Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Emerging evidence suggests dysregulated T cell activation in systemic sclerosis (SSc). Co-inhibitory-receptors such as TIM-3, PD-1 and LAG-3 are key factors in immune homeostasis and autoimmunity. These receptors regulate T-cell responses by inhibiting effector T-cell activation directly by affecting antigen presentation. Soluble forms of these molecules are generated by proteolytic cleavage of membrane-bound proteins. We evaluate the potential role of these soluble co-inhibitory markers in SSc and their impact on disease outcomes in diffuse SSc (dcSSc).
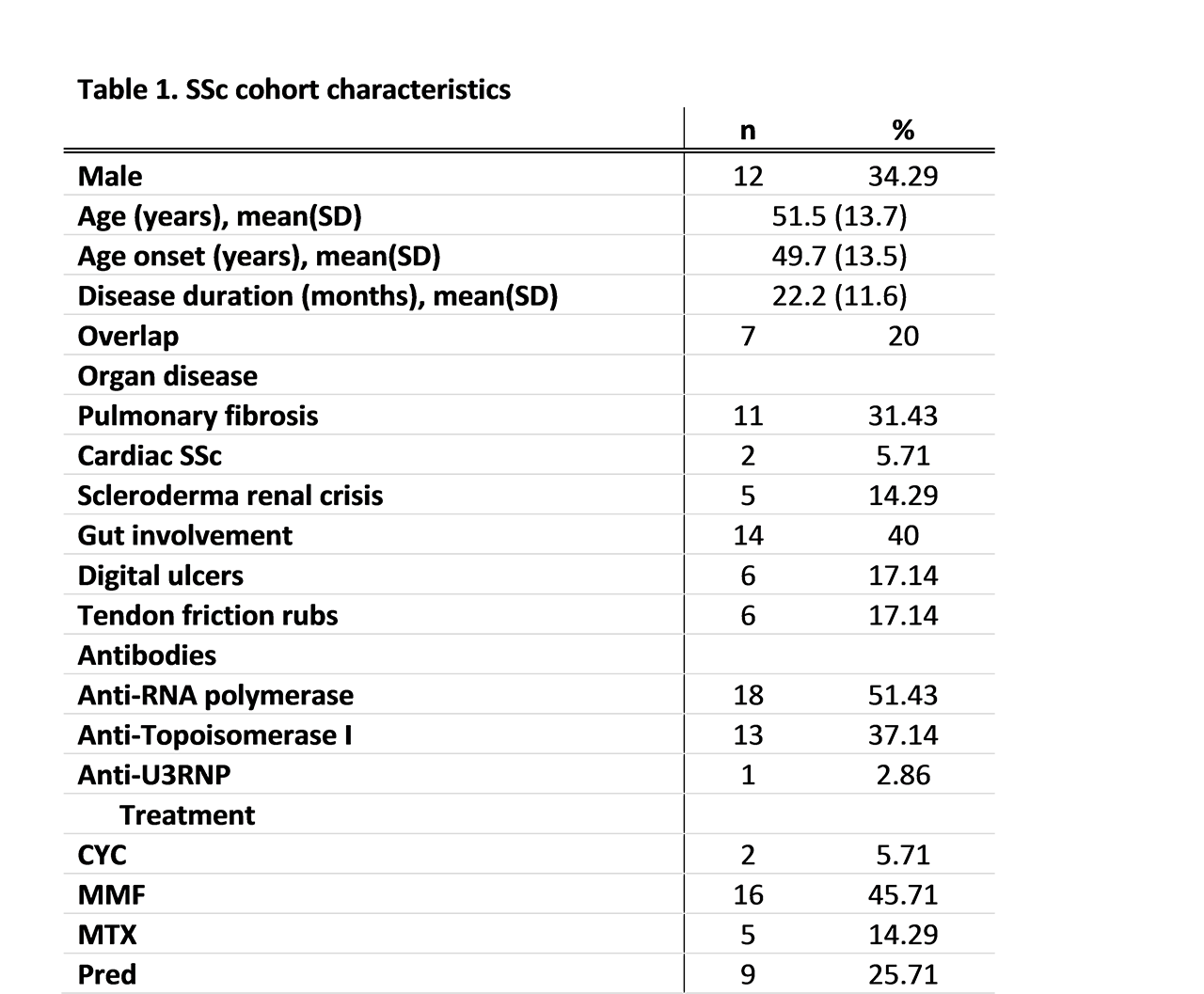
Methods: sPD-1, sLAG-3 and sTIM-3 were measured in sera from 35 patients with dcSSc and 26 healthy controls. All patients had disease duration of less than 5 years. Modified Rodnan skin sore (mRss) varied between 8-39, mean 22. Correlation with key clinical parameters including possible effect of disease modifying agents (DMARDs: methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil and prednisolone) was determined. Patient characteristics are summarised in Table 1.
Results: For sPD-1, compared to healthy controls with below detection levels, the mean level was increased (136pg/ml) among dcSSc patients. There was no association between sPD-1 and organ involvement or autoantibodies. Comparison of sPD-1 levels in patients on DMARDs with those without treatment demonstrated significant effect of immunosuppressive therapies, with mean sPD-1 95.1 pg/ml among patients on DMARD compared to 216.7 pg/ml among those on no treatment (p=0.02).sPD-1 demonstrated association with ESR (Spearman’s rho=0.3505, p=0.03), but not CRP. There was association between sPD-1 and mRss (Spearman’s rho=0.3759, p=0.04) and FVC (Spearman’s rho=0.3722, p=0.04). Mean sLAG-3levels were significantly lower among dcSSc patients (394.6 pg/ml) vs healthy controls (740.8 pg/ml, p< 0.05). sLAG-3 was inversely associated with disease duration (Spearman’s rho =-0.3438, p=0.04). There was a trend for association between sLAG-3and mRss, with higher levels of sLAG-3 seen in patients with higher skin score (Spearman’s rho =0.3304, p=0.06),and between sLAG-3levels and presence of tendon friction rubs (TFR) (mean sLAG-3366.3 ng/ml among patient without TFR and 531.5 ng/ml among those with TFR, p=0.08). There was highly significant difference in the sTIM-3 levels between healthy controls (mean 4721.9 ng/ml) and dcSSc patients (8728.0 ng/ml, p< 0.05). There was a trend for association between anti-Scl70 (ATA) positivity and sTIM-3 levels (7579.5 ng/ml in ATA+ vs 9406.6 ng/ml in ATA- patients, p=0.09). Hb levels showed significant association with sTIM-3, with higher Hb levels associated with lower sTIM-3 levels (Spearman’s rho =-0.4018, p=0.02). There was a weak association between platelet count and sTIM-3 (Spearman’s rho =0.3267, p=0.06).
Conclusion: Our data show that soluble co-inhibitors are differentially expressed in early dcSSc and correlate with key clinical features. Although they may be selectively affected by some immunosuppressive therapies, this may reflect pathway dysregulation and may provide serological markers for evaluation of disease activity and severity in diffuse SSc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ong V, Nihtyanova S, Abraham D, Aspari M, Denton C, Deleuran B. Aberrant Expression Levels of Soluble Co-inhibitory Receptors Linked to Disease Activity in Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/aberrant-expression-levels-of-soluble-co-inhibitory-receptors-linked-to-disease-activity-in-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/aberrant-expression-levels-of-soluble-co-inhibitory-receptors-linked-to-disease-activity-in-systemic-sclerosis/