Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
A New Approach for Detecting Progressive Joint Damage using 3D Imaging from High-Resolution Peripheral Quantitative Computed Tomography: Measuring Reproducibility
Background/Purpose: Joint space narrowing is an important feature of progressive joint damage and functional impairment in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Methodology to provide longitudinal and sensitive 3D measurements of joint space width have not yet been developed for research or clinical applications. High-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT) (Scanco Medical AG, Switzerland) has recently become available to accurately and reproducibly measure bone microstructure at a nominal isotropic voxel dimension of 82 μm. Given the ability of HR-pQCT to detect bone margins with high precision, we developed a methodology to measure the 3D metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint space width. This work determines the reproducibility of the scan protocol with hand repositioning for application for early detection and longitudinal monitoring of RA.
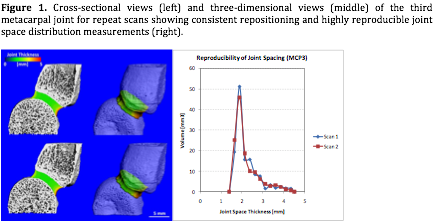
Methods: Two repeated HR-pQCT scans of the 2nd and 3rd MCP joints of ten subjects with early RA (70% female, mean age 45 years) with repositioning between scans were obtained. The periosteal edges of the metacarpal head and proximal phalanx base were detected and segmented, and from these images the joint space width and distribution of joint space thickness were measured using a custom analysis implemented for the HR-pQCT based on direct measurements from the high resolution image data.
Results: In this population, the mean joint space width of the 2nd MCP was 1.82 mm (SD 0.20) and of the 3rd MCP 1.84 mm (SD 0.23). Reproducibility with repositioning was excellent, with overlapping filtered histograms and a root square mean coefficient of variance of 4.8%.
Conclusion: We have established a highly reproducible methodology for evaluating the joint space width, applied here to the MCP joints. Currently, we combine this assessment with measures of joint erosions and periarticular bone density. Together, these measures from HR-pQCT show great promise for a new approach for early RA detection, and monitoring of disease activity and/or treatment.
Disclosure:
C. Barnabe,
None;
H. R. Buie,
None;
M. Kan,
None;
S. G. Barr,
None;
L. Martin,
None;
S. K. Boyd,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-new-approach-for-detecting-progressive-joint-damage-using-3d-imaging-from-high-resolution-peripheral-quantitative-computed-tomography-measuring-reproducibility/