Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 5:00PM-5:50PM
Background/Purpose: Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) is involved in multiple signalling pathways potentially implicated in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Evobrutinib is a highly selective, oral BTK inhibitor. This phase IIb, randomized, double-blind study evaluated efficacy, dose response, and safety to 12 weeks of treatment with evobrutinib versus placebo in RA patients with inadequate response to methotrexate (MTX).
Methods: Patients enrolled were 18–75 years of age, with confirmed diagnosis of RA ≥ 6 months duration (EULAR/American College of Rheumatology [ACR] criteria), with active disease at screening and randomization, defined by ≥ 6 swollen and ≥ 6 tender joints, and with high-sensitivity CRP (hsCRP) ≥ 5.0 mg/L. Participants had received MTX treatment 7.5–25 mg/week for ≥ 16 weeks at stable dose for ≥ 8 weeks, and had not received prior treatment with a biologic DMARD. They were randomized 1:1:1:1 to oral evobrutinib 25 mg once-daily (QD), 75 mg QD, 50 mg twice-daily (BID), or placebo. Stable use of NSAIDs and/or glucocorticoids (≤10 mg daily) was allowed. The primary endpoint was ACR 20% response (ACR20), assessed at Week 12, using hsCRP. Key secondary endpoints were ACR50 and ACR70 and disease activity scores (DAS28)CRP, DAS28CRP < 3.2 and DAS28CRP < 2.6. Safety endpoints included adverse events (AEs), serious AEs (SAEs), and laboratory studies. Other secondary endpoints included change from baseline in OMERACT RAMRIS scores and RAMRIQ scores for synovitis, osteitis and erosion for patients in an MRI substudy.
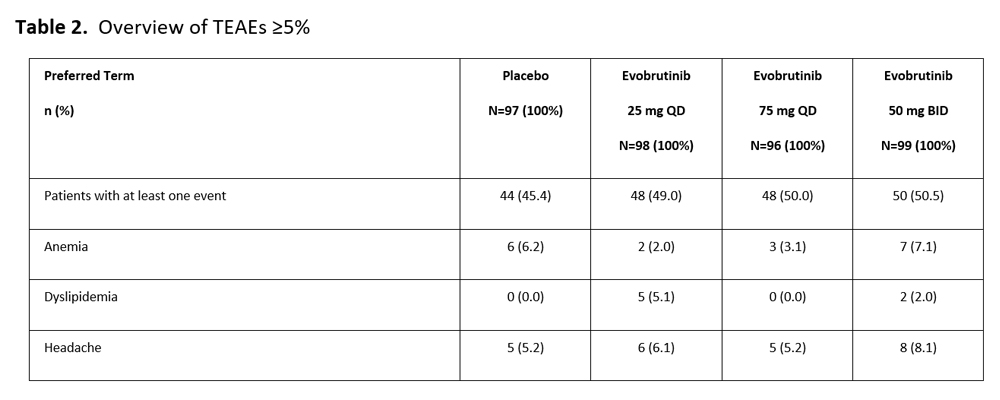
Results: 390 patients were randomized. Baseline age was 52.7±12.2 years (mean±SD), 80.0% were female, hsCRP 21.77mg/L ±24.1 (mean±SD), and time since diagnosis 6.9±6.7 years (mean±SD). The treatment groups were balanced for sex, race, age, time since diagnosis, joint counts, and other baseline disease characteristics. The primary endpoint of ACR20 response was not met (Figure 1). ACR20 response in the placebo group (49.5%) was higher than other trials in RA. Evobrutinib at all doses was nominally significant versus placebo on DAS28CRP < 3.2, and DAS28CRP < 2.6. HsCRP decreased in all evobrutinib arms (Table 1). No dose response was observed. There were no significant differences in MRI scores between placebo and evobrutinib by either RAMRIS (Table 1) or RAMRIQ (data not shown). Evobrutinib was well tolerated at all doses (Table 2). Three patients showed Grade 3 elevations in ALT, all in the 75 mg QD arm. LFT elevations were reported across all groups. Very few patients experienced Grade 3 events, and only one patient experienced a Grade 4 event (unrelated to treatment).
Conclusion: This phase IIb study of evobrutinib in patients with RA with inadequate response to MTX did not meet its primary efficacy endpoint of ACR20 response. MRI endpoints did not show differences between evobrutinib and placebo. However, MRI placebo scores were not consistent with other studies, showing greater improvements in synovitis and osteitis, and less progression of erosions than typically reported. Evobrutinib was well tolerated at all doses. No dose effect was identified.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Peterfy C, Buch M, Choy E, Schett G, Parsons-Rich D, Patel A, Zima Y, Le Bolay C, Genovese M. A Phase IIb, Randomized, Double-blind Study in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Evaluating the Safety and Efficacy of Evobrutinib Compared with Placebo in Patients with an Inadequate Response to Methotrexate [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-iib-randomized-double-blind-study-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-evaluating-the-safety-and-efficacy-of-evobrutinib-compared-with-placebo-in-patients-with-an-inadequate-response-to-met/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-iib-randomized-double-blind-study-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-evaluating-the-safety-and-efficacy-of-evobrutinib-compared-with-placebo-in-patients-with-an-inadequate-response-to-met/