Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: SLE – Animal Models Poster
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: MSCs, exposed to a disease-specific cytokine profile, can accurately sense the composition of the inflammatory microenvironment. We have harnessed this adaptive ability of MSCs to create our product, HXB-319. HXB-319 is a multi-targeted cell therapy developed by training MSCs using Design of Experiments (DoE)-based methodology to mount an adaptive counter-response to the unique inflammatory profile of the tissue microenvironment seen in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In this study, we tested whether HXB-319 ameliorates inflammatory injury in a mouse model of SLE.
Methods: Intraperitoneal (IP) administration of pristane was used to induce lupus in female BALB/c mice at day 1, and either naïve MSCs or HXB-319 cells were delivered IP on day 28 (2X106/mouse) in a first set of mice which were monitored for an additional 9 months. Urine for albumin and creatinine ratio (A/C), tissue (spleen, kidney) for histopathology and gene expression, and blood for assessment of levels of cytokines were collected.
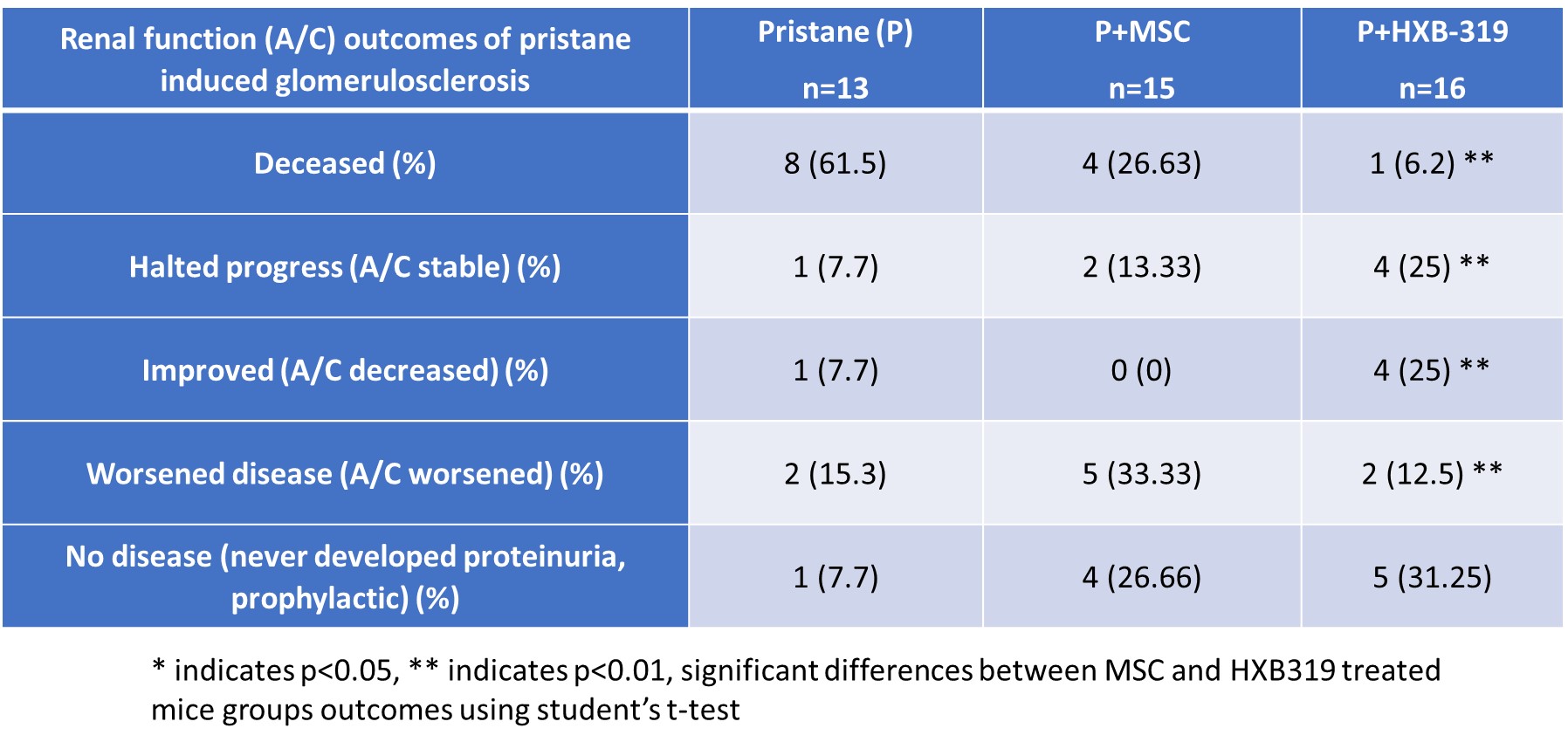
A second set of pristane-induced BALBc/J female mice with glomerulonephritis were randomized to receive no treatment (Pristane, P), or either naïve MSC (P+MSC group) or HXB-319 cells (P+HXB-319) 2X106/mouse intravenous (IV). Mice were randomized after they developed proteinuria. Urinalysis was repeated at 6 months post pristane induction, and just before sacrifice.
Results: First set of mice (Figure 1):
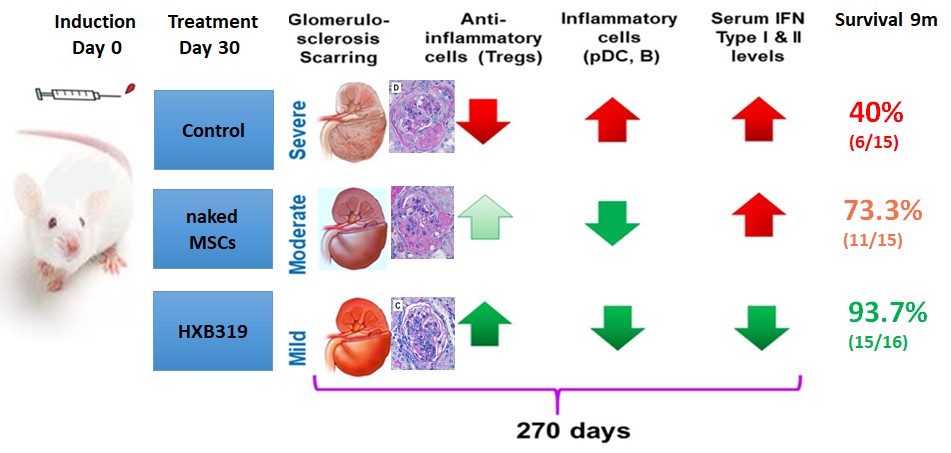
1) Flow cytometry analysis of splenocytes showed significant changes in the CD4+Foxp3+, CD4+PD-L1+, and CD8+RORgT+ (Th17 cells) subsets after HXB-319 treatment. pDCs (p< 0.008) and Th17 cells (p< 0.018) were significantly decreased in HXB-319 treatment arm.
2) Serum levels of, IFN-γ (p< 0.001), and IL-17A (p=0.014) were significantly lower in HXB-319 treated lupus mice
3) The histopathologic evaluation of kidney samples showed that HXB-319 prevented reduced global scarring and preserved kidney function.
4) HXB-319 treatment (n=16) led to a significant improvement in survival, 93.7% versus 40% in the untreated lupus mice (n=15) (p< 0.01).
2nd set of mice:
The A/C ratio in spot urine (Table 1) indicated that both MSCs and HXB-319 intravenous treatment reduced progression to end stage kidney disease (ESKD). HXB-319 either halted the disease progression or significantly improved the A/C ratio (4+4/16, 50%), more effectively than MSCs in lupus mice. Five HXB-319 treated lupus mice never developed proteinuria (35.7%), compared to untreated group (7.7%). Urinary protein excretion remained stable in 28.6% and improved in 28.6% in HXB-319 treated lupus mice.
Calculated from the time point of randomization (6m), mice with advanced disease) with an A/C ratio >300 showed a 100% survival rate (8/8) after HXB-319 treatment, while only 67% after MSC treatment (4/6). Histopathology showed that untreated lupus mice (n=13) had over twice the risk of experiencing irreversible nephron loss and glomerulosclerosis compared to HXB-319 treated lupus mice (n=16). The HXB-319 treatment group showed significant and sustained improvement of A/C for more than 3 months (X2=12, p< 0.002).
Conclusion: Overall, our data suggest that treatment with HXB-319 can halt the inflammation in SLE causing tissue damage often leading to ESKD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bukulmez H, Dennis A, Highland k, Emancipator S. A New Generation Mesenchymal Stromal Cell (MSC)-based Cell Therapy Using Design of Experiments Halts Pristane Induced Glomerulosclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-new-generation-mesenchymal-stromal-cell-msc-based-cell-therapy-using-design-of-experiments-halts-pristane-induced-glomerulosclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-new-generation-mesenchymal-stromal-cell-msc-based-cell-therapy-using-design-of-experiments-halts-pristane-induced-glomerulosclerosis/