Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Proinflammatory cytokine activation of JAK/STAT signal pathway is critical in the pathogenesis and progression of RA. SHR0302, a potent and selective inhibitor of JAK1, demonstrated promising anti-inflammatory effects for RA in both preclinical and phase 1 studies. A multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind phase 2 study was performed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of SHR0302 in Chinese subjects with RA.
Methods: Eligible subjects were 18–70 years; had a diagnosis of RA according to 2010 ACR/EULAR RA criteria; had moderately to severely active disease defined by ≥6 tender joints, ≥6 swollen joints (out of 68- or 66-joints examined), and ESR>28 mm/h or CRP >1.2 times upper limit of normal; were either treatment-naive or inadequately responded or intolerant to conventional synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (csDMARDs). Subjects who had prior treatment with JAK inhibitor or biologics were excluded. Eligible subjects were randomized to receive placebo or 0.5, 1, 2, or 4 mg SHR0302 in 1:1:1:1:1 (per protocol v1.1) or to receive placebo, 4 or 8 mg SHR0302 1:1:3 (per protocol v2.0) once daily (oral) for 12 weeks. Afterwards, subjects who initially assigned to placebo were re-assigned to take 2, 4 mg or 8 mg SHR0302 daily for additional 12 weeks, while subjects initially assigned to SHR0302 remained on the same treatment. The primary endpoint was the proportion of subjects who achieved ≥20% improvement according to the American College of Rheumatology response criteria (ACR20) at week 12.
Results: Between Sep 2017 to Oct 2019, 194 eligible subjects were randomized (Figure 1). The ACR20 response rates at week 12 for subjects receiving SHR0302 2 mg (56.5%, p=0.02), 4 mg (67.5%, p< 0.001), and 8 mg (77.8%, p< 0.001) were significantly greater than those of placebo (27.0%). ACR50/70 response rates at week 12 were generally consistent with ACR20 (Table 1). Mean changes from baseline in DAS28-3 (CRP) were numerically greater with the treatment of SHR0302 in comparison with placebo at week 12 (Table 1), and significantly more subjects in 4 mg (25.0%, p=0.02) and 8 mg (33.3%, p=0.002) groups achieved a DAS28-3 (CRP) < 2.6 versus placebo (5.4%) at week 12. SHR0302 2, 4, and 8 mg groups had significantly greater changes from baseline in HAQ-DI scores at week 12 (adjusted mean change: 2 mg, -0.68, p=0.02; 4 mg, -0.48, p=0.048; 8 mg -0.75, p< 0.001) as compared with placebo (-0.30). Above-mentioned improvements were sustained at week 24 (Table 1). The proportion of subjects with any treatment emergent adverse events was higher for SHR0302 (73.9%) vs placebo (62.2%) through week 12, particularly infection (Table 2). A total of four cases of herpes zoster and one case of opportunistic infection (cryptococcal pneumonia) were reported, all in SHR0302 8 mg group. No tuberculosis, malignancy, important cardiovascular events or death were reported. Safety results were presented in Table 2.
Conclusion: SHR0302 showed sustained efficacy in improving signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in a dose-dependent manner and had a generally acceptable safety profile. Further confirmatory studies with SHR0302 in RA will be planned accordingly.
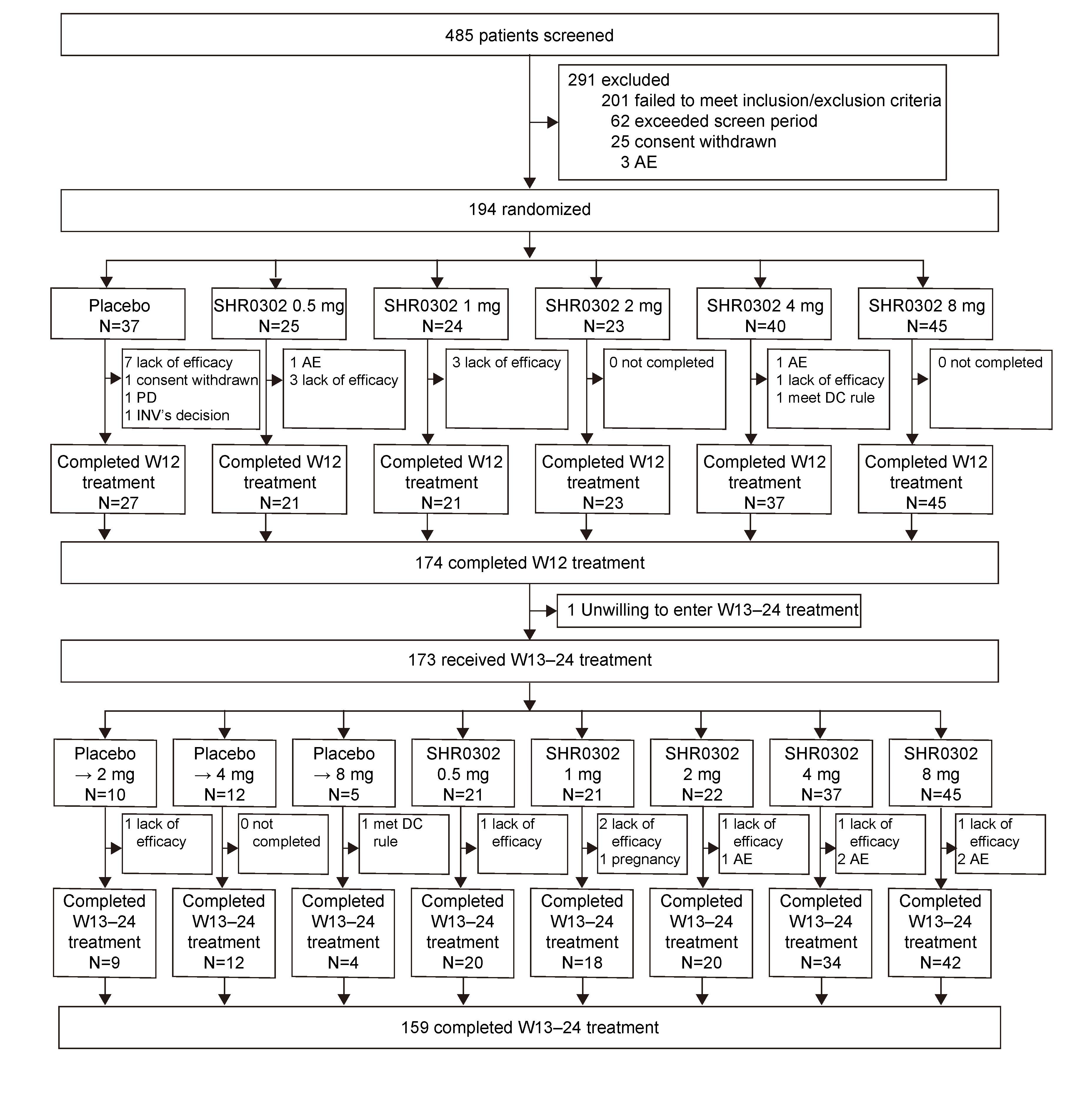 Figure 1. Trial profile. The SHR0302 8 mg group was added in protocol v2.0 to explore the maximum safe and effective dose according to latest preclinical data. AE, adverse events; INV, investigator; PD, progressive disease; DC, discontinuation.
Figure 1. Trial profile. The SHR0302 8 mg group was added in protocol v2.0 to explore the maximum safe and effective dose according to latest preclinical data. AE, adverse events; INV, investigator; PD, progressive disease; DC, discontinuation.
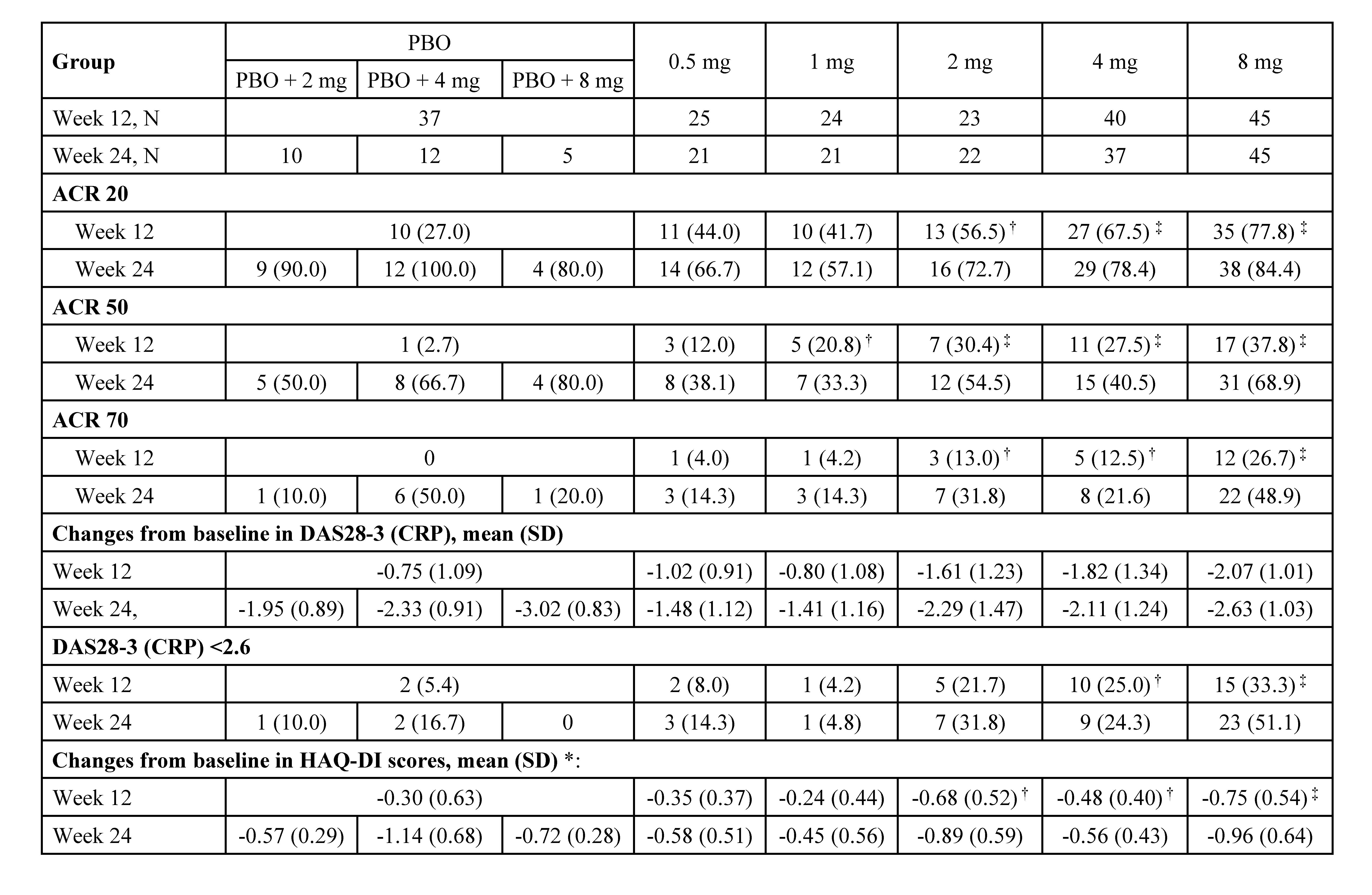 Table 1. Efficacy results. †: P < 0.05; ‡: P < 0.01 vs PBO; *: adjusted for baseline HAQ-DI score and previous inadequate response to csDMARDs or not; Data are n (%), unless otherwise specified; PBO, placebo; DAS28-3 (CRP), 3-variable 28-joint Disease Activity Score using C-Reactive Protein; HAQ-DI, Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index.
Table 1. Efficacy results. †: P < 0.05; ‡: P < 0.01 vs PBO; *: adjusted for baseline HAQ-DI score and previous inadequate response to csDMARDs or not; Data are n (%), unless otherwise specified; PBO, placebo; DAS28-3 (CRP), 3-variable 28-joint Disease Activity Score using C-Reactive Protein; HAQ-DI, Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index.
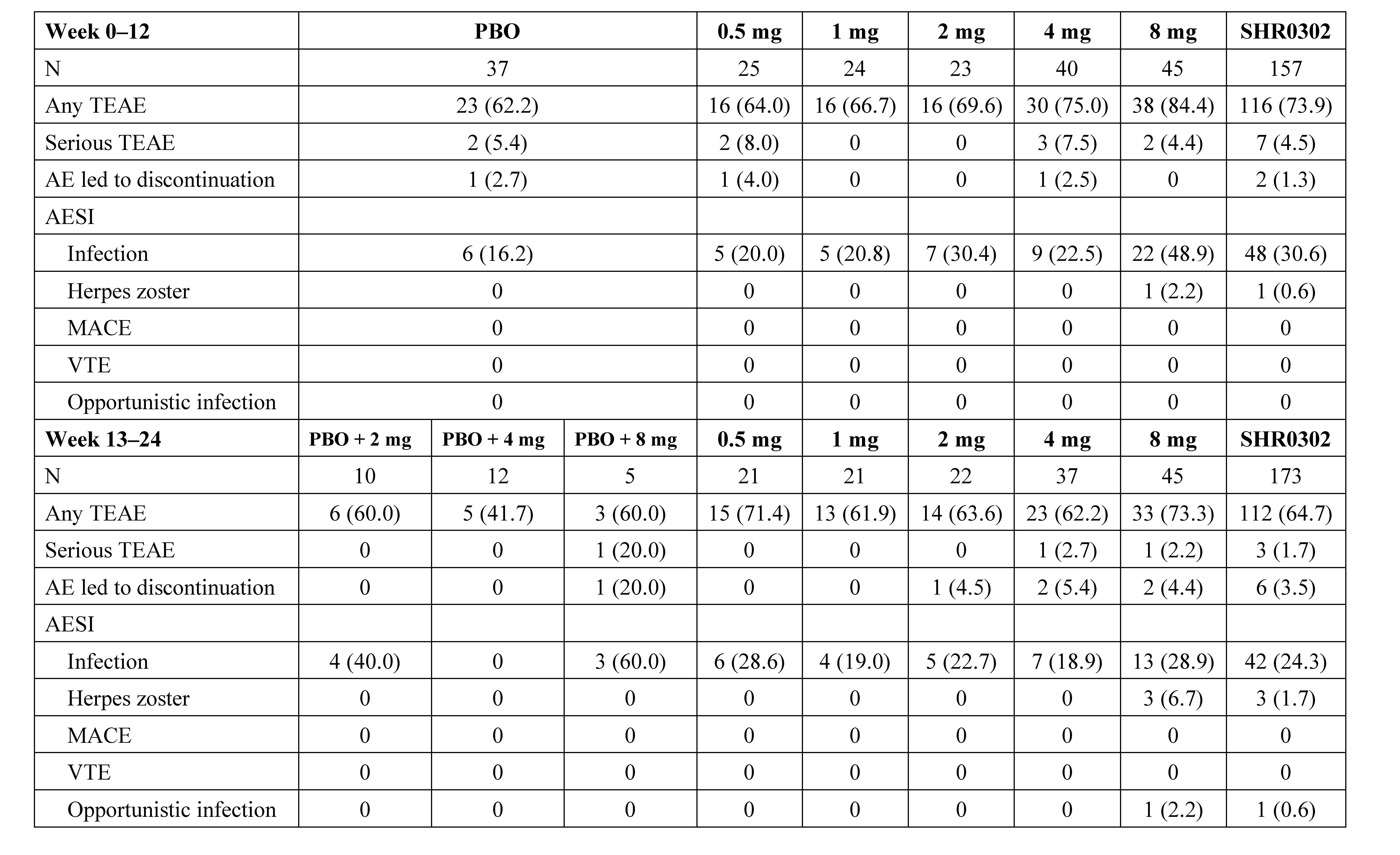 Table 2. Safety profile. Data are n (%), unless otherwise specified. PBO, placebo; TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event; AESI,adverse event of special interest; MACE, major adverse cardiovascular events; VTE, venous thromboembolism.
Table 2. Safety profile. Data are n (%), unless otherwise specified. PBO, placebo; TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event; AESI,adverse event of special interest; MACE, major adverse cardiovascular events; VTE, venous thromboembolism.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zeng X, Jiang Y, Yang Y, Li H. A Multicenter, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-blind Phase 2 Study of SHR0302 versus Placebo in Chinese Subjects with Moderate to Severe Active Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-multicenter-randomized-placebo-controlled-double-blind-phase-2-study-of-shr0302-versus-placebo-in-chinese-subjects-with-moderate-to-severe-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-multicenter-randomized-placebo-controlled-double-blind-phase-2-study-of-shr0302-versus-placebo-in-chinese-subjects-with-moderate-to-severe-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra/
