Session Information
Title: Imaging of Rheumatic Diseases I: Imaging in Gout, Pediatric, Soft and Connective Tissue Diseases
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Structural joint damage, including erosion, joint space narrowing (JSN) and new bone formation (NBF), is frequently observed in patients with tophaceous gout. Although imaging studies have implicated tophi in the development of these changes, the relationship between monosodium urate (MSU) crystals and structural joint damage has not been examined. The aim of this work was to examine the relationship between joint damage and MSU crystal deposition in patients with tophaceous gout.
Methods: Plain radiographs and dual energy computed tomography (DECT) scans of the feet were prospectively obtained from 92 patients with tophaceous gout. Two readers analysed the 10 metatarsophalangeal joints (MTPJs) for the presence of MSU crystals using DECT (920 total joints analysed, inter-reader agreement 94.2% and kappa 0.82). For the purposes of analysis, DECT MSU crystal deposition was considered present if recorded by both readers. A further reader, who was blinded to the DECT results, scored the same joints on plain radiography for Sharp-van der Heijde erosion score (0-10), JSN score (0-4) and presence of NBF features (spur, sclerosis and osteophyte).
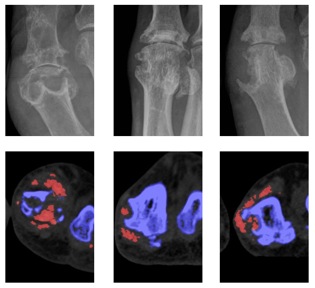
Results: DECT MSU crystal deposition was more frequently observed in joints with erosion (odds ratio (OR) 11.2), JSN (OR 5.1), spur (OR 13.4), osteophyte (OR 5.3) and sclerosis (OR 9.1), p <0.0001 for all. For those joints with any erosion, erosion scores were higher in joints with DECT urate deposition compared with those without MSU crystals (mean (SD) erosion scores 5.2 (2.7) and 3.3 (2.11) respectively, p<0.0001). A strong linear relationship was observed in the frequency of joints affected by MSU crystals with increasing radiographic erosion score (p<0.0001). In contrast, for those joints with any narrowing, JSN scores were no different in those with and without DECT urate deposition (p=0.75). DECT MSU crystal deposition and all features of joint damage were most frequently observed at the 1st MTPJ (Figure). There was a very high correlation between the number of joints at each site affected by MSU crystal deposition and all features of radiographic joint damage (r>0.88 for all, p<0.05 for all).
Conclusion: MSU crystals are frequently present in joints affected by radiographic damage in patients with gout. These findings support the concept that MSU crystals directly interact with articular tissues to influence the development of structural joint damage in this disease.
Figure: Examples of plain radiographs (upper panel) and corresponding axial DECT images (lower panel) of eroded 1st MTPJs from three separate participants. MSU crystals are shown as red on DECT images.
Disclosure:
N. Dalbeth,
None;
O. Aati,
None;
R. Kalluru,
None;
A. Horne,
None;
A. Doyle,
None;
F. M. McQueen,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/relationship-between-structural-joint-damage-and-urate-deposition-in-gout-a-site-by-site-analysis-using-plain-radiography-and-dual-energy-computed-tomography/