Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Calcinosis affects approximately 25% of patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) and is associated with substantial morbidity. There are currently no validated outcome measures to assess calcinosis severity. We sought to develop and validate a novel radiographic scoring system for calcinosis affecting the hands of patients with SSc for potential use in future clinical trials.
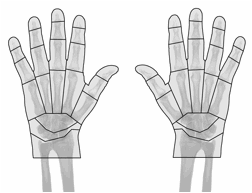
Methods: We assessed the reliability of two types (termed “simple” and “complex”) of radiographic scoring systems using hand radiographs from patients with SSc obtained from the University of Manchester. The simple scoring system defined calcinosis severity as mild (single site of low density), moderate (medium density at one or more sites OR a single site of high density), or severe (more than one site of high or mixed density). The complex scoring system was calculated as the sum of scores for 22 weighted areas affecting each hand: % area coverage (0-100) X density (1-3) X weight for each area (Figure 1). Following a 1-hour teleconference training session, 12 investigators (8 rheumatologists, 1 dermatologist, 3 radiologists) scored 12 hand radiographs in random order using both simple and complex scoring systems. After a minimum of 24 hours, each investigator re-scored at least one radiograph. Inter-rater and intra-rater reliability were assessed using a Fleiss kappa or weighted kappa coefficient for the simple system, and intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) for the complex system.
Results: Of 144 assessments, 10 were categorized as mild, 67 as moderate, and 67 as severe using the simple scoring system. The mean time to complete the complex scoring system was significantly longer than the simple scoring system (4.0 vs. 0.4 min, p<.0001), and increased with increasing severity of calcinosis (2.0±1.2 min for mild, 3.2±2.3 min for moderate, 5.1±3.7 min for severe). Overall inter-rater reliability for the simple scoring system was poor (kappa=0.39, 95% CI 0.1-0.52), but improved if dichotomized as mild/moderate vs. severe (kappa=0.51, 95% CI 0.26-0.7). Inter-rater reliability was excellent for the complex scoring system (ICC=0.89, 95% CI 0.86-0.92). Intra-rater reliability was moderate for the simple scoring system (kappa=0.67, 95% CI 0.37-0.96), but almost perfect for the complex scoring system (ICC=0.93, 95%CI 0.89-0.97).
Conclusion: We developed a novel radiographic scoring system that accounts for the area coverage, density, and anatomic location of calcinosis affecting the hands in patients with SSc. This scoring system is feasible with excellent reliability and should undergo further validation testing for use in clinical trials.
Figure 1. Anatomic Regions of Hand Radiographs for Complex Scoring System
Disclosure:
L. Chung,
None;
A. M. Valenzuela Vergara,
None;
D. Fiorentino,
None;
K. Stevens,
None;
S. Li,
None;
J. Harris,
None;
C. E. Hutchinson,
None;
S. Assassi,
None;
L. Beretta,
None;
S. Lakshminarayanan,
None;
T. Rodriguez Reyna,
None;
C. P. Denton,
None;
R. G. Taillefer,
None;
S. Tatibouet,
None;
A. Herrick,
None;
M. Baron,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validation-of-a-novel-radiographic-scoring-system-for-calcinosis-affecting-the-hands-of-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis/