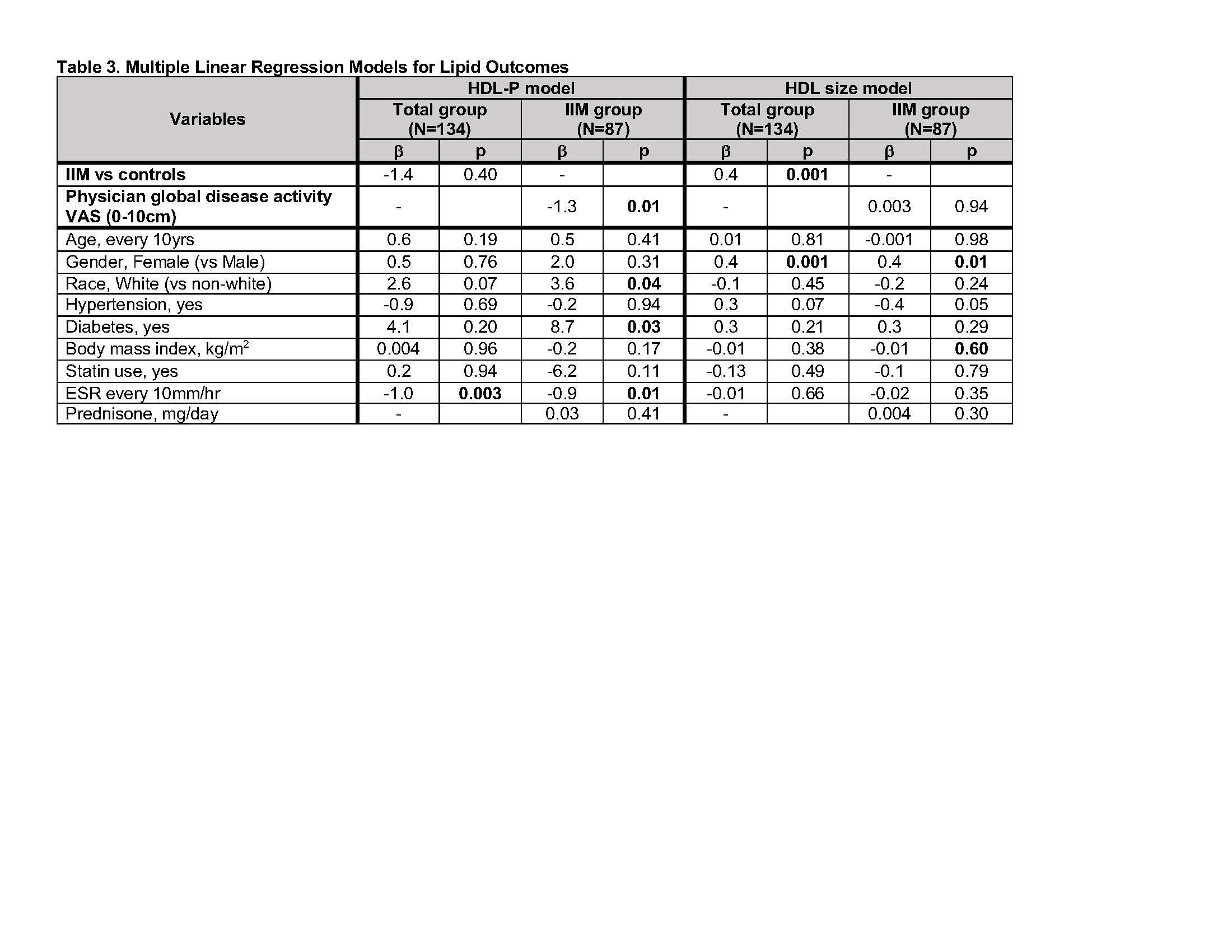
Results: The majority of patients in the IIM group had DM with a mean disease duration of 5 years and moderate disease activity (Table 1). Traditional fasting cholesterol levels were generally similar between patients with IIM and HC with mildly elevated triglycerides in the IIM group. Multiple differences in particular size and number including higher LDL particle number (LDL-P), larger HDL and VLDL size, and lower HDL particle number (HDL-P) were noted between IIM patients and HC. Multivariate (MV) models adjusted for demographics, factors known to affect lipid particle size/number (hypertension, diabetes, body mass index, statin use) and variables different in univariate comparison (ESR), were constructed for each significant lipid variable in table 1. Larger HDL size was strongly associated with IIM diagnosis, and smaller HDL-P was associated with disease activity in MV models. Triglycerides, LDL-P number and VLDL size were no longer associated with IIM diagnosis or disease activity in MV analysis. Patients with p155/140 ab had significantly larger HDL size, and patients with MDA5 ab had significantly lower HDL-P compared to patients without ab.
Conclusion: In a cross sectional analysis of IIM patients and healthy controls, larger HDL size was strongly associated with IIM diagnosis, and lower HDL-P was associated with higher physician global disease activity by VAS. Altered HDL size and particle number have previously been associated with vascular risk, and further work is needed to evaluate their role in vascular damage in patients with IIM.
IMAGE UNAVAILABLE
IMAGE UNAVAILABLE
>
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bae S, Golub I, Shahbazian A, Wang J, Charles-Schoeman C. Abnormal High Density Lipoprotein Particle Size and Number in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/abnormal-high-density-lipoprotein-particle-size-and-number-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/abnormal-high-density-lipoprotein-particle-size-and-number-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathies/