Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 10:00AM-10:50AM
Background/Purpose: Consensus-based recommendations guide standards of care for clinical practice. Pharmaceutical-industry involvement in producing such recommendations may undermine their objectivity. We performed a systematic review to quantify the extent of pharmaceutical company involvement in rheumatology consensus based recommendations in the field of rheumatology.
Methods: A comprehensive search of several databases from their inception to April 21st, 2020 was conducted. The search strategy was designed by an experienced librarian with input from the study’s investigators. Eligibility criteria included (1) English language (2) consensus-based recommendations that assessed (3) pharmacotherapy of (4) rheumatic diseases after (5) January 1st, 2000. Pairs of reviewers screened articles and extracted data. Categorical variables were assessed using Fisher’s exact test; yearly publications were analyzed using a linear regression.
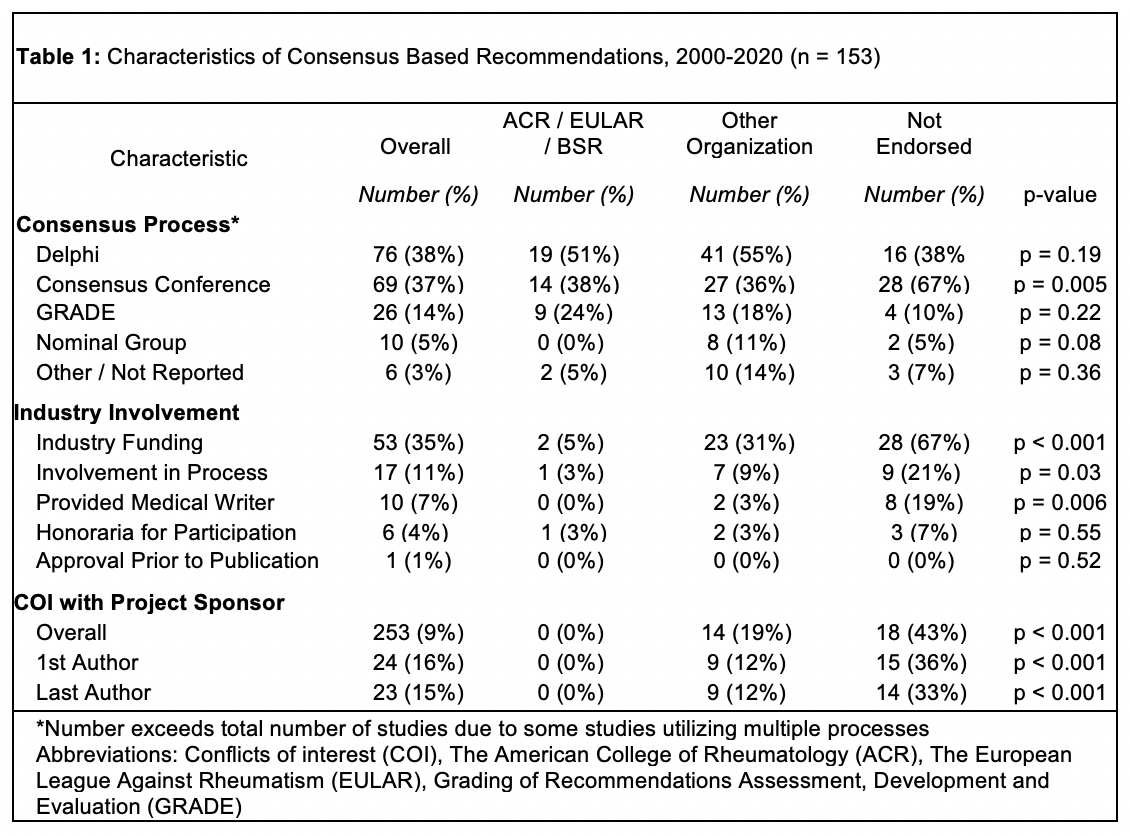
Results: The search identified 1,686 articles, of which 153 were included. The most common subjects were rheumatoid arthritis 31/153 (20%), spondyloarthritis 18/153 (12%), osteoarthritis 10/153 (7%), crystal arthropathies 9/153 (6%), and vasculitis 9/153 (6%). The most common consensus-based methodologies were Delphi processes 77/187 (41%) and consensus conferences 69/187 (37%) (Figure 2A). Major societies (ACR, EULAR, BSR) endorsed 37/153 (24%), other organizations (professional societies or governments) endorsed 74/153 (48%), and 42/153 (28%) were not endorsed (Figure 2B). Major society-endorsed guidelines were less likely to accept industry funding (5% vs. 31% other organizations vs. 67% not endorsed, p < 0.001), allow pharmaceutical involvement in the consensus process (3% vs. 9% other organizations vs. 21% not endorsed, p = 0.03), or allow an industry funded medical writer (0% vs. 3% other organizations vs. 19% not endorsed, p = 0.006). The percent of authors who declared any conflicts of interest increased over time across all consensus-based recommendations (p < 0.001) (Figure 2C). With regard to the projects that accepted funding from pharmaceutical companies, the industry sponsor was involved in the consensus based process in 16/53 (30%), provided a medical writer in 10/53 (19%), and was allowed to approve the final draft in 1/53 (2%) (Figure 2D).
Conclusion: The yearly production of consensus-based recommendations has significantly increased over time. Consensus-based recommendations that are not endorsed by major rheumatology societies frequently receive funding from pharmaceutical companies, which may be involved in the consensus-finding process or provide editorial support. Rheumatologists should be aware of this potential influence and policymakers should consider strategies to mitigate their impact.
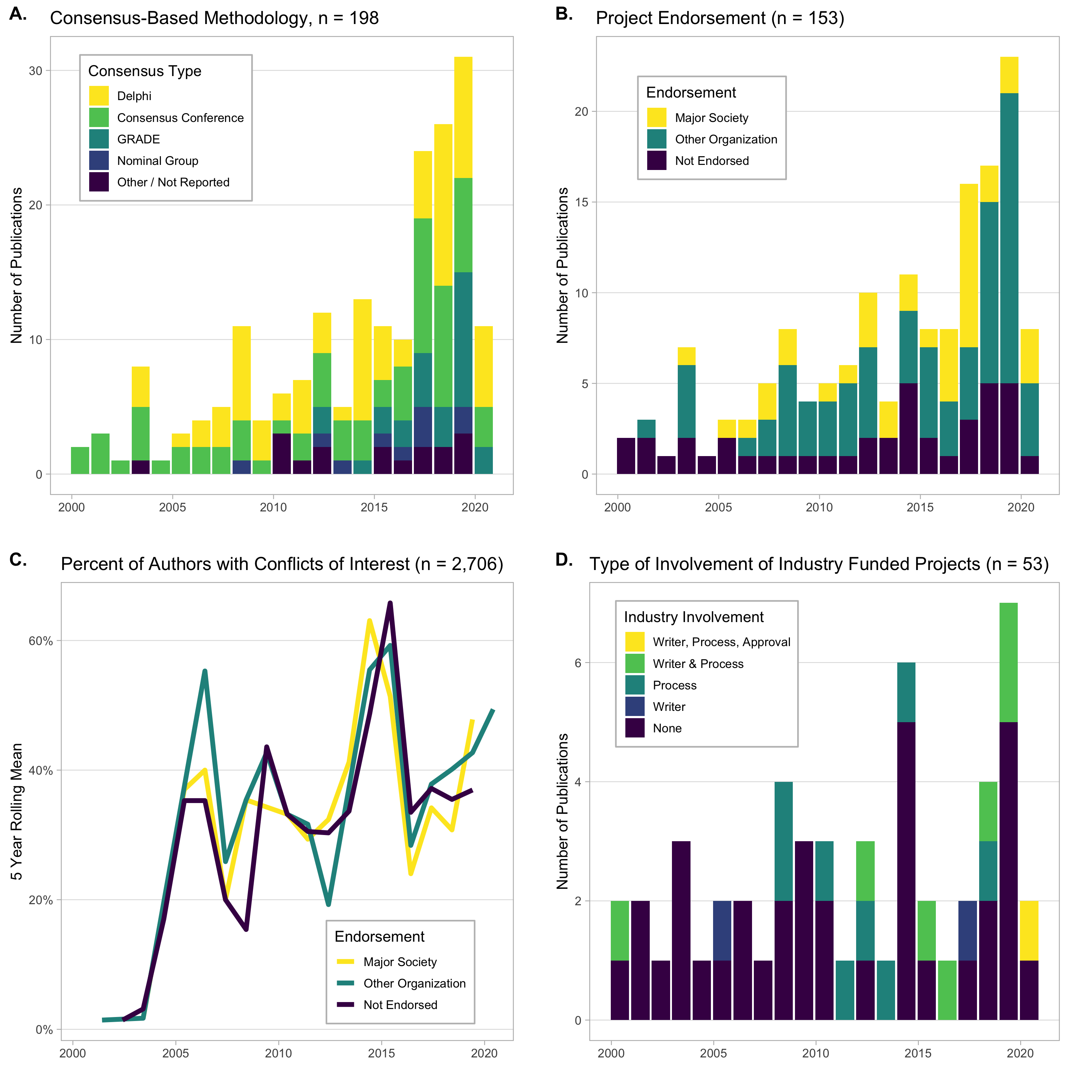 Figure 2: A. Number of publications utilizing major consensus-finding methodologies, n = 198. Number exceeds total number of publications because of studies that utilized mixed methods. B. Project endorsement by major society (ACR, EULAR, BSR), other organization (other professional societies, government groups), or not endorsed, n = 153. C. Percentage of authors per year who declared conflicts of interest, stratified by project endorsement. Data displayed as five year rolling mean for reporting clarity. D. Types of involvement by industry in industry funded projects over time, n = 53. Involvement categories were “Writer” (medical writer or editorial support), “Process” (involvement in the consensus-finding process), and “Approval” (pharmaceutical company having right to edit or approve the final manuscript).
Figure 2: A. Number of publications utilizing major consensus-finding methodologies, n = 198. Number exceeds total number of publications because of studies that utilized mixed methods. B. Project endorsement by major society (ACR, EULAR, BSR), other organization (other professional societies, government groups), or not endorsed, n = 153. C. Percentage of authors per year who declared conflicts of interest, stratified by project endorsement. Data displayed as five year rolling mean for reporting clarity. D. Types of involvement by industry in industry funded projects over time, n = 53. Involvement categories were “Writer” (medical writer or editorial support), “Process” (involvement in the consensus-finding process), and “Approval” (pharmaceutical company having right to edit or approve the final manuscript).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Feterman Jimenez D, Duron G, Duarte-Garcia A, Sufka P, Whittle S, Robinson P, Prokop L, Putman M. A Systematic Review to Quantify the Extent of Pharmaceutical Company Involvement in Rheumatology Consensus-Based Recommendations [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-systematic-review-to-quantify-the-extent-of-pharmaceutical-company-involvement-in-rheumatology-consensus-based-recommendations/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-systematic-review-to-quantify-the-extent-of-pharmaceutical-company-involvement-in-rheumatology-consensus-based-recommendations/