Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2524–2546) Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Glucocorticoids (GCs) are essential for managing giant cell arteritis (GCA) and polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR), but prolonged use poses risk due to cumulative dosing and side effects. (1) Accurate tracking of GC exposure is vital, yet electronic medical record (EMR) documentation is often inconsistent. (2) A meta-analysis of 25 studies found that the mean cumulative GC dose over one year was up to 5600 mg for PMR and 8200 mg for GCA patients. (3) We propose a natural language processing (NLP) tool to standardize GC data extraction from EMRs, an advancement over prior tools to improve care and research. (4)
Methods: Patients > 50 years of age with an ICD code for GCA or PMR were identified. Individuals without prescription GC coverage for > 75% of the first year, defined as 365 days following the initial ICD code entry, were excluded. A rule-based NLP model was created using EMR data to calculate systemic prednisone and methylprednisolone doses over time. Methylprednisolone doses were transitioned into prednisone equivalent doses at a 4:5 ratio. A validation cohort of 89 patients was created where a clinician performed chart review and documented dosage changes over time. Cumulative GC dose was estimated at 3 months and 12 months and model error recorded. The model was then applied to the entire cohort to record the average 90 day and 1-year cumulative GC dose.
Results: 956 patients met inclusion criteria. Of these, 714 had isolated PMR and 242 had GCA. 89 patients (45 GCA and 44 isolated PMR) were included for comparison of the model to physician-extracted data. The NLP-driven model compared to EMR data extracted by a physician revealed a mean relative error rate of 0.25% and 3.93% at 3 and 12 months for isolated PMR, respectively, with rates of 11.89% and 18.55% for GCA (Figure 1). Bland-Altman plots in Figure 2 showed low systemic bias (90 day mean difference 61.0, 95% CI -295.4 to 417.47; 1 year mean difference -512.1, 95% -1119.1 to 94.8). The mean cumulative full cohort dose is described in Figure 3.
Conclusion: The mean 1-year cumulative GC doses observed in our cohort for GCA and PMR are consistent with previous studies. An NLP-based model is a valid approach for estimating GC exposure over time. This can have relevance in large datasets and EMR’s where GC doses have been difficult to calculate.References:1. González-Gay MA BR, Rodríguez-Valverde V, Martínez-Taboada VM, Delgado-Rodriguez M, Figueroa M, Uriarte E. Permanent visual loss and cerebrovascular accidents in giant cell arteritis: predictors and response to treatment. 1998.2. Cohen GR FC, Ryan AM, Richardson CR, Adler-Milstein J. Variation in Physicians’ Electronic Health Record Documentation and Potential Patient Harm from That Variation. J Gen Intern Med. 2019.3. Lai LYH HE, West RM, Mackie SL. Association between glucocorticoid therapy and incidence of diabetes mellitus in polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. RMD Open. 2018.4. Hannah L Weeks CB, Elizabeth McNeer, Michael L Williams, Cosmin A Bejan, Joshua C Denny, Leena Choi. medExtractR: A targeted, customizable approach to medication extraction from electronic health records. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association.
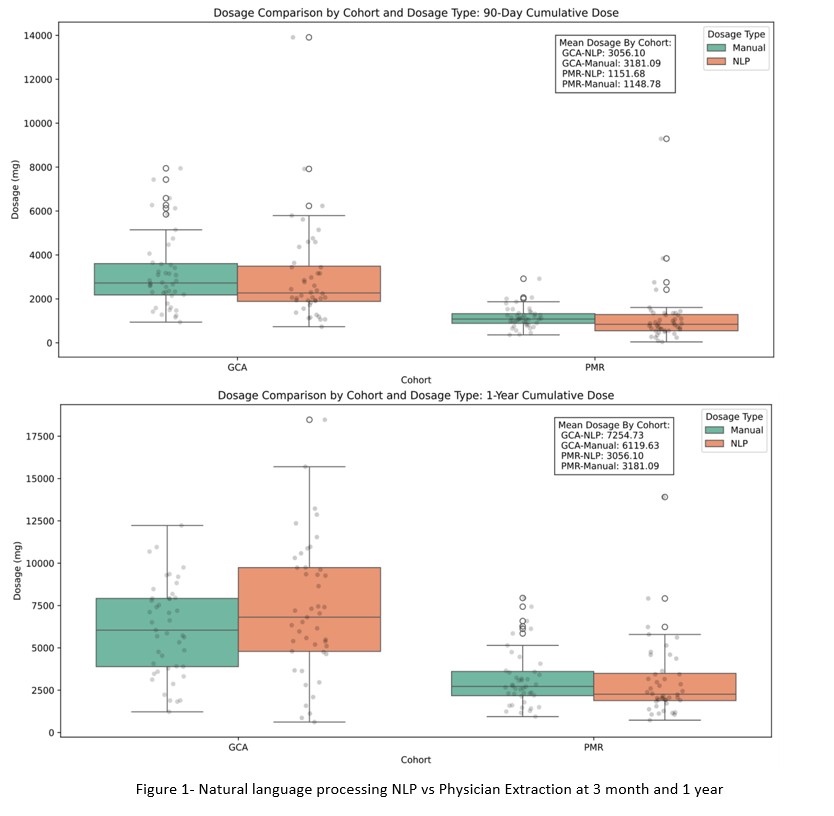 Figure 1- Natural language processing NLP vs Physician Extraction at 3 month and 1 year
Figure 1- Natural language processing NLP vs Physician Extraction at 3 month and 1 year
.jpg) Figure 2 – Bland Altman Plot of NLP model vs physician-extracted data at 3 months and 1 year
Figure 2 – Bland Altman Plot of NLP model vs physician-extracted data at 3 months and 1 year
.jpg) Figure 3 – Cumulative dose of entire GCA and PMR cohorts at 3 and 12 months.
Figure 3 – Cumulative dose of entire GCA and PMR cohorts at 3 and 12 months.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nimal S, Sullivan M, Conyers C, Rosen J, Grilli C, Warrington K, Ortega V. A Rule Based NLP Pipeline for Glucocorticoid exposure [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-rule-based-nlp-pipeline-for-glucocorticoid-exposure/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-rule-based-nlp-pipeline-for-glucocorticoid-exposure/
