Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To assess the efficacy of abatacept (ABA) in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) patients with Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) (RA-ILD).
Methods: Observational multicenter study of RA-ILD patients treated with at least 1 dose of ABA. ILD was diagnosed by high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT). We analyzed the following variables at baseline (ABA initiation), 12 months, and at the end of the follow-up: a) Modified Medical Research Council (MMRC) scale (1-point change), b) Forced Vital Capacity (FVC) or Diffusion Lung Capacity for Carbon Monoxide (DLCO) (improvement or worsening ≥10%), c) HRCT, d) DAS28ESR, and e) corticosteroid sparing effect
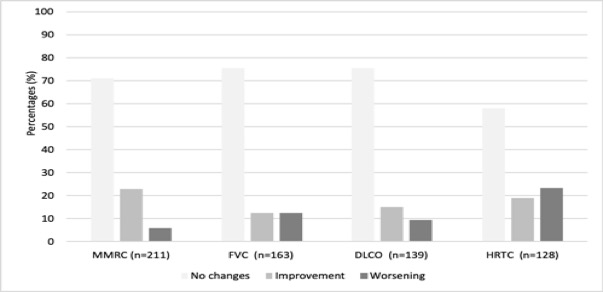
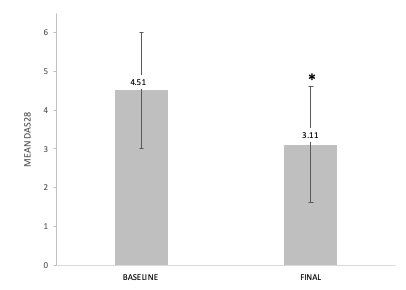
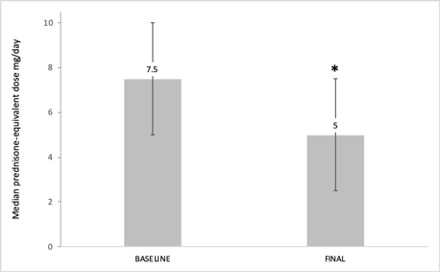
Results: We studied 263 RA-ILD patients (150 women/113 men; mean age 64.6±10 years). At baseline, they had a median duration of ILD of 1 [0.25-3.44] years, moderate or severe degree of dyspnea (MMRC grade 2, 3 or 4) (40.3%), FVC (% of the predicted) mean±SD 85.9±21.8%, DLCO (% of the predicted) 65.7±18.3, and DAS28ESR: 4.5±1.5. The ILD patterns were: Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) (40.3%), Non-Specific Interstitial Pneumonia (NSIP) (31.9%), and others (27.8%). ABA was prescribed at standard dose, intravenously (25.5%) or subcutaneously (74.5%). After a median follow-up of 12 [6-36] months the following variables did not show worsening: dyspnea (MMRC) (91.9%); FVC (87.7%); DLCO (90.6%); chest HRCT (76.6%). A significant improvement of DAS28ESR from 4.5±1.5 to 3.1±1.3 at the end of follow-up (p< 0.001) and a corticosteroid sparing effect from a median 7.5 [5-10] mg/day to 5 [2.5-7.5] mg/day at the end of follow-up; p < 0.001 was also observed. ABA was withdrawn in 62 (23.6%) patients due to adverse events (n=30), articular inefficacy (n=27), ILD worsening (n=3), and other causes (n=2).
Conclusion: ABA may be an effective and safe treatment for patients with RA-ILD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fernandez-Diaz C, Castañeda S, Melero R, Ortiz Sanjuan F, Juan-Mas A, Carrasco Cubero C, Almodovar R, Rodriguez-Garcia S, Aguilera-Cros C, Villa I, Ordoñez S, Raya E, Ojeda C, Moreno-Ramos M, Bonilla G, Romero-Yuste S, Ruibal-Escribano A, Andreu Sanchez J, Exposito R, Loricera J, Mena-Vazquez N, Urriticoechea A, Peralta C, Arboleya L, Narváez F, Maiz O, Fernandez Melon J, Vela P, Castellvi I, Cabezas I, Lopez Robles A, Carreira Delgado P, Blanco-Madrigal J, Del-val-del-amo N, Salgado E, Garcia-magallon B, Hidalgo Calleja C, Corbeto Lopez M, Perez A, Castro S, De dios J, García Valle A, Lopez R, García Aparicio A, Cervantes E, Gonzalez C, Alvarez-Rivas N, Perez L, González-Gay M, Blanco R. Abatacetp in Spanish Patients with Arthritis Rheumatoid and Interstitial Lung Disease. Multicenter Study of 263 Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/abatacetp-in-spanish-patients-with-arthritis-rheumatoid-and-interstitial-lung-disease-multicenter-study-of-263-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/abatacetp-in-spanish-patients-with-arthritis-rheumatoid-and-interstitial-lung-disease-multicenter-study-of-263-patients/