Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Prior research suggests that medication decision-making in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients is affected by disease activity, satisfaction with care, trust in their health care provider, and quality of patient-provider communication.(1-3) Because few studies have used quantitative methodologies to do such, we will describe changes in these key decision-making factors over time.
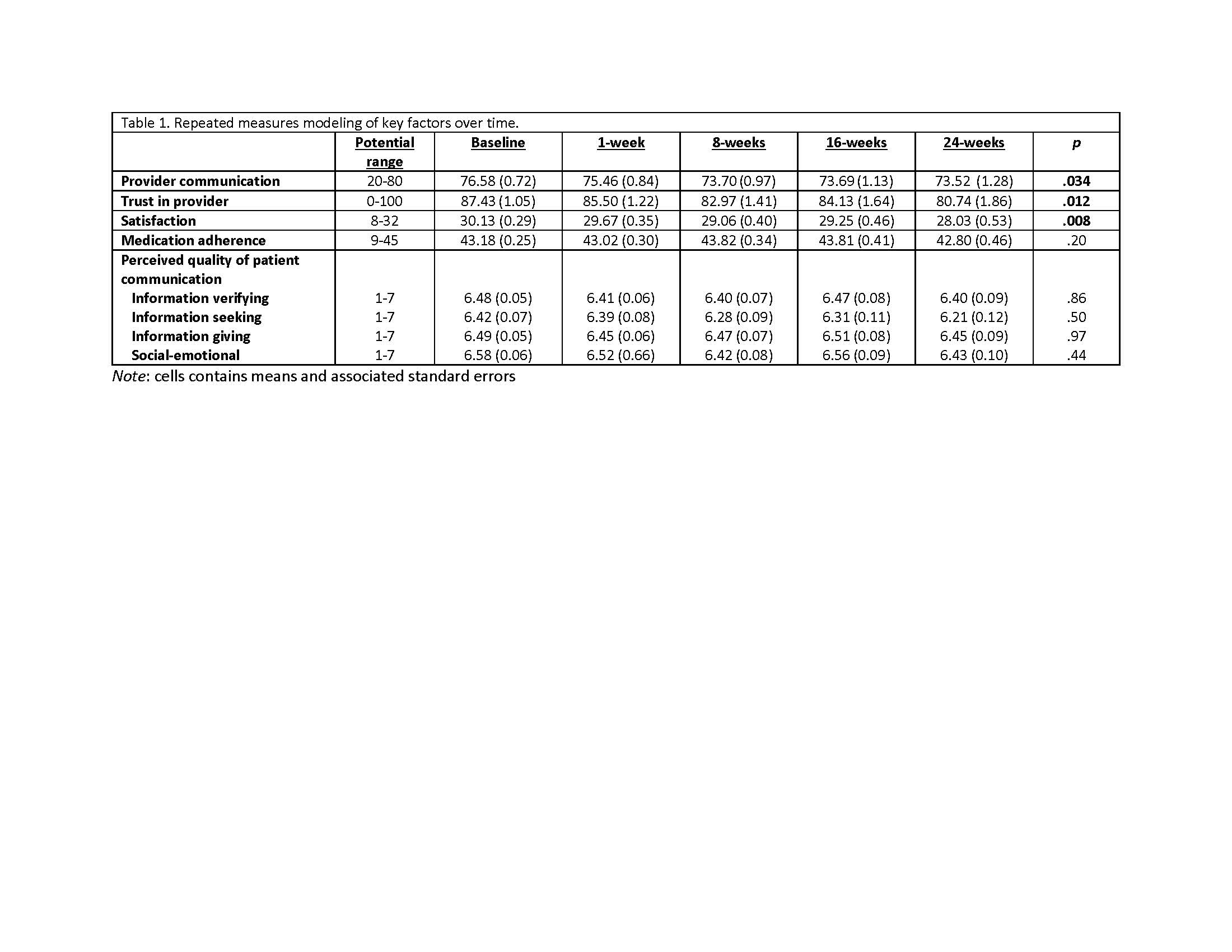
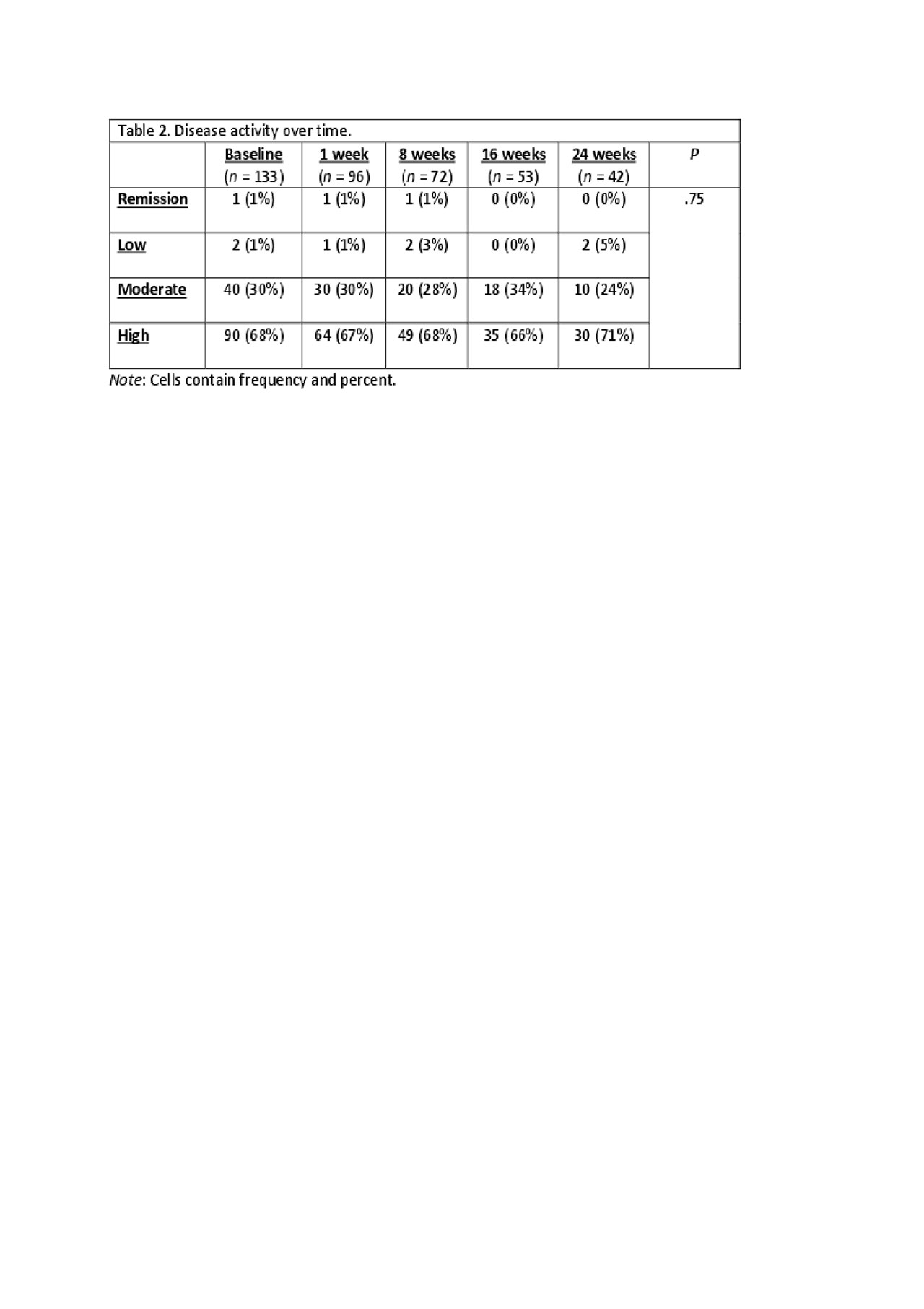
Methods: We collected data over 6 months (baseline, 1 week, 8 weeks, 16 weeks and 24 weeks) in a sample of 143 RA patient at one University health system. We measured medication adherence with the Medication Adherence Report Scale-9RA, a 9-item scale using a 5-point Likert scale (5 = never and 1 = very often; score range: 9 – 45; Cronbach’s α =.77; test-retest reliability = .73).(4-6) Satisfaction with care was measured with the Client Satisfaction Questionnaire-8, an 8-item scale using a 4-point Likert-type scale where 4 indicates increased satisfaction (score range 8 – 32; Cronbach’s α = .93). A significant correlation with client-reported symptoms supports scale validity.(7) Trust in provider was measured with the Trust in Physician Scale (TPS), an 11-item scale using a 5-point Likert scale (1 = strongly disagree – 5 strongly agree; Cronbach’s α = .87).(8) The scale has significant negative correlations with measures of skepticism supporting scale validity.(8) Disease activity was measured with the Routine Assessment of Patient Index Data 3 (RAPID3) on three domains: physical function, pain, and patient global assessment on a scale of 0 to 10 (range 0 – 30).(9, 10) The RAPID3 has been significantly correlated with other measures of disease activity.(9, 10) We used repeated measure mixed modeling and Friedman’s test to describe the factors over time.
Results: We identified a significant decrease in the patient’s perceived quality of provider communication (p=.034), trust in the provider (p=.012) and satisfaction with care over time (p=.008). We did not identify changes over time in medication adherence, any of the four subscales measuring the patient’s perception of the quality of their communication with their health care provider, or disease activity overtime (Tables 1 and 2).
Conclusion: Despite stable medication adherence, disease activity did not change significantly over time. Although trust in the provider, satisfaction with care, and quality of provider communication scores were high, these values decreased over time suggesting that providers must make concerted efforts to maintain these key factors during the patient care experience.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Salt E, Wiggins A, Lohr K, Rayens M. A Prospective Analysis of Factors Impacting Medication Decision-Making in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-prospective-analysis-of-factors-impacting-medication-decision-making-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-prospective-analysis-of-factors-impacting-medication-decision-making-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/