Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2020
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster II: Miscellaneous Rheumatic Diseases
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Mindfulness Based Interventions (MBIs) are well-established self-management programs shown to be beneficial for pain, depression, and anxiety that focus on learning how to respond to bodily sensations and emotions through guided meditative practices. However, due to time constraints, scheduling, and physical limitations, we found it difficult for patients to attend in-person MBIs; we therefore implemented a mobile MBI, using the commercially available smartphone application, Calm©.
Methods: Established patients with rheumatic disease in our Rheumatology Division at a tertiary referral center were eligible for inclusion. Participants were asked to engage in the app for a minimum of 5 minutes/day for 30 days, provide baseline clinical and demographic information, and complete baseline and 30-day questionnaires pertaining to health-related quality of life (HRQL). Questionnaires included the Patient Reported Outcome Measurement Information System (PROMIS) (v2.0) 4a short forms (physical function, social participation, fatigue, sleep disturbance, pain interference), computer adaptive tests (CATS) (v1.0) for anxiety, depression, self-efficacy for managing emotions, and for managing symptoms and the NIH Toolbox Perceived Stress FF v2.0. Demographics, clinical characteristics, and mean T-scores were compared between groups using t-tests or chi-square. A sensitivity analysis was performed for participants who fully completed the program.
Results: 40 participants consented, 35 participants completed baseline questionnaires, 17 participants completed post survey questionnaires and used Calm, 17 participants completed baseline questionnaires but were lost to follow up, and 1 participant completed both surveys but did not use Calm. Participants had a mean age (SD) of 50 years (13), were mostly female (91%), white (74%), well-educated (66% with a college degree or greater) and working full time (56%). Most participants had inflammatory arthritis (60%); patients with lupus (17%), Sjogren’s syndrome (9%), and scleroderma (14%) were also included. Compared to non-completers, full completers had similar demographics and use of medications that could potentially impact mood. However, full completers had higher patient global assessment of disease activity (PGA) scores, more pain (VAS), higher perceived stress, and more anxiety at baseline (Table 1). Full completers meditated on average for 302 minutes (SD 254; n=15). For completers, significant improvements were noted in fatigue by course end with trends for improvement in perceived stress, anxiety, sleep disturbance, and self-efficacy (Table 2).
Conclusion: Results from a pilot study on use of a 30-day smartphone mindfulness meditation application for patients with rheumatic disease revealed that this is a feasible and acceptable non-pharmacologic modality to target HRQL. Participants with higher baseline stress, anxiety, pain, and PGA scores were more likely to complete the mobile MBI program. Among completers, preliminary results showed improvements in fatigue and perceived stress. More rigorous study on mindfulness application use and barriers, as well as potential effect on HRQL, is needed.
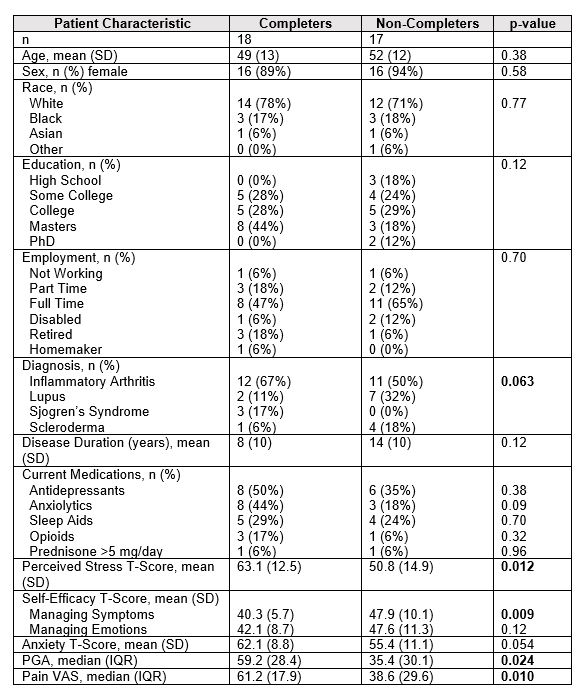 Table 1. Baseline patient characteristics comparing those who completed the full program compared to those lost to follow up.
Table 1. Baseline patient characteristics comparing those who completed the full program compared to those lost to follow up.
 Table 2. HRQL domains pre/post 30-day mobile, mindfulness meditation trial for participants who completed pre/post questionnaires (n=18). * Derived from PROMIS 4a form extracted from Global-29 collection of surveys; **CATs, ***NIH Fixed Form.
Table 2. HRQL domains pre/post 30-day mobile, mindfulness meditation trial for participants who completed pre/post questionnaires (n=18). * Derived from PROMIS 4a form extracted from Global-29 collection of surveys; **CATs, ***NIH Fixed Form.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
DiRenzo D, Hunt C, Sibinga E, Gould N, Shah A, Bartlett S, Bingham III C. A Mobile Mindfulness Meditation Program May Improve Health-Related Quality of Life for Patients with Rheumatic Disease, a Pilot Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-mobile-mindfulness-meditation-program-may-improve-health-related-quality-of-life-for-patients-with-rheumatic-disease-a-pilot-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-mobile-mindfulness-meditation-program-may-improve-health-related-quality-of-life-for-patients-with-rheumatic-disease-a-pilot-study/
