Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose
Leflunomide is an effective treatment for rheumatoid arthritis. An association between pulmonary adverse events, in particular interstitial lung disease, and leflunomide use has been reported. Incident respiratory events may result in cessation of leflunomide treatment. Clarification of its potential role in pulmonary disease is therefore of clinical importance.
Methods
We performed a systematic literature search of Pubmed and Cochrane databases with no date limits for double-blind randomised controlled trials of leflunomide versus placebo or active comparator agents in adults with rheumatoid arthritis. We evaluated the association between leflumonide use and pulmonary adverse events by performing a meta-analysis of the results. Studies with less than 50 subjects, of less than 12 weeks duration, or with no reporting of respiratory adverse events were excluded. Random effects meta-analysis using the Mantel-Haenszel method was used to assess total respiratory adverse events, infectious respiratory adverse events, non-infectious respiratory adverse events, pneumonitis, and death. Results were expressed as relative risks (RR) with 95% confidence intervals.
Results
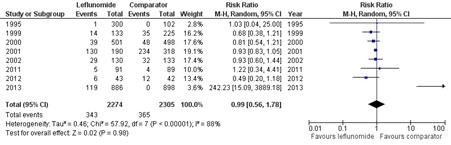
Our literature search returned 884 results. A total of 8 studies, 4 with placebo comparators, met our inclusion criteria. Seven hundred and eight respiratory adverse events were documented in 4579 participants. Six cases of pneumonitis occurred, all in the comparator group. Four pulmonary deaths were reported, none in the leflunomide group. Leflunomide was not associated with an increased risk of total adverse respiratory events, RR 0.99 (95% CI 0.56-1.78), or infectious respiratory adverse events, RR 1.02 (95% CI 0.58-1.82). Leflunomide was associated with a decreased risk of non-infectious respiratory adverse events, RR 0.64 (95% CI 0.41-0.97).
Conclusion
Our study found no evidence of increased respiratory adverse events with leflunomide treatment.
Figure 1: Forest Plot of Total Adverse Respiratory Events
Disclosure:
R. Conway,
None;
C. Low,
None;
R. J. Coughlan,
None;
M. O’Donnell,
None;
J. J. Carey,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/leflunomide-use-is-not-associated-with-an-increased-risk-of-lung-disease-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-meta-analysis-of-randomised-controlled-trials/