Session Information
Date: Wednesday, November 13, 2019
Title: 6W021: RA – Treatments V: Switching & Tapering RA Medications (2906–2911)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Although biologic therapies have transformed the outlook for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), the lack of a major treatment response in over 50% of patients, the potential side effects and the high cost of these drugs have highlighted the need to define predictive markers of response and to stratify patients according to therapeutic outcome. B-cells are pivotal to RA pathogenesis, validated by the efficacy demonstrated by the B cell depleting agent rituximab (RTX). RTX is licensed for use following failure of conventional synthetic (cs)-DMARDs and TNF inhibitor (TNFi) therapy. However, in this increasing therapeutically resistant cohort only 30% of patients achieve an ACR50 response at 6 months. We have recently demonstrated in an early RA cohort1synovial heterogeneity with over 50% of patients showing low/absence of synovial B-cell infiltration. This prompted us to test the hypothesis that in these patients an alternative biologic agent targeting alternative pathways maybe more effective. We report results from the first pathobiology-driven randomised controlled trial (RCT) in RA (R4RA) evaluating whether patient stratification according to the synovial B-cell rich/poor status enriches for response/non response to RTX.
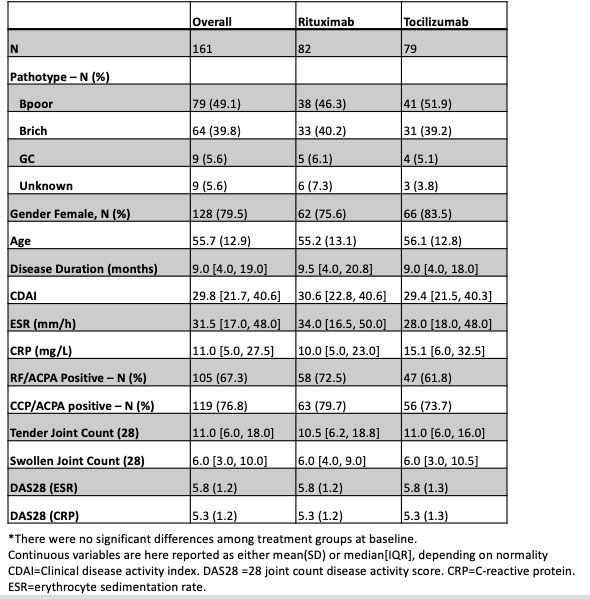
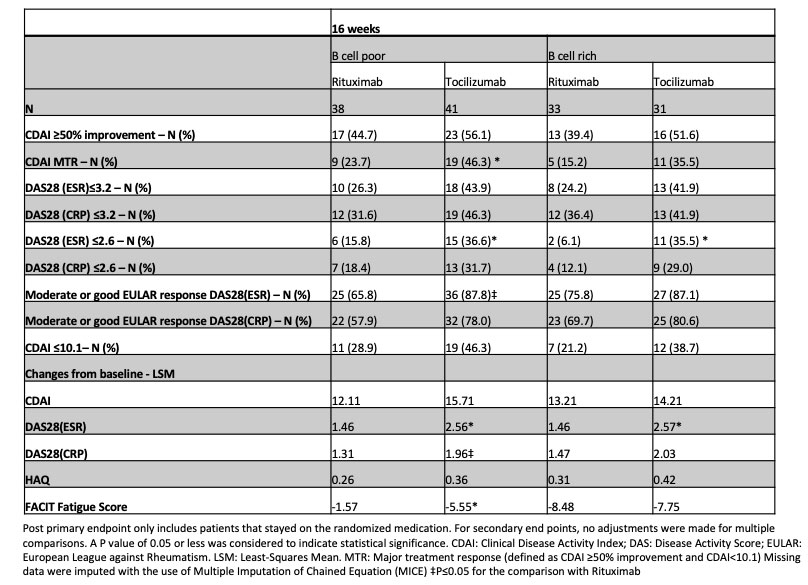
Methods: R4RA is a 48 week phase IV open-label RCT conducted in 19 European centres that recruited patients failing or intolerant to csDMARD therapy and at least one TNFi. Synovial tissue was obtained at trial entry and classified histologically as B-cell rich (BCR) or B-cell poor (BCP). Patients were randomised to receive standard therapy with RTX or tocilizumab (TCZ) stratified according to histological classification. The study was powered to test in the BCP population superiority of TCZ over RTX at 16 weeks. The primary and co-primary end-points were defined respectively as Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) ≥50% improvement from baselineand Major Treatment response (MTR)= CDAI improvement ≥ 50% and CDAI ≤10.1. Secondary outcomes included assessment of CDAI response in the BCR cohort where non-inferiority of RTX compared to TOCI was evaluated. Safety data up to week 48 is reported.
Results: The trial recruited to target with a power of 89.5%. 164 patients were randomised, 83 received RTX and 81 TCZ. 81/83 RTX and 73/81 TCZ patients completed treatment to week 16 (primary endpoint). Baseline characteristics were comparable among treatment groups (Tab 1). In the BCP population a numerically higher number of patients achieved the primary outcome and a statistically significantly higher number of patients achieved co-primary endpoint (MTR) as well as in a number of additional secondary endpoints in the TCZ group (Tab 2). In the BCR population there was no significant difference in the majority of endpoints (Tab 2). A higher number of adverse and serious adverse events such as infections in patients treated with TCZ compared to RTX were recorded (Tab 3).
Conclusion: In a RA BCP population failing csDMARDs and TNFi therapy,TCZ is more effective than RTX in achieving both low levels and significant falls in disease activity. In a BCR RA population RTX is non inferior to TCZ for the majority of outcome measures evaluated.
1. Humby, M.Lewis et al Ann Rheum Dis. 2019 Mar 16. pii: annrheumdis-2018-214539.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
humby F, Buch M, Durez P, Lewis M, Bombardieri M, Rizvi H, Kelly S, Fosatti L, Hands R, Giorli G, Mahto A, Montecucco C, Lauwerys B, Romao V, Pratt A, Bugatti S, Ng N, Rivellese F, Ho P, Bellan M, Congia M, Verschueren P, Sainaghi P, Gendi N, Dasgupta B, Cauli A, Reynolds P, Cañete J, Moots R, Taylor P, Edwards C, Isaacs J, Sasieni P, Eurico Fonseca J, Choy E, Pitzalis C. A Randomised, Open Labelled Clinical Trial to Investigate Synovial Mechanisms Determining Response – Resistance to Rituximab versus Tocilizumab in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Failing TNF Inhibitor Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-randomised-open-labelled-clinical-trial-to-investigate-synovial-mechanisms-determining-response-resistance-to-rituximab-versus-tocilizumab-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-failing-tnf-inhibitor-t/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-randomised-open-labelled-clinical-trial-to-investigate-synovial-mechanisms-determining-response-resistance-to-rituximab-versus-tocilizumab-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-failing-tnf-inhibitor-t/