Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: To assess efficacy, including inhibition of radiographic progression, and safety with upadacitinib (UPA), a JAK1- selective inhibitor, vs placebo (PBO) and active comparator, originator adalimumab (ADA), in patients (pts) with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) continuing on prior methotrexate (MTX).
Methods: In SELECT–COMPARE, pts with active RA despite MTX were randomized 2:2:1 to once-daily (QD) UPA 15mg, PBO, or ADA 40mg every other week (wk) in a double-blind manner, while continuing stable background MTX. Primary endpoints were ACR20 and the proportion of pts achieving DAS28CRP<2.6 (NRI) at Wk12. Key secondary endpoints included non-inferiority (and superiority) of UPA vs ADA at Wk12 (for ACR50, DAS28CRP≤3.2, change from BL (Δ) in Pain, and ΔHAQ-DI), and radiographic inhibition (ΔmTSS) for UPA vs PBO at Wk26. Pts with <20% improvement in TJC and SJC were rescued between Wks14- 26 (from PBO to UPA, UPA to ADA, or ADA to UPA).
Results:
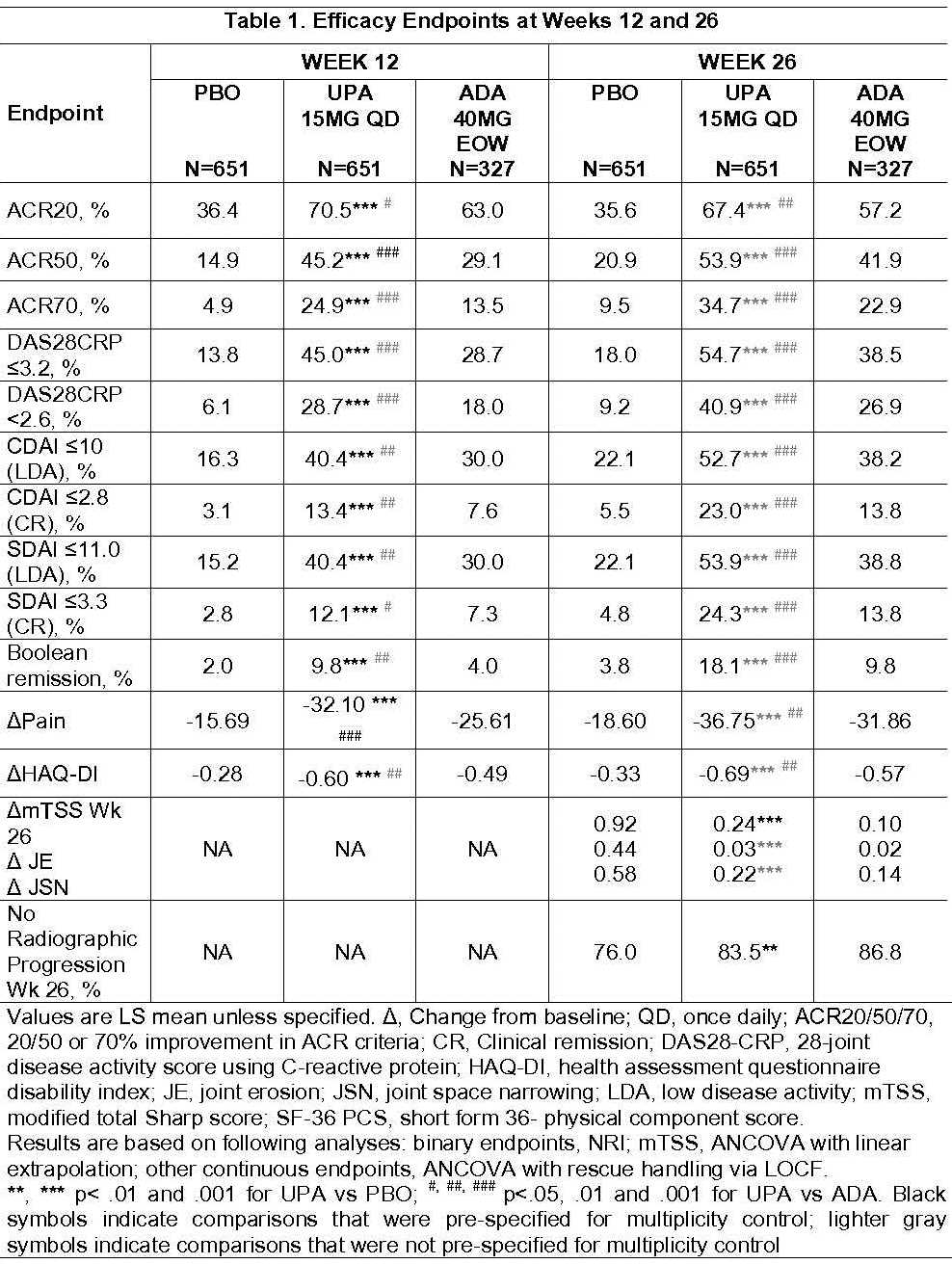
Of 1629 randomized pts, 91% completed Wk26 (including rescued pts). BL characteristics were similar across arms. All primary and key secondary endpoints were met. At Wk12, significantly more pts on UPA vs PBO achieved ACR20 (70.5% vs 36.4%) and DAS28CRP<2.6 (28.7% vs 6.1%) (Table 1). Superiority was met for UPA vs ADA at Wk12 for ACR50 (45.2% vs 29.1%), DAS28CRP≤3.2 (45.0% vs 28.7%), ΔPain (-31.76 vs -25.31) and ΔHAQ-DI (-0.60 vs -0.49). These differences were maintained through Wk26. At Wk26, pts on UPA vs PBO had significantly less radiographic progression (ΔmTSS, 0.24 vs 0.92), and significantly more pts had no radiographic progression (ΔmTSS ≤0) (83.5% vs. 76.0%). At Wk26, more pts on UPA vs PBO or ADA achieved low disease activity or remission by various criteria (nominal p<.001).
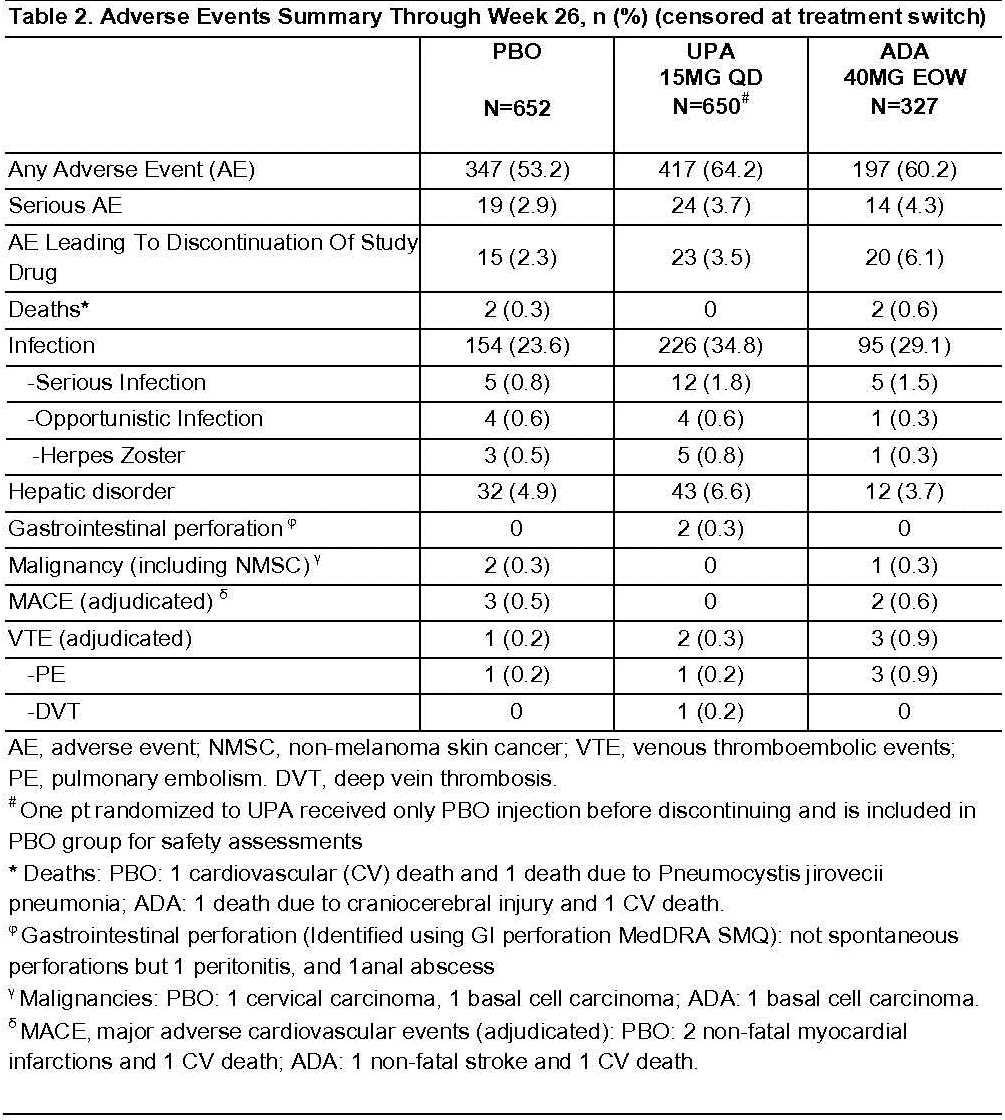
Up to Wk26, the proportion of pts with adverse events (AEs) and serious infections, censored at rescue, was higher for UPA vs PBO but similar vs ADA (Table 2). The proportion of pts with SAEs and AEs leading to discontinuation for UPA was numerically higher vs PBO and lower vs ADA. Herpes Zoster was numerically higher in UPA vs ADA and PBO. Three malignancies, 5 major adverse cardiovascular events, and 4 deaths were reported, none on UPA. Six venous thromboembolic events (VTEs) were reported (1 on PBO, 2 on UPA and 3 on ADA). For pts who were rescued, no deaths, adjudicated MACE, or adjudicated VTE were observed between rescue and Wk26.
Conclusion: UPA 15mg QD showed superiority on improvement in RA signs & symptoms vs PBO and ADA in this MTX-IR population. Radiographic progression was significantly lower with UPA vs PBO. Safety events were consistent with Ph 2 and 3 studies in RA to date.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fleischmann R, Pangan AL, Mysler E, Bessette L, Peterfy C, Durez P, Ostor A, Li Y, Zhou Y, Othman AA, Song IH, Genovese MC. A Phase 3, Randomized, Double-Blind Study Comparing Upadacitinib to Placebo and to Adalimumab, in Patients with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis with Inadequate Response to Methotrexate [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-study-comparing-upadacitinib-to-placebo-and-to-adalimumab-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-with-inadequate-response-to-methotrexate/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-study-comparing-upadacitinib-to-placebo-and-to-adalimumab-in-patients-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-with-inadequate-response-to-methotrexate/