Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic inflammatory arthritis that often develops in patients (pts) with psoriasis. Secukinumab (SEC) inhibits IL-17A, a key inflammatory cytokine in the pathogenesis of PsA. SEC is approved for treatment of PsA based on the phase 3 FUTURE studies, where SEC proved superior to placebo (PBO) in improving signs and symptoms of PsA. Although pts from several countries were included, US pts were under-represented. We report findings from CHOICE (NCT02798211), a phase 4 study which evaluated SEC vs PBO in US biologic-naive pts with PsA with psoriatic skin lesions.
Methods: CHOICE was a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial conducted in the United States. Biologic-naive pts with active PsA by CASPAR criteria and psoriatic skin lesions (PASI ≥ 1) were enrolled. Pts were randomized 2:2:1 to receive SEC 300 mg, SEC 150 mg, or PBO, respectively, with a weekly loading dose up to Week 4, and every 4 weeks thereafter for 16 weeks. After Week 16, all pts randomized to PBO, and nonresponders from the SEC 150-mg group received SEC 300 mg up to Week 52. The primary objective was to show superiority of SEC 300 mg vs PBO in ACR20 response at Week 16. Secondary and exploratory objectives included the effect of SEC on dactylitis, enthesitis, psoriasis, remission status, RAPID3 score, and safety. Long-term (up to Week 52) efficacy and safety were also assessed.
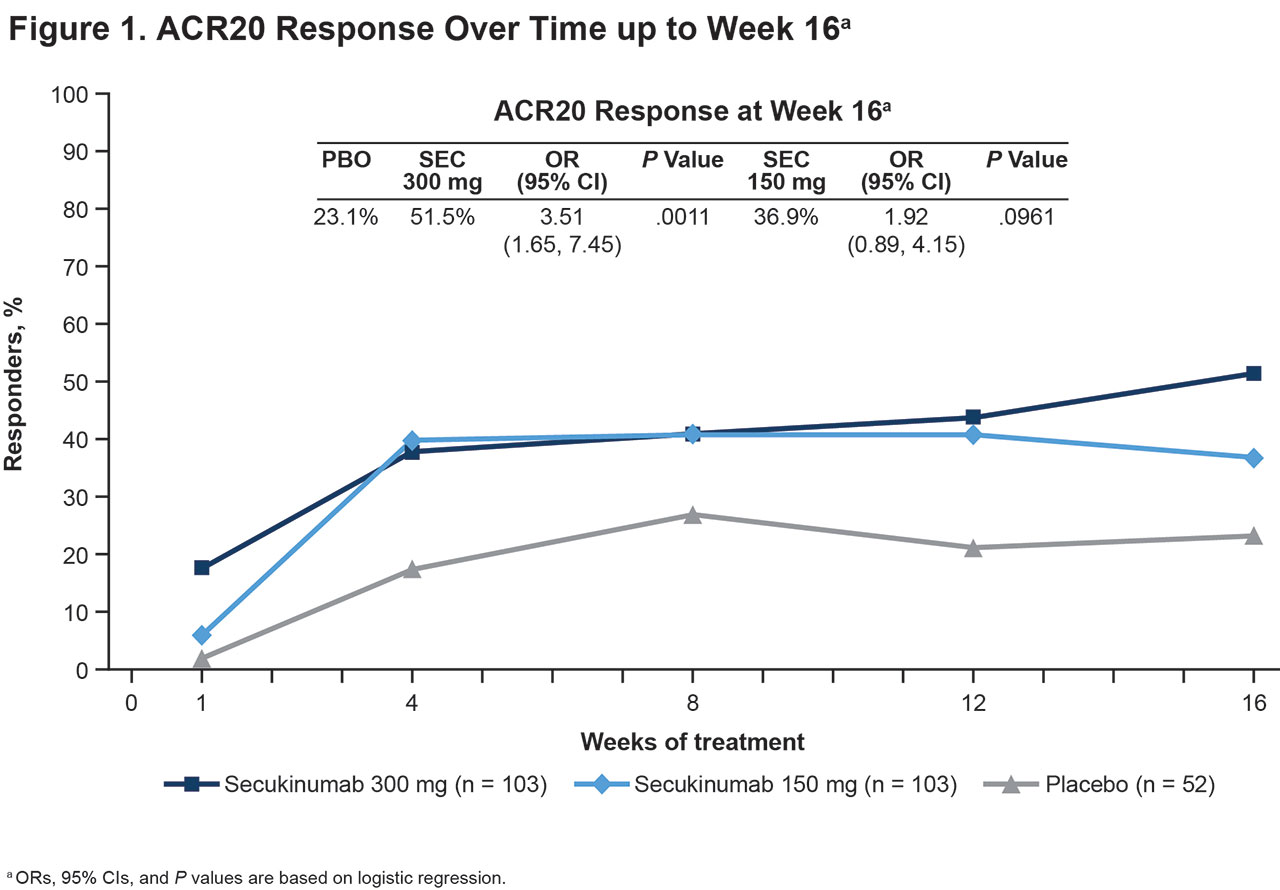
Results: In total, 258 pts were randomized to SEC 300 mg (n = 103), SEC 150 mg (n = 103), or PBO (n = 52). Pts in all treatment groups had comparable baseline characteristics. In general, pts in CHOICE were older, had a higher mean weight, and higher baseline joint involvement than pts in the FUTURE studies. The study met its primary objective with a greater percentage of pts treated with SEC 300 mg achieving ACR20 response at Week 16 compared with PBO (51.5% vs 23.1%; odds ratio [OR], 3.51 [95% CI: 1.65, 7.45]; P = .0011, using logistic regression) (Figure 1). ACR20 responses were numerically higher with SEC 150 mg than PBO (36.9%; OR, 1.92 [95% CI: 0.89, 4.15]; P = .0961). SEC also led to higher ACR50/70 response rates, higher rates of minimal disease activity, lower RAPID3 scores, and improvements in other variables compared with PBO (Table 1). Response rates were generally sustained over time with SEC, with the percentage of responders increasing after uptitration of SEC dose. The most commonly reported adverse events (AEs) with SEC at Week 16 were diarrhea and upper respiratory tract infections (Table 2). No inflammatory bowel disease was reported; 3 pts (SEC 300 mg, n = 1; SEC 150 mg, n = 2) had Candida infections at Week 16. Only 1 pt in each SEC group discontinued treatment by Week 16 due to AEs. One death occurred during the study (cardiac arrest, PBO group).
Conclusion: SEC 300 mg was superior to PBO in leading to rapid and significant improvements in symptoms of PsA in US biologic-naive patients. Benefits were observed with both SEC doses; however, responses were generally higher with SEC 300 mg. Overall, findings in CHOICE were consistent with previous studies and suggest that SEC 300 mg is safe and efficacious as a first-line biologic treatment for pts with PsA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nguyen T, Churchill M, Levin R, Valenzuela G, Merola J, Ogdie A, Orbai A, Scher J, Kavanaugh A, Agawane S, Kianifard F, Rollins C, Chambenoit O. A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study Evaluating the Safety and Efficacy of Secukinumab in US Biologic-Naive Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis and Psoriatic Skin Lesions [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-randomized-placebo-controlled-study-evaluating-the-safety-and-efficacy-of-secukinumab-in-us-biologic-naive-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-and-psoriatic-skin-lesions/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-randomized-placebo-controlled-study-evaluating-the-safety-and-efficacy-of-secukinumab-in-us-biologic-naive-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-and-psoriatic-skin-lesions/