Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Title: 3S103 ACR Abstract: Genetics, Genomics & Proteomics: Precision Medicine (916–921)
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Bechet’s disease (BD) is a heterogeneous multifactorial auto-inflammatory condition characterized by recurrent episodes of oral and genital ulceration, uveitis and skin lesions, with less frequent involvement of the gastrointestinal tract, large blood vessels and central nervous system. The NF-κB pathway is a ‘master-regulator’ of immune and inflammatory signaling, with the ability to control the expression of key inflammatory genes and genes associated with apoptosis and proliferation.
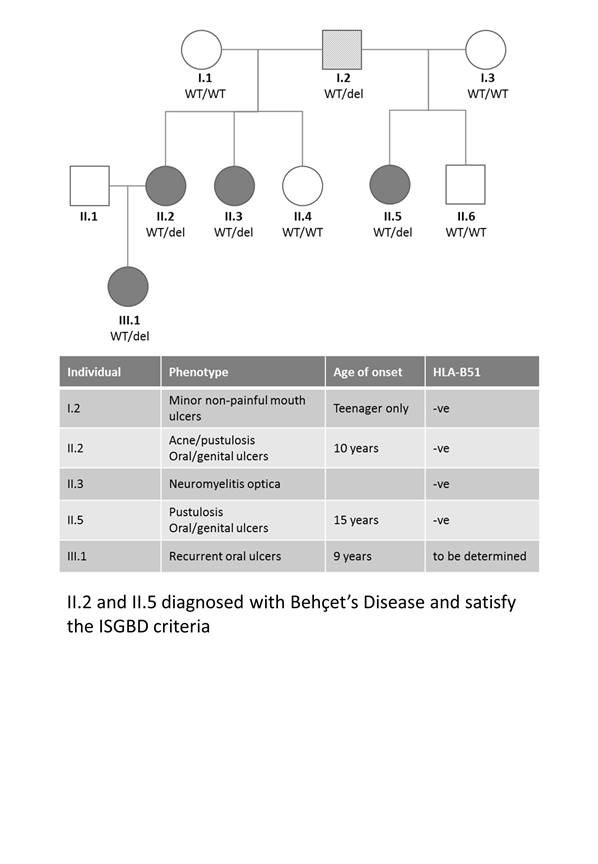
Methods: This study involved a 3-generation family with Behçet’s-like mucocutaneous ulceration syndrome; primarily involving childhood-onset chronic oral and genital ulcers (figure 1). ISGBD criteria were used to diagnose Behçet’s Disease (BD). DNA was isolated from PBMCs from affected patients and non-affected familial controls. DNA sequencing identified a cysteine deletion at position 1459 in RELA which segregated with the condition. Immunoblot analysis of RELA confirmed protein truncation. PBMCs were stimulated with TNF and NFkB phosphorylation was measured relative to unstimulated controls.
Results: A heterozygous cysteine deletion at position 1459 in RELA was detected in affected individuals. This mutation is coding, inducing a frameshift His487ThrfsTer7, predicted to produce a truncated protein of 492 amino acids which would result in a ~6kDa smaller protein. This truncation was confirmed by immunoblot, with the affected individuals producing two bands: the wild-type and truncated protein whereas unaffected controls produced only the wildtype protein. Preliminary data indicates RelAHis487ThrfsTer7 heterozygotes have different kinetics in response to TNF, as measured by phosphorylation of RELA.
Conclusion: This study gives novel information on both the genetic basis and biological mechanisms of BD in individual families. Familial mutations that induce haploinsufficiency of RELA have recently been associated with BD. However, the His487ThrfsTer7 results in protein truncation rather than haploinsufficiency. Crucially, the His487ThrfsTer7 mutation interrupts the two C-terminal RELA transactivating domains. Our study supports several recently published studies that loss-of-function mutations in the NF-κB pathway are linked with the development of familial early-onset BD-like syndromes. Understanding both the genetic basis and biological mechanisms facilitates personalized medicines approaches that target the primary disease mediators, which result in earlier disease control and reduced tissue damage.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dorris E, Adeeb F, Cummins E, Savic S, Fraser S, Wilson AG. A Novel Familial RELA Truncation Is Associated with Behçet’s-like Mucocutaneous Ulceration Syndrome [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-novel-familial-rela-truncation-is-associated-with-behcets-like-mucocutaneous-ulceration-syndrome/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-novel-familial-rela-truncation-is-associated-with-behcets-like-mucocutaneous-ulceration-syndrome/