Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: RA patients who have failed biologic DMARDs represent an unmet medical need. We explored the impact of baseline demographics and clinical characteristics on filgotinib efficacy in patients with active RA who have inadequate response to ≥1 prior bDMARD (bDMARD-IR).
Methods: In the global, phase 3 FINCH-2 study (NCT02873936), 449 patients with moderately-to-severely active RA and inadequate response to ≥1 prior bDMARDs were randomized 1:1:1 to once-daily filgotinib 200 mg, filgotinib 100 mg, or placebo.1 We evaluated prespecified subgroups including baseline demographic and clinical characteristics such as sex at birth, seropositivity for RF and/or ACPA, disease duration, disease activity, hsCRP levels, concurrent use of corticosteroids, and different classes of DMARDs on filgotinib efficacy as measured by ACR20 and DAS28(CRP) for low disease activity and remission in patients with active RA who were bDMARD-IR.
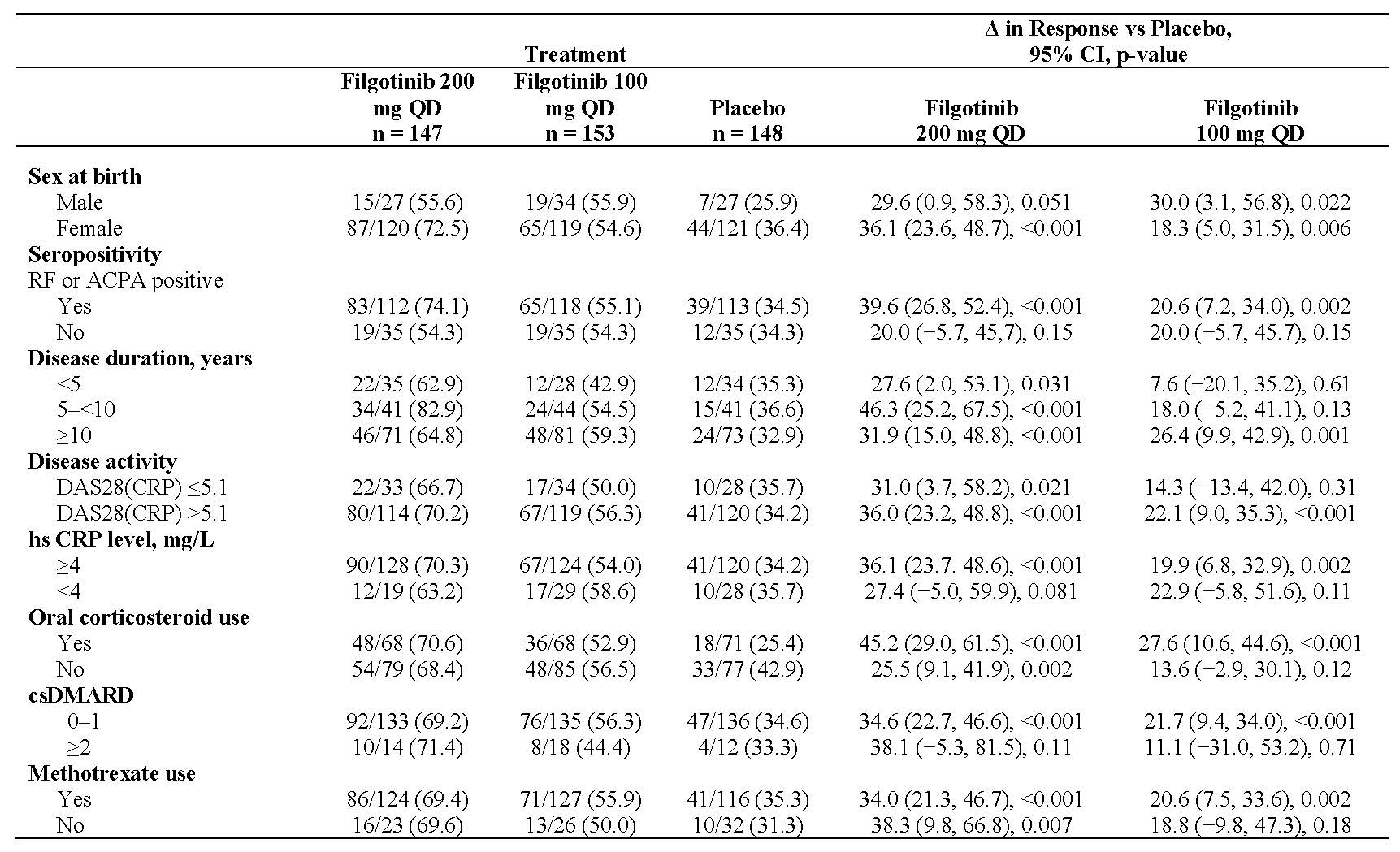
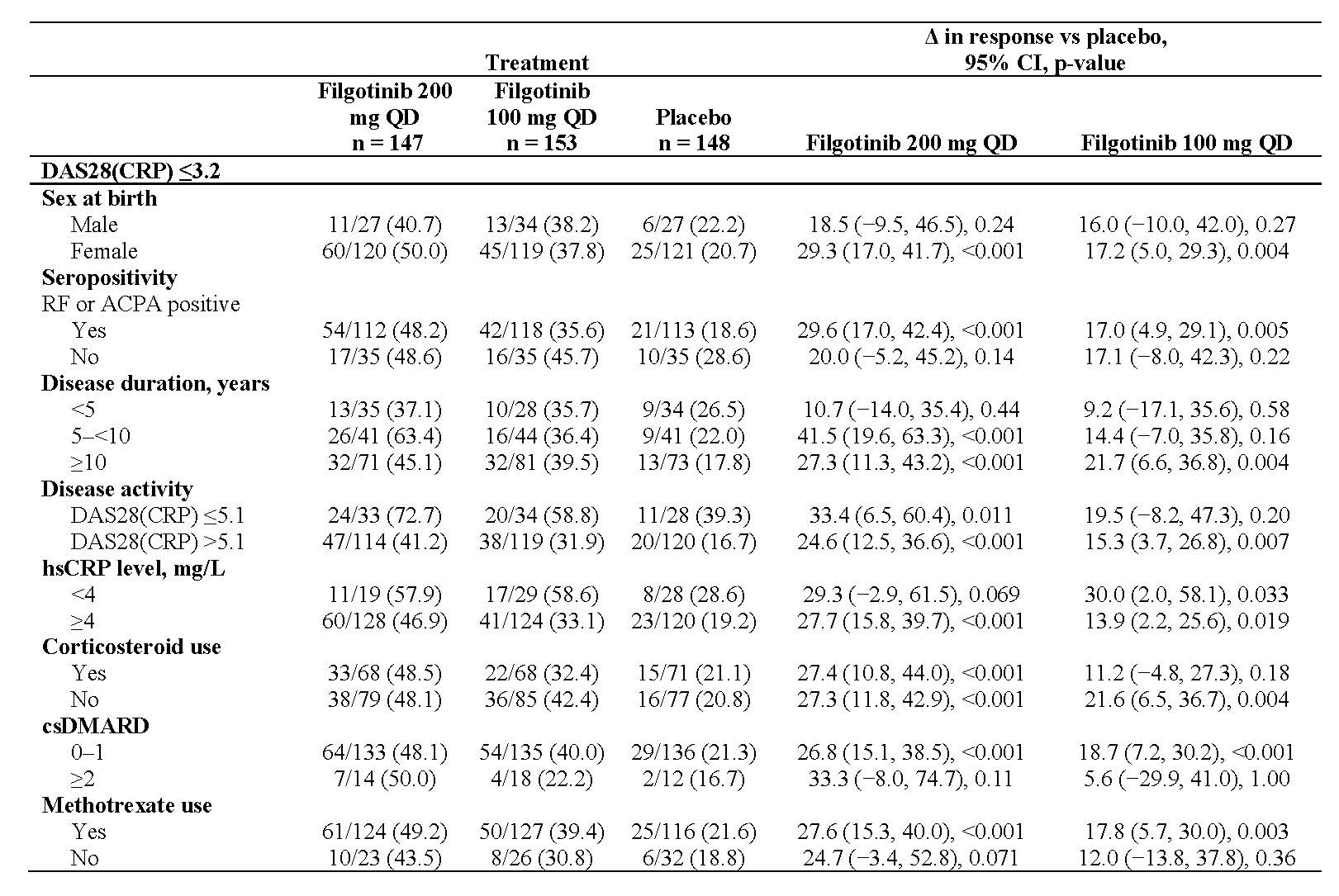
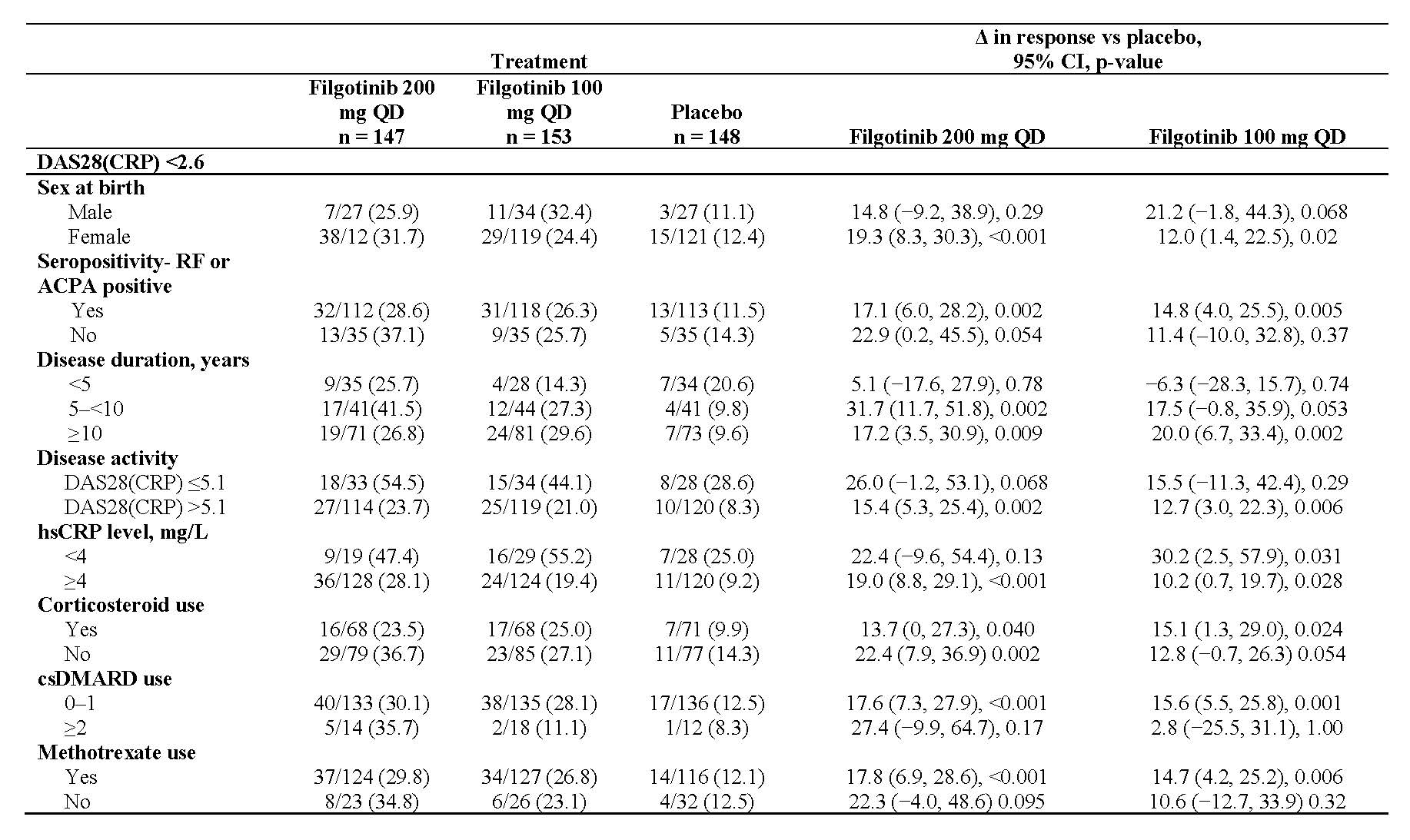
Results: Of the 448 patients randomized and treated at baseline, 80.4% were female with a mean age of 56 years and a mean RA duration of 12.4 years. Clinical efficacy outcomes at week 24 as measured by ACR20, DAS28(CRP) ≤3.2 and DAS28(CRP) < 2.6 by patient demographics and clinical baseline characteristics are described in Tables 1, 2, and 3, respectively.
Conclusion: Compared with placebo, filgotinib consistently improved clinical outcomes in bDMARD-refractory patients. Benefits were observed for filgotinib across subgroups defined by various demographic and clinical baseline characteristics. There was an absence of impact of disease duration, seropositivity, disease activity and concurrent medication use, notably on the effectiveness of filgotinib.
References:
1. Genovese MC, et al. Safety and Efficacy of Filgotinib in a Phase 3 Trial of Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis and Inadequate Response or Intolerance to Biologic Dmards [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 10).
Unless otherwise noted, data presented as n/N -%-
CI, confidence interval; csDMARD, conventional synthetic DMARD; hsCRP, high-sensitivity CRP; QD, once daily.
Unless otherwise noted, data presented as n/N -%-.
CI, confidence interval; csDMARD, conventional synthetic DMARD; hsCRP, high-sensitivity CRP; QD, once daily.
Unless otherwise noted, data presented as n/N -%-.
CI, confidence interval; csDMARD, conventional synthetic DMARD; hsCRP, high-sensitivity CRP; QD, once daily.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kalunian K, Genovese M, Gottenberg J, Bartok B, Pechonkina A, Guo Y, Tasset C, Sundy J, de Vlam K, Walker D, Takeuchi T. A Subgroup Analysis of the Efficacy of Filgotinib in Demographic and Clinical Subgroups of Patients with Refractory Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-subgroup-analysis-of-the-efficacy-of-filgotinib-in-demographic-and-clinical-subgroups-of-patients-with-refractory-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-subgroup-analysis-of-the-efficacy-of-filgotinib-in-demographic-and-clinical-subgroups-of-patients-with-refractory-rheumatoid-arthritis/