Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Osteoarthritis (OA) involves thinning cartilage and increased subchondral bone. Amongst many cellular processes, inflammation has been associated with OA. Wnt signaling plays a role in mediating inflammation. SM04690, a novel, small-molecule Wnt pathway inhibitor that has previously been shown to regenerate and protect cartilage in an animal model of OA, was evaluated in a series of preclinical studies to determine its potential to inhibit inflammation.
Methods: Wnt pathway inhibition was measured using a cell-based reporter assay. Anti-inflammatory activity was evaluated by measuring TNF-α and IL-6 secretion using ELISA in synovial fibroblasts stimulated with IL1b, THP-1 monocyte cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharides (LPS), and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) stimulated with anti-CD3/anti-CD28. A panel of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, IL-17A, IL-17F, IFNγ, and PGE2) was evaluated by ELISA, T and B cell proliferation by flow cytometry in PBMCs, and T and B cell co-cultures stimulated with super-antigen or LPS, compared to vehicle or benchmark steroids (Cyclosporin A and Prednisolone). The effect of SM04690 on the LPS-induced expression and phosphorylation of NFkB in THP-1 cells was evaluated by qPCR and Western Blot.
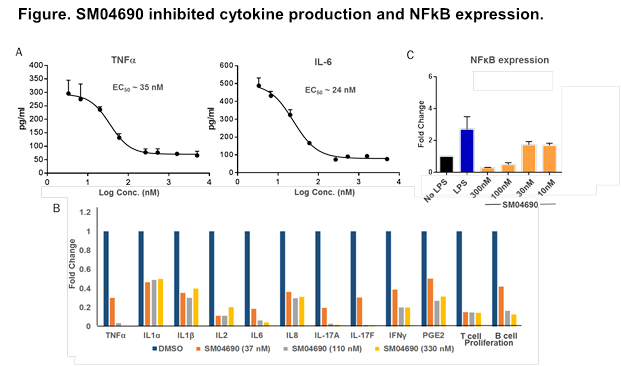
Results: SM04690 demonstrated potent (EC50 =11nM) and selective inhibition of Wnt signaling. SM04690 inhibited IL-1b-induced TNF-α and IL-6 secretion in synovial fibroblasts (EC50 =30nM; Figure A). SM04690 also inhibited LPS and anti-CD3/anti-CD28-induced TNF-α and IL-6 secretion in THP-1 cells (EC50 =10nM), and PBMCs. SM04690 significantly inhibited (p<0.01, effect size >40%, no toxicity) super-antigen- and LPS-stimulated production of various pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, IL-17A, IL-17F, IFNγ, PGE2), and T and B cell proliferation in PBMCs and T and B cell co-cultures (Figure B). The anti-inflammatory activity of SM04690 in these assays was comparable to or better than the activities of Cyclosporin A and Prednisolone. Additionally, SM4690 treatment decreased LPS-induced gene expression (3-fold, p<0.01) and phosphorylation of NFkB in THP-1 cells (Figure C).
Conclusion: SM04690, a small molecule Wnt pathway inhibitor was a potent anti-inflammatory agent in various cell types, with inhibition of NFkB signaling in vitro. This anti-inflammatory activity of SM4690 may provide beneficial effects in the treatment of various diseases, including OA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Deshmukh V, Ibanez M, Barroga C, Hood J, Yazici Y. A Small Molecule, SM04690, Has Inhibitory Effects on the Wnt Pathway and Inflammation in Vitro, with Potential Implications for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-small-molecule-sm04690-has-inhibitory-effects-on-the-wnt-pathway-and-inflammation-in-vitro-with-potential-implications-for-the-treatment-of-osteoarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-small-molecule-sm04690-has-inhibitory-effects-on-the-wnt-pathway-and-inflammation-in-vitro-with-potential-implications-for-the-treatment-of-osteoarthritis/