Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Osteoarthritis (OA) affects 595 million people globally; cases are projected to increase 49-95% for various joints by 2050 as populations age (GBD 2023). OA patients have high comorbidities of insomnia, depression, anxiety, and poor quality of life. Knee OA ranks the highest in disability and pain compared to OA of other joints. Efficacious and safe therapeutics for chronic use in OA pain and other symptoms remain an unmet medical need. This trial assessed XG005, a non-opioid, new chemical entity inhibiting both inflammatory and neuropathic signals via the COX enzymes and the calcium subunit, in knee OA patients.
Methods: The Phase 2b trial (2021LP01217) was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging, parallel-group study evaluating the safety and efficacy of XG005 tablets in Chinese patients with knee OA. Patients with moderate to severe OA pain and Kellgren-Lawrence (KL) grade of II-III from 22 study sites were randomized in a 2:1:2 ratio to XG005 750 mg BID, 500 mg BID or placebo, respectively. Patients were assessed for Daily Walking Pain, WOMAC, KOOS, Patient and Clinician Global Impression of Changes (PGIC and CGIC), rescue medication use and quality of life (SF-12) at both baseline and during 4 weeks of follow-up. Serial gatekeeping multiplicity adjustment was used.
Results: 318 patients were randomized. The average Daily Walking Pain, WOMAC Pain, and KOOS Pain at the Baseline were 5.87, 4.59 (0-10 NRS scale), and 52.46, respectively. 62.2% of patients had KL grade II, and 43.2% had painDETECT scores ≥ 13 (indicating neuropathic pain components). These and other baseline characteristics were well-balanced among arms. The drug was well-tolerated and safe, with no drug-related serious adverse events.
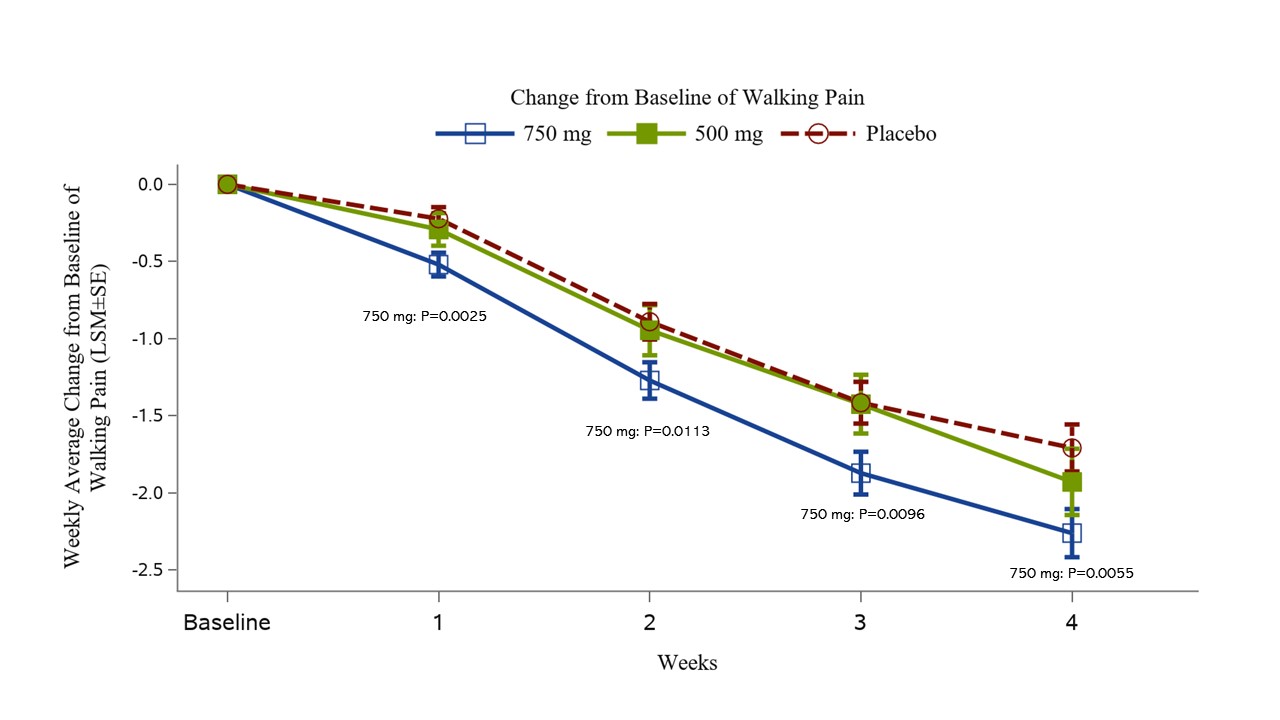
The primary efficacy endpoint of change from Baseline in Weekly Average of Daily Walking Pain at Week 4 for the 750 mg group versus placebo was statistically significant, favoring XG005. This significance was maintained at other timepoints (Fig. 1).
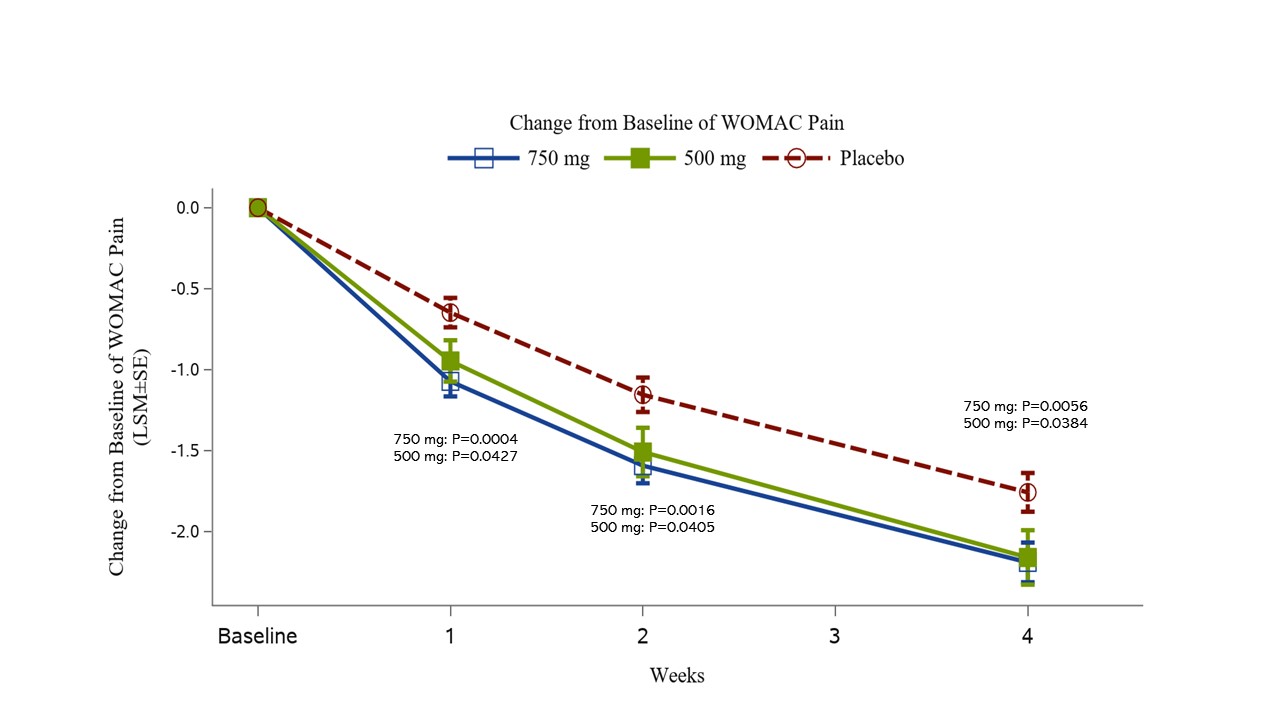
All Key Secondary Efficacy Endpoints at Week 4 achieved statistical significance compared with placebo for both 500 mg and 750 mg arms in change from Baseline of WOMAC Pain subscore (Fig. 2) and KOOS Pain subscore.
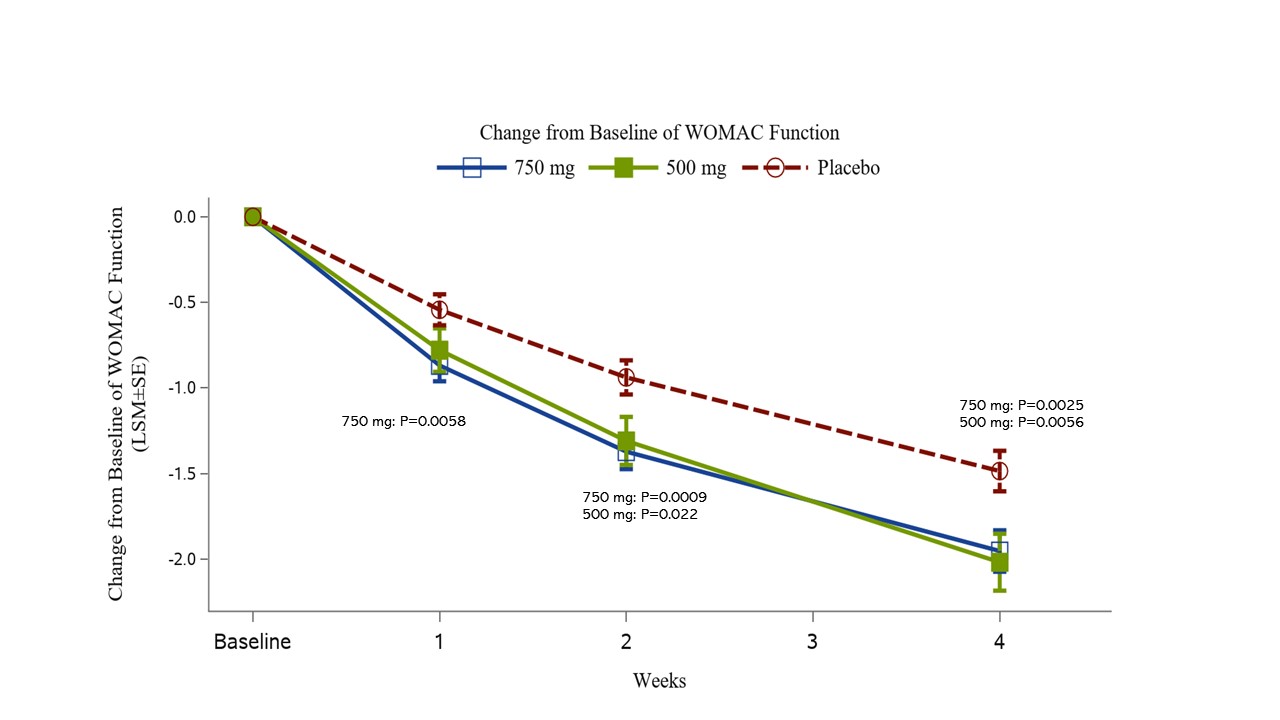
Other efficacy measures, including WOMAC Stiffness, Function (Fig. 3) and Total scores, KOOS subscores, Sleep Interference Score, PGIC, CGIC, OMERACT-OARSI responder rate, proportion of patients with ≥ 30%, 50%, or 70% improvement of Walking Pain, and SF-12 General Health and Mental Health, were statistically superior in the treatment arms compared to placebo. Rescue medication was barely used and with no difference among groups.
Conclusion: XG005 tablets demonstrated robust and consistent efficacy in relieving symptoms of OA with good tolerability. The non-opioid, dual mechanistic action of blocking both nociceptive and neuropathic pain distinguishes XG005 from other analgesics. These results strongly suggest that XG005 represents a promising, more efficacious, and safer addition to chronic OA management.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ren L, Zheng W, Guan Z, Zhang Y, Huang Z, Li T, Peng Y, Wu Q, Gou W, Zhao W, Qiao P, Pan X, Jiang G. A Phase 2b, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled, Dose-ranging and Parallel-group Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of XG005 in Subjects with Painful Osteoarthritis of the Knee [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-2b-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-dose-ranging-and-parallel-group-study-to-evaluate-the-safety-and-efficacy-of-xg005-in-subjects-with-painful-osteoarthritis-of-the-knee/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-2b-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-dose-ranging-and-parallel-group-study-to-evaluate-the-safety-and-efficacy-of-xg005-in-subjects-with-painful-osteoarthritis-of-the-knee/