Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Vascular adhesion molecule-1 Overexpression in collagen-induced arthritis: modeling vascular dysfunctionS in rheumatoid arthritis
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) patients are at risk of developing primary coronary heart disease earlier than general population. Increased cardiovascular risk in RA is attributed to both traditional Framingham risk factors and systemic inflammation over a long period.
Limited experimental data exist on vascular involvement in arthritis models.
The aim of our study was to model vascular dysfunctions and inflammation in RA using CIA. We focused on VCAM-1, IL-17 and iNOS expression in aorta removed 15 weeks after arthritis induction.
Methods:
Arthritis was induced in C57BL mice (11 week old) by 2 injections within 21 days of chicken CII (cCII) emulsioned in Adjuvant (CFA). Half of these mice (n=12) were fed with a hyperlipidic diet (HD and the other half (n=12) with a standard diet. The control mice were not immunized (NI) but were fed either the standard diet (n=12) or HD (n=12). Aorta and synovial membranes were removed 15 weeks after the first immunization. We analysed VCAM-1, iNOS and IL-17 mRNA level in aorta by real time quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR). VCAM-1 localisation in the aortic sinus layers (intima, media and adventitia) was determined by immunohistochemistry (IHC).
Results:
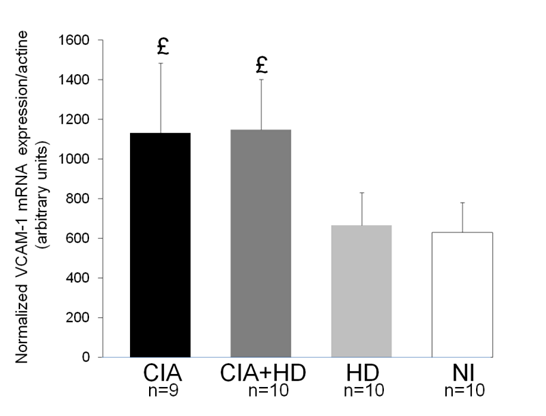
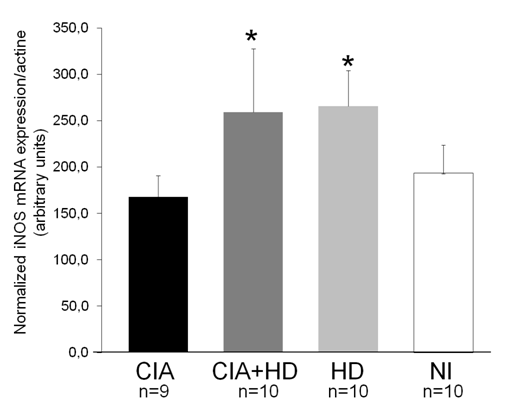
VCAM-1 expression was increased in aorta from CIA mice compared to NI mice, regardless of the fed diet (fig.1). Conversely, iNOS expression was increased in aorta from HD fed mice, whether immunized or not (fig.2). The expression of IL-17 in the aorta was not affected by collagen immunization or diet
Conclusion:
CIA in C57BL6 mice is accompanied by large vessel inflammation. Collagen immunization induced vascular dysfunctions marked by VCAM-1 overexpression independently of the diet. Conversely, HD diet induced a distinct profile of vessel inflammation characterized by high iNOS expression. CIA may be a pertinent model to study cardiovascular disease in RA.
£: p<0.05 vs.HD and NI *: p<0.05 vs. CIA and NI
Disclosure:
L. Semerano,
None;
G. Clavel,
None;
D. Lemeiter,
None;
M. C. Boissier,
None;
A. Denys,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/vascular-adhesion-molecule-1-overexpression-in-collagen-induced-arthritis-modeling-vascular-dysfunction-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/