Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1100–1123) Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Distinguishing crystalline from septic arthritis is a common challenge in patients admitted with acute joint inflammation. Arthrocentesis for synovial fluid analysis is considered the gold standard for both entities, but it is not always available. The aim of this study was to compare the demographic, clinical, and laboratory characteristics of patients admitted with septic and crystalline arthritis confirmed by synovial fluid analysis to identify factors to develop a diagnostic rule.
Methods: Our study population consisted of patients admitted to our institution between 1999-2020 with the diagnosis of gout, pseudogout and septic arthritis identified using ICD9 and 10 codes. We reviewed medical records and included those with diagnoses confirmed by synovial fluid analysis. Demographic data including sex, race, body mass index, comorbidities, distribution of affected joints, physical exam characteristics, medications, and laboratories including estimated glomerular filtration rate, white cell and neutrophil count, inflammatory markers, and serum urate were recorded. We summarized continuous variables with medians and interquartile ranges (IQR) and categorical variables with frequencies and proportions. We used Wilcoxon rank sum and Fisher’s exact test to analyze for differences between the septic and crystalline groups. We considered significant a p value of < 0.05, but we further adjusted the assessment of significance for multiple comparisons using the Bonferroni correction. All analysis was completed using R studio.
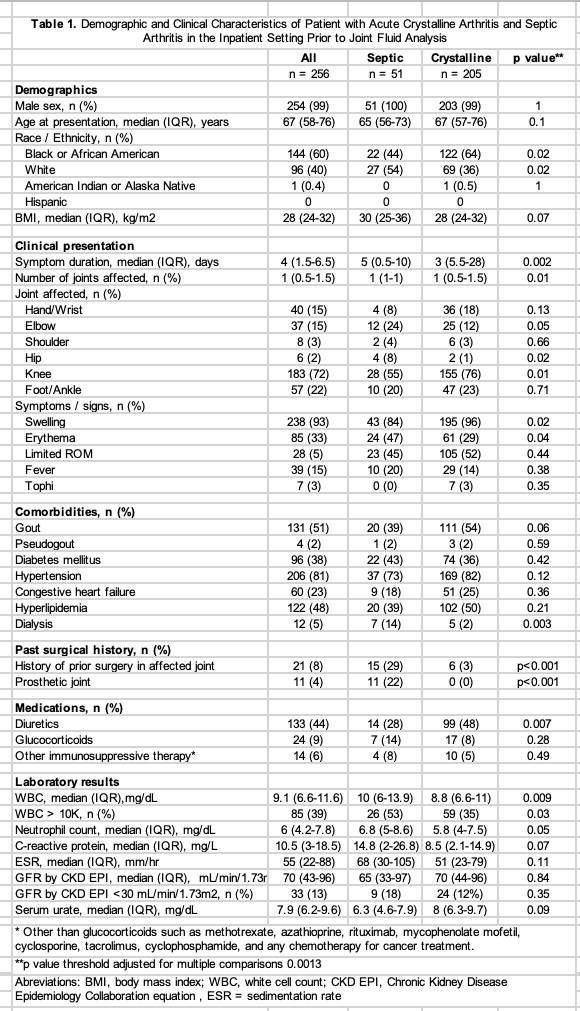
Results: Of the 256 patients identified, 51 had a diagnosis of septic arthritis and 205 a diagnosis of crystalline arthritis. Two hundred and fifty-four (99%) were men, one hundred forty-four (60%) were African-American, and ninety-six (40%) self-identified as White. The median duration of symptoms was 4 days. Compared to patients with crystalline arthritis, septic arthritis patients were more commonly of White race (Table) (54 vs 36% p=0.02), had longer symptom duration (median of 5 versus 3 days, p=0.002), tended to have fewer joints affected (p=0.001), had higher proportion of involvement of elbows (24 vs 12%) and hips (8 versus 1%), and lower proportion of knee involvement (55 versus 76%). Patient with septic arthritis had more joint erythema (47 versus 29%) but less joint swelling (84 versus 96%) and had higher proportions of history of prior surgery in the affected joint (29% vs. 3%, p< 0.001), and involvement of a prosthetic joint (22% vs. 0%, p= < 0.001). Absolute leukocyte counts and neutrophil counts were higher in patients with septic arthritis. After adjustment for multiple comparisons only the proportion of prior surgery and involvement of a prosthetic joint met the more stringent significance threshold.
Conclusion: History of prior surgical intervention in the affected joint, and prosthetic joint were strongly associated with septic arthritis. Many other demographic, clinical, and laboratory factors were also different between patients with septic and crystalline arthritis. Future steps will include the development of a prediction model for septic and crystalline arthritis when synovial fluid analysis is not available.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Salgado Guerrero M, Urquiaga M, Panchani N, Gaffo A. A Comparison of Characteristics of Patients with Crystalline and Septic Arthritis Confirmed by Synovial Fluid Analysis: Towards the Development of a Diagnostic Rule [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-comparison-of-characteristics-of-patients-with-crystalline-and-septic-arthritis-confirmed-by-synovial-fluid-analysis-towards-the-development-of-a-diagnostic-rule/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-comparison-of-characteristics-of-patients-with-crystalline-and-septic-arthritis-confirmed-by-synovial-fluid-analysis-towards-the-development-of-a-diagnostic-rule/