Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Methotrexate (MTX) is the first-line therapy for rheumatoid arthritis (RA). While therapeutic adherence is essential to the successful management of the patient, an estimated 40% of patients are thought to be non-adherent. Adherence to MTX is challenging to monitor as no objective MTX assay is currently available.
Our objective was to describe the urinary kinetics of MTX and its major 7-OH-MTX metabolite in treated patients and to evaluate the possibility to use one or both of these markers as an objective MTX-adherence assay.
Methods: Fifty-nine patients with RA (2010 ACR/EULAR criteria) treated with subcutaneous MTX were recruited.
Patients underwent urinary MTX pharmacokinetic assessment using high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) analysis. The urine sample was analyzed before and after subcutaneous injection (from 2 hours to 10 days after injection). Confirmed administration at hospital therapy was the reference of MTX-adherence.
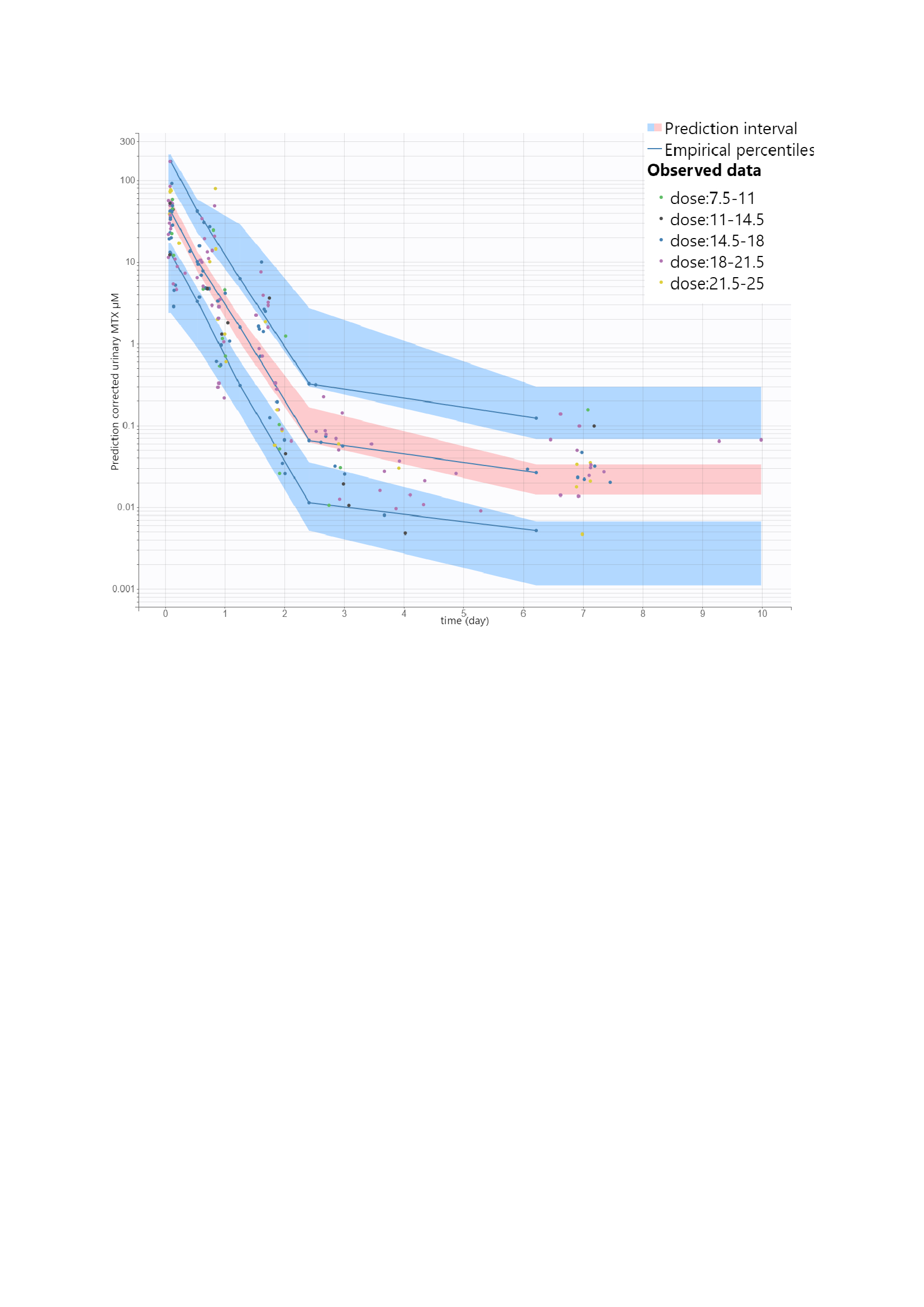
MTX and 7-OH-MTX concentrations were analyzed, and a population pharmacokinetic model was developed to describe the kinetics of MTX as a function of time and weekly dose.
From this model, the urinary MTX concentrations in treated patients were compared with the urinary concentrations of controls (n = 18 referent patient adherent and 10 patient with undifferentiated inflammatory arthritis without mtx treatment).
Results: A total of 363 urine samples (range 2-6 per patient) were obtained from patients treated with subcutaneous MTX. The average weekly dose of MTX was 17.2 mg/week (7.5-25mg)
A 2-compartment model with nonlinear renal elimination kinetic best described the urine MTX concentration versus time curves. This model allowed us to characterize the standard kinetic profiles of the observant patients as a function of different associated factors. Thus, 95% of MTX urine concentration values were above 0.9 nM regardless of the delay between MTX injection and urine sampling and independently associated MTX-adherence. A discriminatory cut-off value of 0.9 nM (v.s control group 0.22, CI95% [0.19-0.25] µM) made it possible to have an assay sensitivity and specificity of more than 93% and an AUC-ROC above 96 %, regardless of the MTX doses.
Conclusion: Using urine MTX concentration, we developed a pharmacostatistical model to monitor subcutaneous MTX adherence of RA patients. This allowed us to propose a new and objective MTX-adherence assay, which could help in current practice to differentiate patients who do not respond to methotrexate from non-adherent patients. After further validation, this test could therefore improve patient management by avoiding unnecessary intensification in non-adherent patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Geoffroy M, Gozalo C, Pauvele L, Abboud E, Djerada Z, Salmon J. A New Pharmacostatistical Model to Assess MTX-adherence in RA Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-new-pharmacostatistical-model-to-assess-mtx-adherence-in-ra-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-new-pharmacostatistical-model-to-assess-mtx-adherence-in-ra-patients/