Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1082–1099) Measures & Measurement of Healthcare Quality Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: People with systemic rheumatologic diseases are more susceptible to herpes zoster (HZ) infection and its complications due to their underlying diseases and the medications used to treat them. Janus kinase inhibitors (JAKi) confer a substantial risk for HZ, resulting in morbidity and cost to the healthcare system. The Division of Rheumatology at the study site recognized the rate of recombinant zoster vaccine (RZV) uptake among people receiving JAKi was unacceptably low. The goal of this quality improvement study was to increase the number of RZV prescriptions written for patients on JAKi via a streamlined patient outreach campaign.
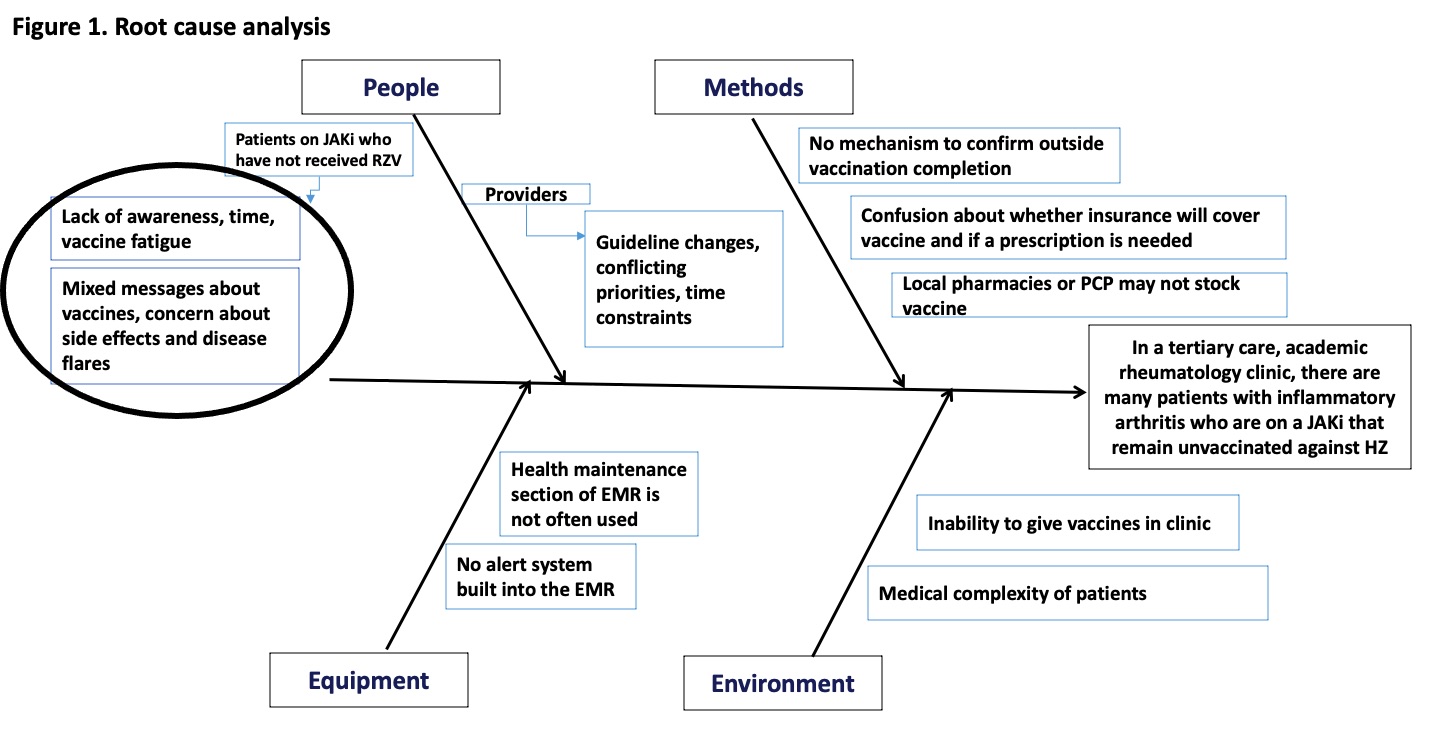
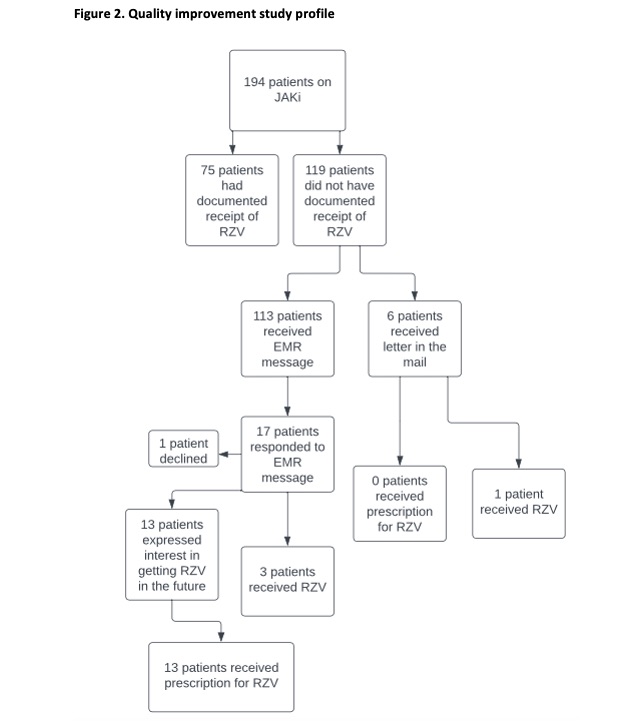
Methods: In September 2022, patients in a tertiary care, academic rheumatology clinic with inflammatory arthritis and a current prescription for a JAKi were identified using a query of the electronic medical record (EMR). A process map and root cause analysis were created to understand why there was a low rate of RZV uptake. Lack of awareness and vaccine fatigue were the main barriers identified (Figure 1). On January 10, 2023, a customized EMR message or letter was sent to the identified patients outlining the importance of RZV, including efficacy and safety, and requesting a reply from those interested in a prescription for RZV (Figure 2). A standardized nursing protocol was used to process responses. The outcome measure was the percentage of patients who received a RZV prescription by April 10, 2023 (goal >10%, starting from 5%).
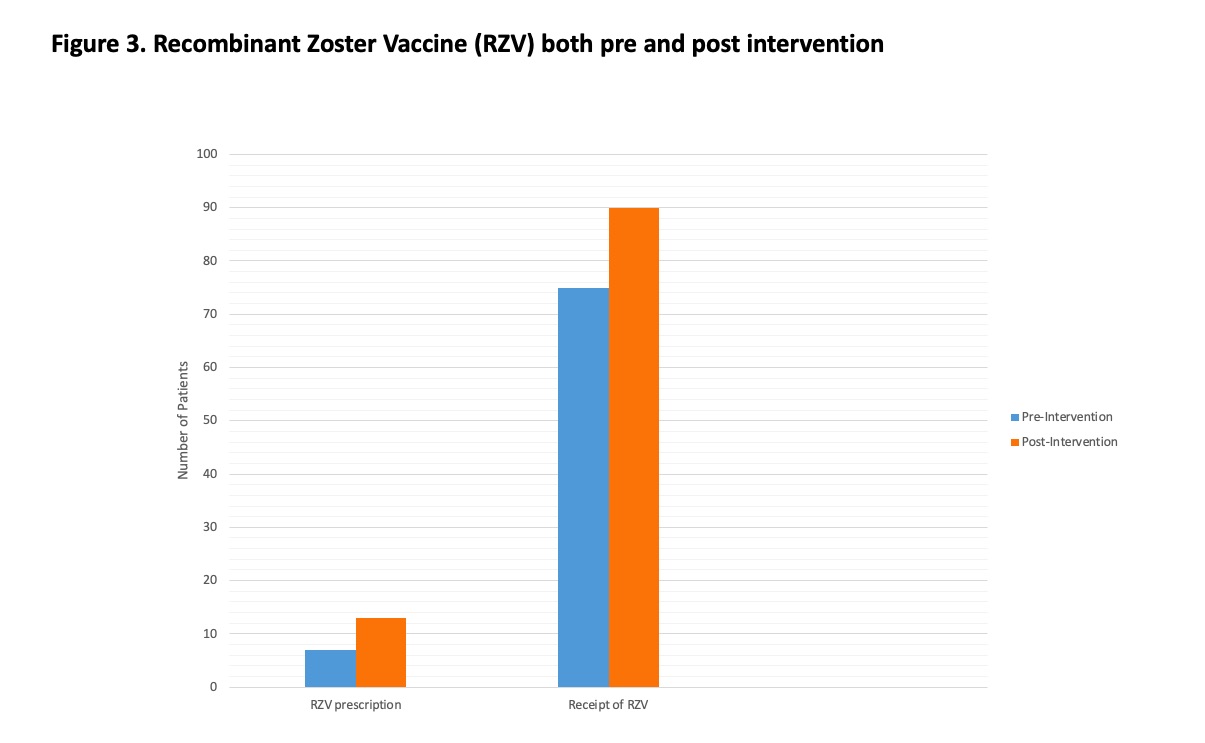
Results: There were 194 patients identified as being on a JAKi for inflammatory arthritis. Seventy-five (39%) had documentation of RZV, and 119 (61%) did not have documentation of RZV. A message was sent via the EMR to 113 patients and via mailed letter to 6 patients without EMR access. Thirteen of 119 patients (11%) responded with a request for RZV vaccination and received a prescription for RZV between January 10, 2023 and April 10, 2023, which met the outcome measure. A total of 90 patients (46%) had documentation of RZV following the intervention (Figure 3). Fifty-one patients (43%) had a rheumatology follow-up appointment by April 9, 2023. Three patients expressed vaccine hesitancy when discussed with the provider at their appointment. One patient was concerned about side effects of RZV. Twenty-two patients (18%) had a recommendation for RZV documented in follow-up clinic notes.
Conclusion: Utilizing a targeted EMR message is a low-cost intervention that helps address barriers to recombinant zoster vaccination in patients on janus kinase inhibitors without increasing provider burden. This intervention helps empower patients who are motivated to improve their health, allowing vaccination between clinic visits or prompting discussions with providers at subsequent visits. These results will inform a broader multi-modality, patient- and provider-facing program to increase vaccination rates at the study institution, including offering in-clinic vaccinations.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dayno R, Capponi S, Song S, Bayefsky S, Riley T, Bean M, Oghene J, Kotzin J, Romich E, Breslin-Perry P, Sandorfi N, Thomas P, George M. A Patient-Centered Approach to Increase Herpes Zoster Vaccination in Patients on Janus Kinase Inhibitors: A Fellowship Quality Improvement Initiative [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-patient-centered-approach-to-increase-herpes-zoster-vaccination-in-patients-on-janus-kinase-inhibitors-a-fellowship-quality-improvement-initiative/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-patient-centered-approach-to-increase-herpes-zoster-vaccination-in-patients-on-janus-kinase-inhibitors-a-fellowship-quality-improvement-initiative/