Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Whilst methotrexate (MTX) is the first-line treatment of
rheumatoid arthritis (RA), response is not universal. Rates of adherence
reported in the literature range from 59% to 107% and non-adherence is
associated with poor treatment response. There is no gold standard measurement
of adherence and currently no biochemical test of MTX levels in blood samples is
available to objectively assess adherence. The aim, therefore, was i) to develop
a liquid chromatography-selected reaction monitoring mass spectrometry
(HPLC-SRM-MS) method to measure the concentrations of both MTX and its major
metabolite 7-OH-MTX in plasma; ii) to apply the assay to a cohort of patients
with RA undergoing MTX therapy and iii) to develop a population pharmacokinetic
model to explore the relationship of MTX ingestion with ability to detect the analytes
over time.
Methods:
A HPLC-SRM-MS method to detect MTX and 7-OH-MTX was
developed according to the European Medicines Agency guidelines. RA patients
(n=20) using oral MTX were admitted for 24 hours and on 2 subsequent days
within 7 days of MTX administration. Nine blood samples were taken during the
study period to measure MTX and 7-OH-MTX levels in plasma. All samples were analysed
in triplicate, and the data were used to develop a population pharmacokinetic
model. Effects of covariates (body weight and serum creatinine levels) on the
model parameters were tested. Finally, simulations were performed to predict
the proportion of patients with detectable concentrations of both MTX and
7-OH-MTX over time.
Results:
Twenty RA patients (65% female) completed the study with
median (IQR) age of 66 (56-70) years, serum creatinine 72
(68-79) umol/l and weight 77 (68-84) kg. MTX
dose ranged from 7.5 to 25mg. The lower limit of quantification for MTX and
7-OH-MTX was 0.5 and 0.75nM respectively. The model that best described the
plasma concentration-time data was a two-compartment model with a first-order
absorption process for MTX, and one linked compartment for 7-OH-MTX. Bodyweight
was included as a covariate. The effect of serum creatinine levels on the
systemic clearance of MTX was negligible. Inter-subject variability could be
estimated for all parameters and appeared to be highest for the absorption
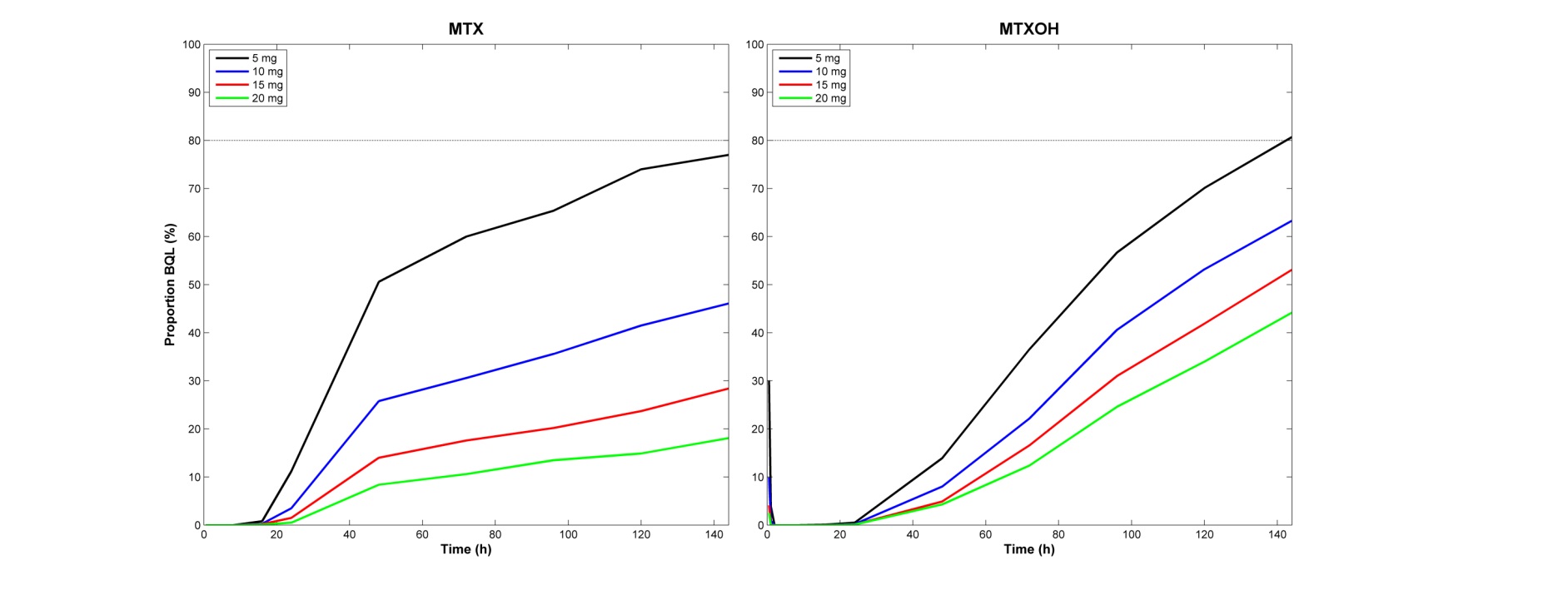
parameter. The simulations suggest that after administration of 15 mg of MTX,
approximately 70% of patients will have detectable MTX plasma concentrations
144 hours (6 days) post-dose (figure 1) but that the optimal time for testing
would be within 60 hours (10% undetectable).
Conclusion:
A HPLC-SRM-MS assay to measure MTX and 7-OH-MTX levels in
patients on low dose MTX has been developed. A population pharmacokinetic model
of plasma MTX and 7-OH-MTX levels can be used as a qualitative tool to evaluate
patients’ adherence to treatment.
Figure 1. Simulated (n=1000) expected proportion of
subjects with undetectable MTX/7-OH-MTX levels over time after administration
of different oral MTX doses.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bluett J, Wendling T, Ogungbenro K, Riba-Garcia I, Unwin R, Verstappen SM, Barton A. A HPLC-SRM-MS Based Method for the Detection of Adherence to Low-Dose Oral Methotrexate [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-hplc-srm-ms-based-method-for-the-detection-of-adherence-to-low-dose-oral-methotrexate/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-hplc-srm-ms-based-method-for-the-detection-of-adherence-to-low-dose-oral-methotrexate/