Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose:
The mechanism of action of methotrexate (MTX) in the management of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) remains incompletely understood. It is nonetheless capable of inducing clinical remission as a monotherapy in approximately 30% of cases, being the most cost-effective therapeutic choice in such individuals. We investigated the CD4+ T-cell transcriptome in early RA patients, seeking biomarkers for drug survival on MTX monotherapy and associated pharmacological insights.
Methods:
RNA was extracted from highly purified peripheral blood CD4+ T-cells from consenting early RA patients within 4 hours of blood draw, at which time patients had been symptomatic for a median of 12 weeks, and were naïve to immunomodulatory treatments. All patients were subsequently treated with MTX monotherapy, which was continued for as long as this treatment was deemed successful between patient and consulting rheumatologist, over an 18 month follow-up period. Intra-muscular steroid bolus administration (but not oral steroid therapy) was permitted during the study at the discretion of the consulting rheumatologist. Transcriptional profiling of baseline samples was undertaken using Illumina WG6v3 BeadChip oligonucleotide array technology and analysed using GeneSpring XI (Agilent).
Results:
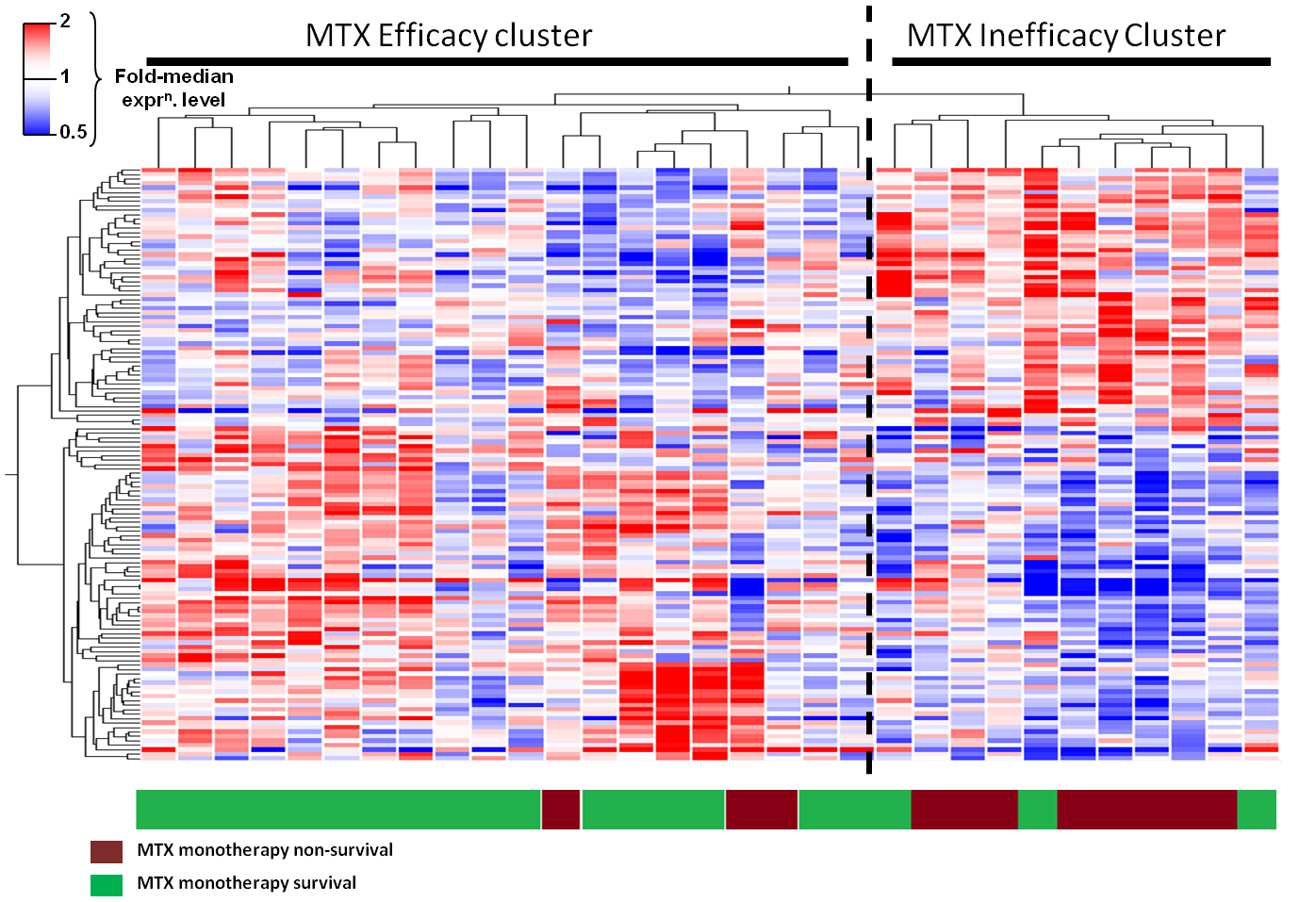
Of 37 recruited patients, 6 were excluded from analysis because of insufficient or defaulted follow-up. Amongst the remaining 31 patients, 19 (61%) remained on MTX monotherapy at the end of follow-up, but the treatment strategy was unsuccessful (and required modification) for the remaining 12 (39%). Baseline characteristics and final methotrexate doses were comparable between the two groups. 133 CD4+ T-cell transcripts were identified as being differentially expressed between comparator groups at baseline (>1.2 fold-change; p<0.05) and, amongst these, functional analysis identified an over-representation of genes involved in apoptosis (11/133 genes; hypergeometric p=0.000045).
Conclusion:
Our pilot study has identified potential transcriptional biomarkers for drug survival on MTX monotherapy amongst early RA patients which, alongside their potential clinical applicability, suggest that the efficacy of this treatment may depend on its ability to regulate CD4+ T-cell survival pathways. Validation amongst a clinically well-characterised, independent early RA cohort is now on-going.
Disclosure:
A. G. Pratt,
None;
P. M. Brown,
None;
S. J. Cockell,
None;
G. Wilson,
None;
J. D. Isaacs,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-cd4-t-cell-gene-expression-signature-predicts-drug-survival-on-methotrexate-monotherapy-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis/