Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 12:00PM-12:15PM
Background/Purpose: Idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM) is a rare, systemic, autoimmune, rheumatic disease, with different subtypes, characterized by muscle weakness and extra-muscular involvement. There are no approved targeted treatments indicated for multiple IIM subtypes. Efgartigimod is an IgG1 antibody Fc fragment engineered for high neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) affinity. ALKIVIA evaluates the safety and efficacy of subcutaneous (SC) efgartigimod PH20 (coformulation of efgartigimod and recombinant human hyaluronidase PH20; EFG) plus standard of care (SOC) vs placebo PH20 (PBO) plus SOC in patients with IIM.
Methods: ALKIVIA (NCT05523167) is an operationally seamless phase 2/3, randomized, double-blinded, PBO-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter study in adults with IIM. The completed phase 2 randomized 89 patients (1:1) with immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy, dermatomyositis, polymyositis, or anti-synthetase syndrome, meeting ACR/EULAR classification criteria to receive weekly EFG or PBO alongside SOC for IIM. The primary endpoint was the 2016 ACR/EULAR Total Improvement Score (TIS) at Week 24, a composite endpoint based on improvement in Physician’s Global Disease Activity (MDGA), manual muscle testing-8 (MMT8), muscle enzymes, Patient Global Disease Activity (PGA), Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI), and Extra-muscular Global Disease Activity. Key secondary endpoints were time to TIS, proportion of patients with TIS ≥20 and ≥40, changes in MMT8, PGA, and MDGA at Week 24.
Results: Of the 89 participants, 76.4% were female and 71.8% white, with a mean (SD) age of 56.6 (13.3) years. Least-squares mean TIS at Week 24 was statistically significantly higher in the EFG than the PBO arm (50.45 vs 35.65; P=0.0004). EFG-treated participants showed significant improvement in all key secondary endpoints compared with PBO, including the proportion of participants with minimal (≥20) and moderate (≥40) TIS, and the exploratory endpoint of major (≥60) TIS (91.5 vs 73.8%; 78.7 vs 47.6%, P=0.0029; and 34.0 vs 9.5%, P=0.0055, respectively) (Figure 1). Median times to TIS ≥20 and ≥40 were shorter with EFG compared to PBO (30 vs 71.5 days, P=0.0020; 113 days vs not estimable, P=0.0293). EFG treatment improved all 6 core set measures (Figure 2A). Both Patient and Clinician Global Impression of Change “much/moderately better” were improved at Week 24 with EFG vs PBO (54.4% vs 40.4%, and 60.8% vs 38.1%, respectively; Figure 2B). Significant improvements were seen in MMT8 (LSM 15.16 vs 7.60, P=0.0011), PGA (LSM –2.72 vs –1.03, P=0.0015), and MDGA (LSM –2.88 vs –1.94, P=0.0379). Safety was comparable between treatment arms (Table 1), with the most common AEs in the EFG arm being injection site erythema (23.4%), rash (17.0%), bruising (10.6%) or reaction (10.6%), and diarrhea (12.8%). Two deaths occurred in the EFG arm (both unrelated to study drug) and none in the PBO arm.
Conclusion: ALKIVIA, the first FcRn inhibitor study in IIM, established proof of concept and highlights the mechanistic relevance of FcRn inhibition in IIM. Results support further evaluation of efgartigimod PH20 SC in patients with IIM in the ongoing phase 3 part of the study.
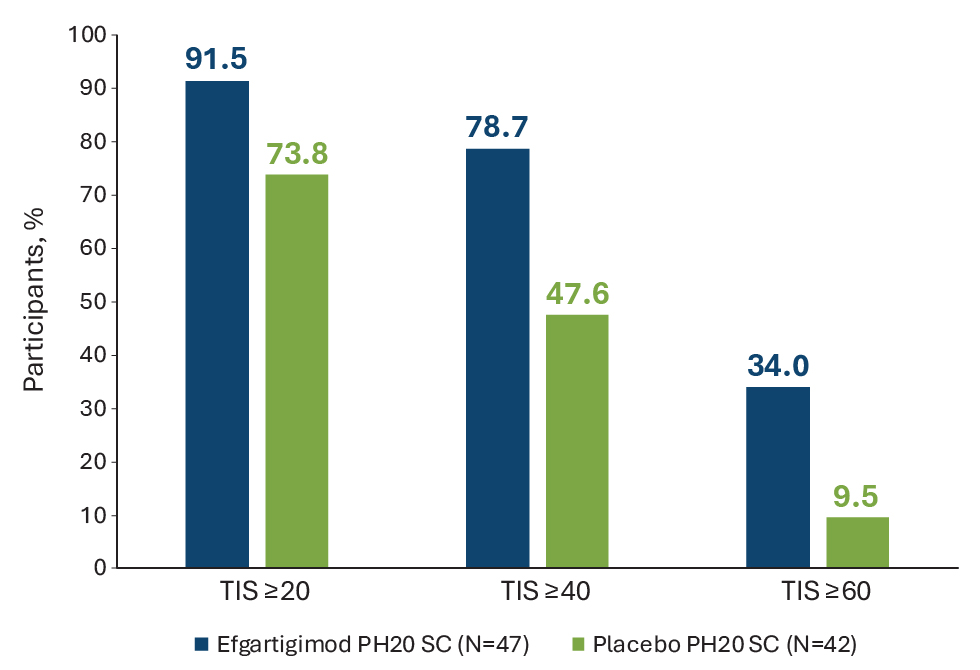 Figure 1. Proportion of participants with TIS ≥20, ≥40, and ≥60 at Week 24
Figure 1. Proportion of participants with TIS ≥20, ≥40, and ≥60 at Week 24
.jpg) Figure 2. (A) Percentage contribution of core set measures to total improvement score (TIS) at Week 24 in efgartigimod vs. placebo (ITT analysis set) (B) PGI-C and CGI-C at last assessment before or at Week 24.
Figure 2. (A) Percentage contribution of core set measures to total improvement score (TIS) at Week 24 in efgartigimod vs. placebo (ITT analysis set) (B) PGI-C and CGI-C at last assessment before or at Week 24.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aggarwal R, Rodriguez-Garcia S, Neto A, Papadopoulou D, Van Baelen B, Duncombe P, De Ceuninck L, van der Woning B, Chinoy H. Effect of Efgartigimod PH20 SC on Total Improvement Score, its Core Set Measures, and Patient/Clinician Impressions of Change: Results from the Phase 2 ALKIVIA Study of Adults with Active Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-efgartigimod-ph20-sc-on-total-improvement-score-its-core-set-measures-and-patient-clinician-impressions-of-change-results-from-the-phase-2-alkivia-study-of-adults-with-active-idiopathic-i/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effect-of-efgartigimod-ph20-sc-on-total-improvement-score-its-core-set-measures-and-patient-clinician-impressions-of-change-results-from-the-phase-2-alkivia-study-of-adults-with-active-idiopathic-i/

.jpg)