Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
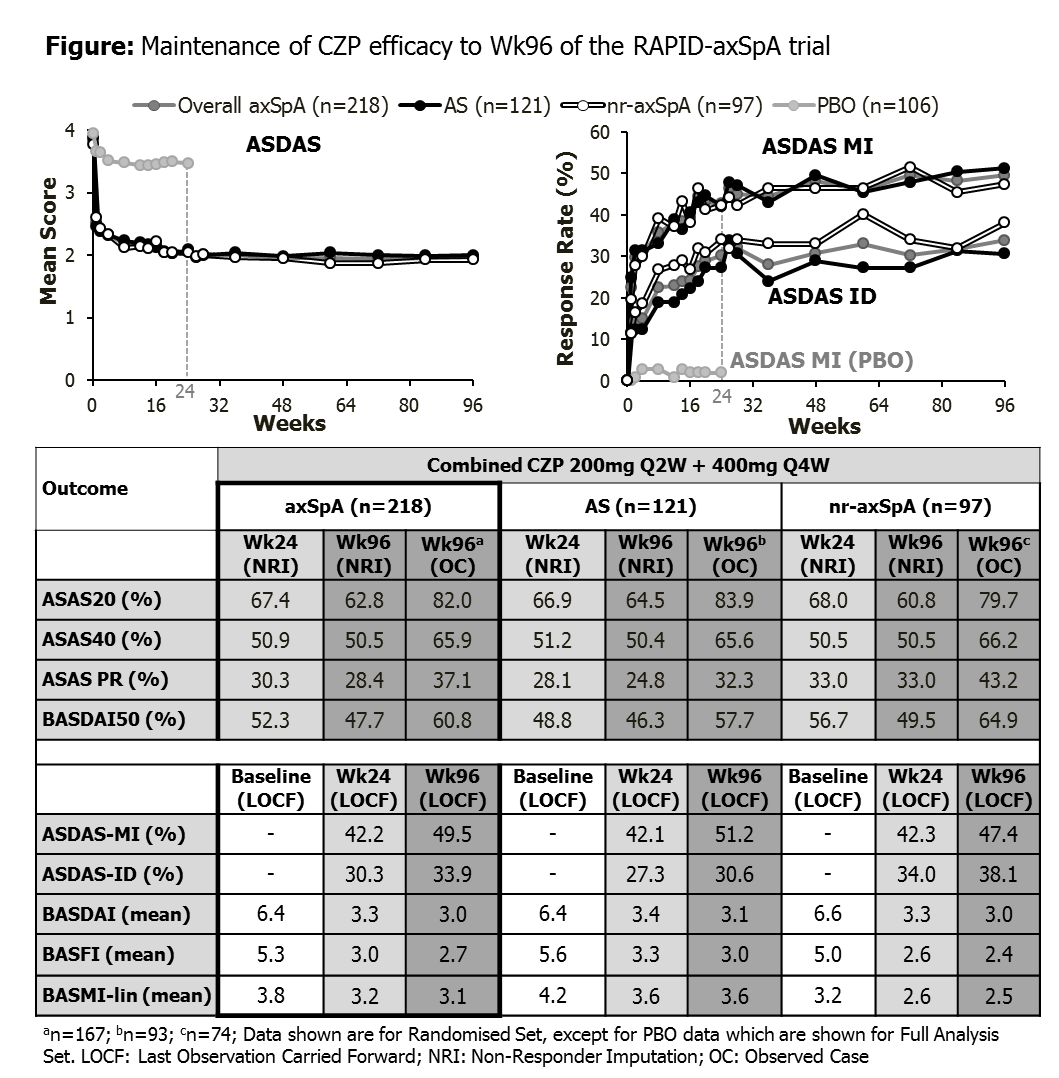
Background/Purpose: Previous reports of RAPID-axSpA (NCT01087762) demonstrated efficacy and safety of certolizumab pegol (CZP) in patients (pts) with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) including pts with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and pts with non-radiographic (nr-)axSpA to Week (Wk) 48.1 Here, we report the clinical efficacy and safety of CZP in axSpA from a 96-wk interim data cut of RAPID-axSpA.
Methods: The RAPID-axSpA trial1 is double-blind and placebo (PBO)-controlled to Wk24, dose-blind to Wk48 and open-label (OL) to Wk204. Pts fulfilled ASAS criteria and had active axSpA. Pts originally randomized to CZP (200mg Q2W or 400mg Q4W, following 400mg loading dose [LD] at Wks 0, 2, 4) continued on their assigned dose in the OL phase; PBO pts entering dose-blind phase were re-randomized to CZP LD followed by CZP 200mg Q2W or CZP 400mg Q4W after Wk24 or, for non-responders, after Wk16. We present efficacy data for all pts originally randomized to CZP (combined dose regimens). Outcome variables assessed included ASAS20/40 and BASDAI50 responses and ASAS PR, ASDAS, ASDAS ID, ASDAS MI, BASDAI, BASFI and BASMI-linear. Data are shown as observed case and with imputation (NRI for categorical measures; LOCF for continuous measures). Safety set consists of all pts treated with ≥1 dose of CZP to Wk96.
Results: 325 pts were randomized, of whom 218 received CZP from Wk0. Of CZP-randomized pts, 203 (93%) completed to Wk24, 191 (88%) to Wk48 and 174 (80%) to Wk96. The proportion of pts achieving ASAS20/40 and PR responses was maintained from Wk24 through to Wk96 (Figure). Improvements in all ASAS and ASDAS response measures, BASDAI, BASFI and BASMI-linear were maintained to Wk96 (Figure). Similar improvements were seen with both dosing regimens (data not shown) and in both AS and nr-axSpA pts. Rapid clinical improvements were also observed in pts originally randomized to PBO who switched to CZP at Wk16 or Wk24 (data not shown). In the safety set (N=315) total exposure to CZP was 486 pt-yrs. Adverse events (AEs) occurred in 279 pts (88.6%; event rate per 100 pt-yrs [ER/100PY]=360.3). The ER/100PY for serious AEs was 10.9, and for serious infections was 2.7, including 1 confirmed case of active tuberculosis. No deaths or malignancies were reported in the overall 96-wk period.
Conclusion: In RAPID-axSpA, improvements in both CZP dosing regimens observed over 24 wks in clinical efficacy and patient-reported outcomes were sustained throughout the dose-blind and OL study periods to Wk96. Similar sustained improvements were observed in both AS and nr-axSpA subpopulations. The safety profile was in line with that previously reported from the RAPID-axSpA trial, with no new safety signals observed with increased exposure.
References: 1. Landewé R. Arthritis Rheum 2013;65(10):S767
Disclosure:
J. Sieper,
Abbott, Merck, Pfizer, UCB Pharma, Novartis, Lilly, Janssen,
5,
Abbott, Merck, Pfizer, UCB Pharma, Novartis, Lilly, Janssen,
8;
M. Rudwaleit,
Abbott, BMS, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, UCB Pharma,
5;
D. M. van der Heijde,
AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Augurex, BMS, Celgene, Centocor, Chugai, Covagen, Daiichi, Eli-Lilly, Galapagos, GSK, Janssen Biologics, Merck, Novartis, Novo-Nordisk, Otsuka, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, Schering-Plough, UCB, Vertex,
5,
Imaging Rheumatology bv,
9;
W. P. Maksymowych,
Abbott, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli-Lilly, Janssen, Merck, Pfizer, Synarc and UCB Pharma,
5,
Abbott, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli-Lilly, Janssen, Merck, Pfizer, Synarc and UCB Pharma,
8;
M. Dougados,
UCB Pharma, Abbvie, Pfizer, Lilly, Novartis,
5,
UCB Pharma, Abbvie, Pfizer, Lilly, Novartis,
2;
P. J. Mease,
Abbott, AbbVie, Amgen, BiogenIdec, BMS, Celgene, Crescendo, Genentech, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma, Vertex,
2,
Abbott, AbbVie, Amgen, BiogenIdec, BMS, Celgene, Covagen, Crescendo, Genentech, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB Pharma, Vertex,
5,
Abbott, AbbVie, Amgen, BiogenIdec, BMS, Crescendo, Genentech, Janssen, Lilly, Pfizer, UCB Pharma,
8;
J. Braun,
Abbott, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Celltrion, Chugai, Johnson & Johnson, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, UCB Pharma,
5,
Abbott, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Celltrion, Chugai, Johnson & Johnson, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, UCB Pharma,
2;
A. A. Deodhar,
AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Amgen, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB,
2,
AbbVie, Amgen, Celgene, Amgen, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and UCB,
5;
B. Hoepken,
UCB Pharma,
3;
T. Nurminen,
UCB Pharma,
3;
R. B. M. Landewé,
Abbott, Ablynx, Amgen, Astra-Zeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Centocor, Glaxo-Smith-Kline, Novartis, Merck, Pfizer, Roche, Schering-Plough, UCB Pharma, Wyeth,
5,
Abbott, Amgen, Centocor, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Schering-Plough, UCB Pharma, Wyeth,
2,
Abbott, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Centocor, Merck, Pfizer, Roche, Schering-Plough, UCB Pharma, Wyeth,
8.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/safety-and-efficacy-of-certolizumab-pegol-over-96-weeks-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-including-ankylosing-spondylitis-and-non-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis/