Session Information
Date: Monday, October 22, 2018
Title: Vasculitis Poster II: Behҫet’s Disease and IgG4-Related Disease
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
IgG4-Related Disease (IgG4-RD) is a chronic immune-mediated fibro-inflammatory disorder of unknown etiology. The differential diagnosis is broad, partly because of the myriad potential organ manifestations. To facilitate diagnosis, the 2018 ACR/EULAR classification criteria were validated using IgG4-RD and mimicker cases. We analyzed the mimickers to establish a framework for considering the differential diagnosis of IgG4-RD.
Methods:
493 IgG4-RD cases and 401 mimickers were submitted during the validation phase. The classification criteria were comprised of exclusion and inclusion criteria. Demographic features, organ involvement and criteria fulfilled were assessed for each diagnosis. Diseases that tend to have multi-organ involvement were studied.
Results:
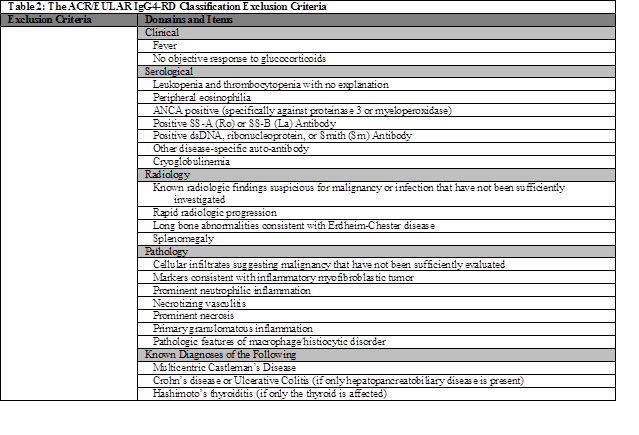
We analyzed 214 mimickers. IgG4-RD, Erdheim-Chester disease (ECD), Rosai-Dorfman disease (RDD) and multicentric Castleman’s disease (MCD) were male predominant, whereas SS, vasculitis, lymphoma and sarcoidosis tended to be female predominant (Table 1). IgG4-RD, lymphoma and GCA tended to have an older age of onset compared with SS, ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) and other mimickers. Organ involvement differed by mimicker, as expected. Submandibular gland involvement was equally common in IgG4-RD and SS, but isolated parotid involvement was more typical of SS and lacrimal gland more characteristic of IgG4-RD. Lymphadenopathy, serum IgG4 elevations, lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates and significant IgG4+ cell infiltrates were observed in many mimickers. Exclusion criteria were crucial to differentiating mimickers from IgG4-RD despite these similarities. 91.1% of mimickers fulfilled exclusion criteria as compared to only 7.1% of IgG4-RD cases (Table 2). Ro or La excluded 78.7% of SS cases. In AAV, ANCA, fever and necrotizing vasculitis on pathology excluded IgG4-RD in 81.2%, 71.0% and 52.2% of cases, respectively. In lymphoma, rapid radiographic progression, splenomegaly and a malignant infiltrate on pathology excluded IgG4-RD in 45.5%, 27.3% and 100% of cases, respectively. Exclusion by pathology (71.4-100%) was vital in separating ECD, MCD, RDD and sarcoidosis from IgG4-RD.
Conclusion:
IgG4-RD and mimickers share many features, including demographics, organ involvement and elevated serum IgG4 levels. Exclusion criteria were critical to the 2018 ACR/EULAR classification criteria development, identifying key features that distinguish IgG4-RD from its mimickers. These clinical, serologic, radiologic and pathology features serve as a useful guide for clinicians considering the IgG4-RD differential.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Matza MA, Wallace Z, Stone JH. A Data-Driven Approach to Guide Physicians When Considering the Differential Diagnosis of IgG4-Related Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-data-driven-approach-to-guide-physicians-when-considering-the-differential-diagnosis-of-igg4-related-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-data-driven-approach-to-guide-physicians-when-considering-the-differential-diagnosis-of-igg4-related-disease/