Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose:
Adherence reported in the literature for RA varies widely (49.5-98%)1. This variability may result in part from different methods used to measure adherence. Our aim was to examine whether adherence is influenced by the method used to measure it through a meta-analysis. We also conducted a systematic literature review (SLR) on factors that are associated with adherence.
Methods:
Systematic literature review was conducted using PubMed and Cochrane central database as well as associated reference lists from reviews from 1970 to Nov. 2012. Papers were included if they reported DMARD adherence data or factors associated with adherence in adult RA patients and if adherence was defined. Aspirin/NSAID or non pharmaceutical therapy were excluded. Papers were divided according to the method used to measure adherence. A Random effects model estimated adherence and a Binomial significance test was used to identify significant factors associated with adherence.
Results:
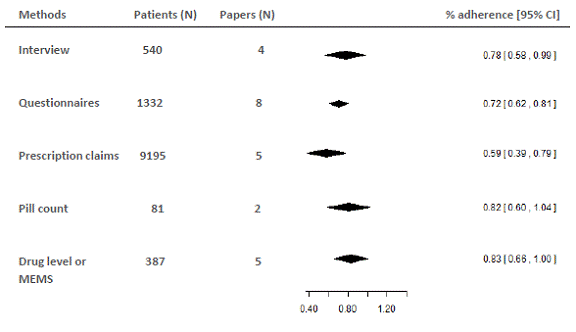
Out of an initial 273 articles, 26 papers were included, including 34,700 RA patients. Figure 1 details the results of the meta-analysis for adherence, showing 2-8 articles for each method. Adherence rates were statistically similar when measured by interview, questionnaires, pill count, drug level or medication effect monitoring system (MEMS), although there was an 11% mean numerical range. There was a numerically but not statistically lower adherence when measured by prescription claims (0.59 for prescription claims versus 0.72-0.83 for the other methods).
Associated factors- Three factors were associated with increased adherence. 1.Patients belief about the necessity of medications and the ability to control pain, disease activity or negative mood related to arthritis. 2. Use of Infliximab compared to either Etanercept, Methotrexate or Anakinra. 3. Use of DMARDs prior to anti TNF therapy. Two factors were associated with decreased adherence, use of Sulfasalazine compared to Methotrexate and use of Anakinra compared to Etanercept. Limitations- there were few articles using any one method and quality was variable, resulting in increased variability and decreased ability to separate the methods.
Conclusion:
There was a numerical tendency for decreased rate of adherence when measured by prescription claims versus the other methods. Patient beliefs and specific DMARDs are associated with adherence.
Ref.
1. Pasma A et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum, 2013.
Disclosure:
A. Scheiman-Elazary,
None;
C. Shourt,
None;
M. C. Hay,
None;
D. Furst,
AbbVie,
2,
Actelion Pharmaceuticals US,
2,
Amgen,
2,
BMS,
2,
Gilead,
2,
GSK,
2,
NIH,
2,
Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation,
2,
Pfizer Inc,
2,
Roche/Genentech,
2,
UCB,
2,
Janssen Pharmaceutica Product, L.P.,
5.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-meta-analysis-and-systematic-literature-review-effect-of-the-method-used-to-measure-adherence-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-on-its-rate-and-evaluation-of-associated-factors/