Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: A physician global estimate (DOCGL) of patient clinical status in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is scored by many rheumatologists entirely based on inflammation, but others may incorporate joint damage and chronic pain, which may affect many RA patients. To address this matter, three 0-10 physician global visual analog subscales (VAS) have been developed to estimate levels of a) inflammation, b) damage, and c) “unexplained symptoms” (e.g., fibromyalgia), in addition to d) overall status.
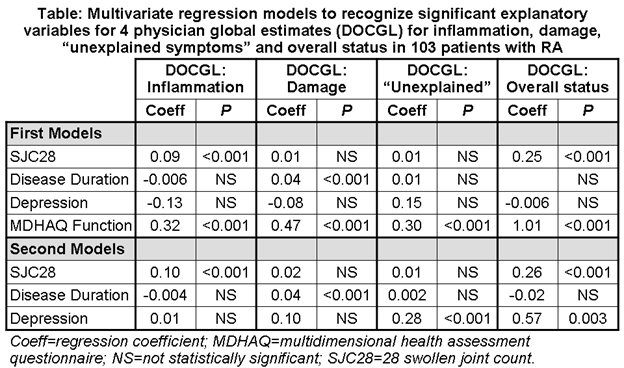
Methods: A random visit was analyzed of all 103 patients with RA seen between Dec 2007 and March 2011 in the private practice of one rheumatologist. All patients complete a multidimensional health assessment questionnaire (MDHAQ) at each visit, which includes 10 physical function items (MDHAQ-FN) and a query, “Are you able to deal with feelings of depression or feeling blue?” with 4 response options in the patient-friendly HAQ format: without any difficulty (=0), with some difficulty (=1), with much difficulty (=2), and unable to do (=3). A formal 28 tender and swollen joint count is performed in all patients with RA. Duration of disease, and 4 DOCGL 0-10 VAS estimates for inflammation, damage, “unexplained’” and overall status are assigned by the rheumatologist. Regression models were computed to explain variation in each of the 4 DOCGL estimates according to variables that were correlated significantly with at least one DOCGL estimate, including swollen joint count (SJC28), duration of disease, depression score and MDHAQ-FN scores.
Results: Mean age of the patients was 61.3 years, disease duration 10.3 years, MDHAQ-FN score (0-10) 1.7, RAPID3 (0-30) 8.5, SJC28 4.2, depression score (0-3) 0.37. The 4 DOCGLs were recorded in about 5 seconds. MDHAQ-FN scores were independently statistically significant to explain variation in all 4 DOCGLs (Table: 1st Models); therefore, a second set of regressions not including MDHAQ-FN was computed (Table: 2nd Models). Variation in DOCGL-Inflammation was explained significantly by SJC28, but not by disease duration or depression score, in both models. Variation in DOCGL-Joint Damage was explained significantly by disease duration, but not by SJC28 or depression score, in both models. Variation in DOCGL-“Unexplained Symptoms” was explained significantly only by MDHAQ-FN in the first model, and by depression score, but not SJC28 or disease duration, in the second model. DOCGL-Overall Status variation was explained significantly by SJC28 (and MDHAQ-FN) in the first model, and SJC28 and depression score in the second model, but not by disease duration.
Conclusion: Variation in DOCGLs for inflammation, damage and “unexplained symptoms” are explained significantly by MDHAQ-FN and/or only 1 of 3 other measures: SJC28, disease duration, and patient self-report depression score, respectively. The 4 DOCGLs have face validity, and are recorded in about 5 seconds.
Disclosure:
I. Castrejón,
None;
M. J. Bergman,
None;
T. Pincus,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quantitation-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-of-inflammation-joint-damage-and-unexplained-symptoms-e-g-fibromyalgia-in-addition-to-overall-status-according-to-4-physician/