Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Treatment of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) has been shown to improve symptoms of the disease such as back pain (BP) and morning stiffness (MS). As a result, early referral of patients suspected of having axSpA is strongly recommended. However, little data is available on the disease course of early axSpA in clinical practice, and particularly in comparison to referred patients who have chronic BP (CBP) but not axSpA. We set out to compare spinal symptoms at baseline and after 2 years (2y) in early axSpA and non-axSpA CBP patients in clinical practice.
Methods: The population consisted of adults (≥16 years) with CBP of unknown origin lasting more than 3 months and less than 2y, starting before 45 years, included in the SPondyloArthritis Caught Early (SPACE) cohort. Patients had a diagnosis of axSpA or non-axSpA at 2y with a high level of confidence by the treating rheumatologist (Marques ML, Ann Rheum Dis 2023;82:3-4). Patients reported the severity of BP (total and at night) and MS in the previous week on a numeric rating scale (NRS) ranging from 0 (no symptom) to 10 (unbearable symptom), both at baseline and 2y. For MS duration, a NRS ranging from 0 (0 hours) to 10 (≥2 hours) was used. For the assessment of each outcome, only patients with data at both timepoints were included. Wilcoxon signed-rank tests (for not normally distributed data) were used to compare baseline and 2y results within groups. For the comparison between groups, linear regression models were built, adjusting for the baseline value of the respective outcome, gender, age and use of NSAID.
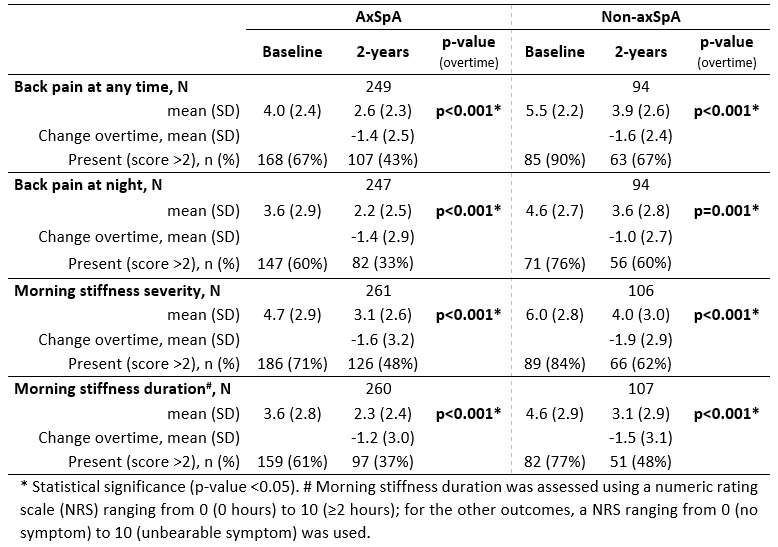
Results: A total of 434 patients (303 axSpA; 131 non-axSpA) had undergone baseline and 2y visits. Data was available for both timepoints on at least one of the four questions related to BP and MS in 266 (88%) axSpA and 110 (84%) non-axSpA patients. Compared to non-axSpA, axSpA patients were more frequently male (52% vs 25%) and had more SpA features (mean (SD): 5 (2) vs 3 (1)), including HLA-B27 positivity (73% vs 29%). Age (mean (SD): 29 (8) vs 31 (8) years) and symptom duration (mean (SD): 13 (7) vs 13 (7) months) were similar between groups.
Overall, lower levels of BP and MS were observed in axSpA (vs non-axSpA) patients at baseline and 2y (Table 1). After 2y, BP (total and at night) and MS severity and duration significantly improved in both groups (all p≤0.001), even though symptoms persisted in a considerable number of patients (mainly in the non-axSpA group). A mean improvement ranging from 1.4 to 1.6 points for axSpA patients and 1.0 to 1.9 points for non-axSpA patients was reported for each outcome. In adjusted multivariate analysis, axSpA (vs non-axSpA) was an independent predictor of a lower BP at night at 2y (Table 2, adjusted coefficient = -0.8, 95% CI (-1.5; -0.2); p=0.012), with no significant differences found for total BP or MS severity and duration.
Conclusion: Over 2y, BP and MS significantly improve in early axSpA. Although a similar improvement is seen in non-axSpA patients, at 2y most patients have persisting symptoms. AxSpA (vs non-axSpA) is an independent predictor of larger improvement in BP at night but not of the observed improvements in total BP and MS.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bento da Silva A, Van Lunteren M, marques M, Fagerli K, Ramiro S, van der Heijde D, Van Gaalen F. A Two-year Comparison of Back Pain and Morning Stiffness in Axial Spondyloarthritis and Non-axial Spondyloarthritis Chronic Back Pain Patients in the Spondyloarthritis Caught Early (SPACE) Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-two-year-comparison-of-back-pain-and-morning-stiffness-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-and-non-axial-spondyloarthritis-chronic-back-pain-patients-in-the-spondyloarthritis-caught-early-space-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-two-year-comparison-of-back-pain-and-morning-stiffness-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-and-non-axial-spondyloarthritis-chronic-back-pain-patients-in-the-spondyloarthritis-caught-early-space-cohort/