Session Information
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Human Etiology and Pathogenesis II: Citrullination, Autoantibodies and Genes
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) risk is strongly associated with variations within the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) region, and in particular to HLA-DRB1 alleles. We aimed to fine-map RA risk alleles within the MHC in Asian populations and conduct trans-ethnic risk comparison to those in European populations.
Methods: We analyzed 2,782 anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA)-positive RA cases and 4,315 controls from Chinese and Korean populations. We applied HLA imputation to infer genotypes at eight class I and II HLA genes (HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C, HLA-DRB1, HLA-DQA1, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DPA1, HLA-DPB1) using SNP2HLA software and a newly constructed pan-Asian imputation reference panel.
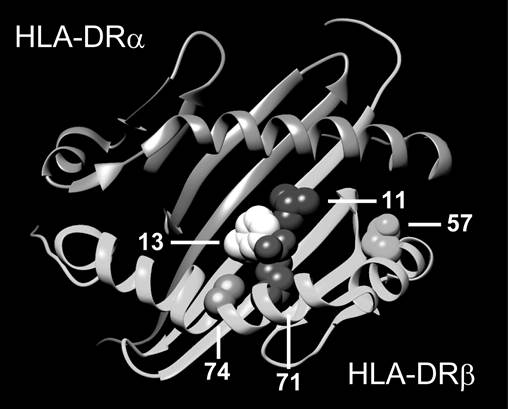
Results: We obtained highly accurate imputation of HLA classical alleles with this reference panel (95.1% and 82.4% concordance for two and four digit classical alleles respectively). We observed the most significant association in HLA-DRb1 at amino acid position 13 (Pomnibus = 6.9×10-135), located outside the classical shared epitope (SE). The individual residues at position 13 have relative effects that are consistent with published effects in European populations (His>Phe>Arg>Tyr≈Gly>Ser) – but Asian effects are generally smaller. Applying stepwise conditional analysis, we identified additional associations at positions 57 (conditional Pomnibus = 2.2×10-33) and 74 (conditional Pomnibus = 1.1×10-8). Outside of HLA-DRb1, we observed independent effects for amino acid polymorphisms within HLA-B (Asp9, conditional P = 3.8×10-6) and HLA-DPb1 (Phe9, conditional P = 3.0×10-5) concordant with European populations. While a common set of amino-acid residue effects in three HLA genes are shared between European and Asian populations, these same effects can induce different classical allelic associations (e.g. HLA-DRB1*09:01) in the two populations due to differences in allele frequencies.
Conclusion: Our trans-ethnic study reveals that a common set of amino-acid residue effects in three HLA genes are largely shared between European and Asian populations. Our study illustrates the value of high-resolution imputation for fine-mapping causal variants in the MHC.
Disclosure:
Y. Okada,
None;
K. Kim,
None;
B. Han,
None;
N. E. Pillai,
None;
R. T. H. Ong,
None;
W. Y. Saw,
None;
M. Luo,
None;
L. Jiang,
None;
J. Yin,
None;
S. Y. Bang,
None;
H. S. Lee,
None;
M. A. Brown,
None;
S. C. Bae,
None;
H. Xu,
None;
Y. Y. Teo,
None;
P. I. de Bakker,
None;
S. Raychaudhuri,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/fine-mapping-major-histocompatibility-complex-associations-in-acpa-positive-rheumatoid-arthritis-identified-shared-hla-amino-acid-polymorphisms-in-asian-and-european-populations/