Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Reproductive Issues in Rheumatic Disorders: Basic and Clinical Aspects
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Women with anti-Ro face a spectrum of fetal consequences when pregnant, from complete wellbeing to death from cardiac neonatal lupus (cardiac NL). Transplacental passage of anti-Ro can result in transient bradycardia, first degree or advanced block, cardiomyopathy and/or death. A cardiac NL severity score was generated to identify demographic and clinical factors associated with morbidity, and serve as a predictor for long term outcomes.
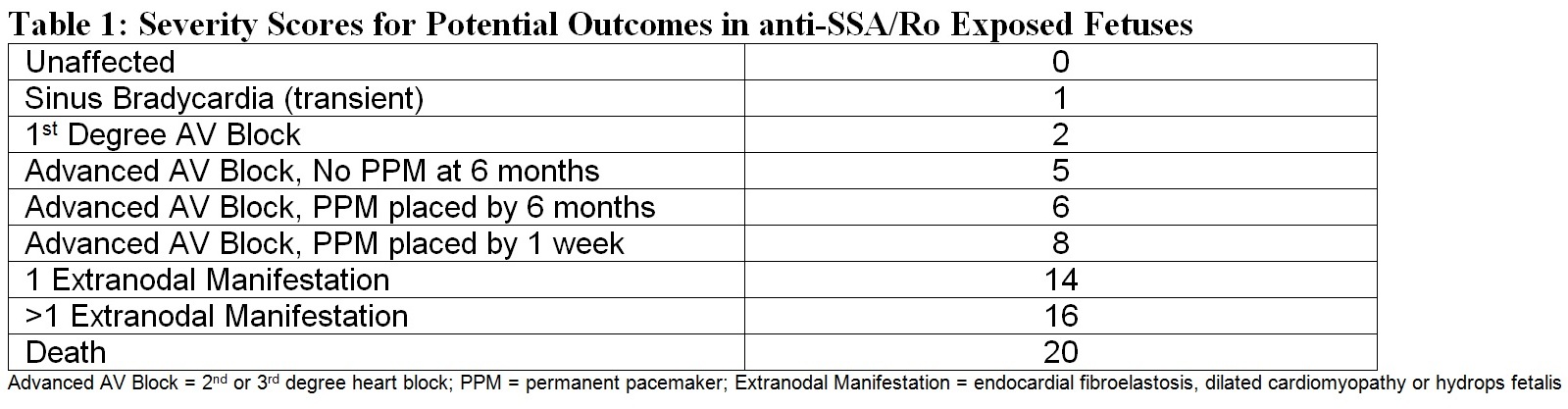
Methods: The severity score (Table 1) was based on reported mortality risk factors, such as lower fetal heart rates (which require earlier pacemaker) and extranodal disease. The score was calculated for anti-Ro positive pregnancies in the Research Registry for Neonatal Lupus. Pregnancies antedating affected children were excluded as anti-Ro could not be verified. The severity score was evaluated in univariate analysis with cord blood biomarkers related to inflammation/fibrosis: CRP (n=108), NT proBNP (n=118), Matrix Metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2) (n=63), and uPA/uPAR/plasminogen (n=49). Clinical correlates were evaluated in 779 pregnancies from 464 mothers, including race and maternal use of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) and fluorinated steroids (FS). The score was also evaluated in relation to long term outcomes in affected children based on postnatal echocardiogram (n=150, mean age 11.7±9.3 y).
Results: Severity score positively associated with cord CRP (Regression coefficient (RC) 2.18, p=0.02), NT proBNP (RC 2.79, p=0.002), MMP2 (RC 1.01, p=0.01), uPA (RC 33.7, p<0.001), uPAR (RC 3.72, p<0.001) and plasminogen (RC 1.01, p=0.01). Mean score in fetuses exposed vs unexposed to HCQ was 2.8±6.9 vs 5.6±6.9 (p<0.001). Severity score was higher in black (7.9±8.4) vs other races (4.9±6.6) (p=0.017). Limiting the analysis to cardiac NL pregnancies, the score in HCQ exposed vs unexposed fetuses was 12.5±6.5 (n=17) vs 10.5±6.3 (n=328) (p=0.32). Histologic evaluation of an autopsy from a 19 week HCQ exposed fetus electively terminated with complete block did not reveal HCQ associated vacuolar changes in myocytes. Severity score was not different in cardiac NL cases exposed (10.9±6.2, n=181) and unexposed (10.1±6.2, n=162) to FS (p=0.26). The score was higher in those with abnormal ventricular function on long term evaluation (10.2±4.0 vs 7.7±3.7) (p=0.002).
Conclusion: This novel cardiac NL severity score can be utilized in pregnancy counseling both as an outcome measure associated with disease risk factors, and as a predictor of future morbidity. Cord blood biomarkers of inflammation/fibrosis positively associate with the score. HCQ use during anti-Ro exposed pregnancies associate with decreased severity score, consistent with its proposed role as a preventative measure. However in affected cases, HCQ and FS do not associate with severity. The association of severity score with long term ventricular function promotes its use for counseling and medical monitoring in cardiac NL cases.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Saxena A, Izmirly PM, Han SW, Briassouli P, Rivera T, Halushka M, Zhong H, Friedman D, Clancy R, Buyon JP. A Novel Severity Score Based on Cardiac Neonatal Lupus Manifestations Serves As a Predictor and Outcome Measure of Morbidity in Anti-Ro Exposed Fetuses [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-novel-severity-score-based-on-cardiac-neonatal-lupus-manifestations-serves-as-a-predictor-and-outcome-measure-of-morbidity-in-anti-ro-exposed-fetuses/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-novel-severity-score-based-on-cardiac-neonatal-lupus-manifestations-serves-as-a-predictor-and-outcome-measure-of-morbidity-in-anti-ro-exposed-fetuses/