Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
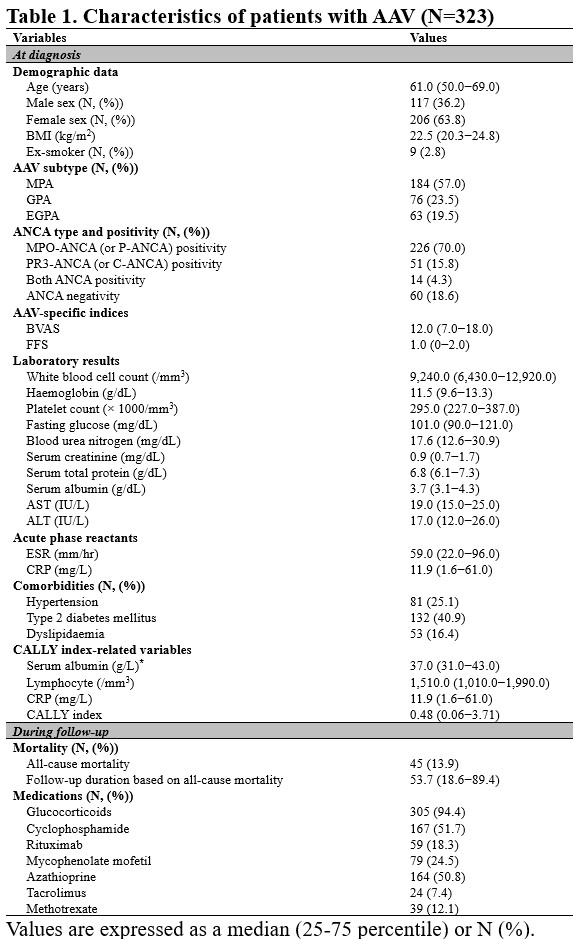
Background/Purpose: This study retrospectively investigated whether the initial C-reactive protein (CRP)-albumin-lymphocyte (CALLY) index at diagnosis can contribute to early prediction of all-cause mortality during follow-up in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV).
Methods: This study included 323 patients with AAV. Clinical data at AAV diagnosis and those during follow-up were collected. The CALLY index was calculated using the following equation: serum albumin (g/L) × lymphocyte count (/mm3) / CRP (mg/L) /10,000. The parameter of serum albumin (g/L) of an equation of the CALLY index was corrected by multiplying the measured serum albumin (g/dL) by 10.
Results: The median age was 61.0 years (36.2% male and 63.8% female). The median CALLY index was calculated as 0.48. Of the 323 patients, 45 (13.9%) died during the follow-up period of 53.7 months. In ROC curve analysis, the optimal cut-off of the CALLY index for all-cause mortality was determined as 0.55 (area 0.715). Patients with the CALLY index ≤0.55 at AAV diagnosis had a significantly higher risk for death (relative risk 7.294), and exhibited a significantly lower cumulative patients’ survival rate than those with the CALLY index >0.55. In multivariable Cox proportional hazard analysis, the CALLY index ≤0.55 (hazard ratio [HR] 3.913), age (HR 1.037) and male sex (HR 2.326) were independently associated with all-cause mortality during follow-up in patients with AAV.
Conclusion: This is the first study to demonstrate that the initial CALLY index at diagnosis could be useful in predicting all-cause mortality during follow-up in patients with AAV.
 *Serum albumin (g/L) = serum albumin (g/dL) × 10
*Serum albumin (g/L) = serum albumin (g/dL) × 10
AAV: ANCA-associated vasculitis; ANCA: antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; BMI: body mass index; MPA: microscopic polyangiitis; GPA: granulomatosis with polyangiitis; EGPA: eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis; MPO: myeloperoxidase; P: perinuclear; PR3: proteinase 3; C: cytoplasmic; BVAS: the Birmingham vasculitis activity score; FFS: the five-factor score; AST: aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: alanine aminotransferase; ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP: C-reactive protein; CALLY: C-reactive protein-albumin-lymphocyte.
.jpg) Fig. 1 Relative risk of the initial CALLY index for all-cause mortality
Fig. 1 Relative risk of the initial CALLY index for all-cause mortality
(A) The cut-off of the CALLY index was determined as 0.55 using ROC curve analysis. (B) Patients with the CALLY index ≤0.55 at AAV diagnosis had a higher risk for death than those without.
CALLY: C-reactive protein-albumin-lymphocyte; ROC: receiver operating characteristic; AAV: ANCA-associated vasculitis; ANCA: antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody; RR: relative risk; CI: confidence interval.
.jpg) Fig. 2 Cumulative survival rates
Fig. 2 Cumulative survival rates
Patients with the CALLY index ≤0.55 at AAV diagnosis exhibited a significantly lower cumulative patients’ survival rate than those without.
CALLY: C-reactive protein-albumin-lymphocyte; AAV: ANCA-associated vasculitis; ANCA: antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ha J, Lee S. Contribution of the CALLY index at diagnosis to early prediction of all-cause mortality in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/contribution-of-the-cally-index-at-diagnosis-to-early-prediction-of-all-cause-mortality-in-patients-with-anca-associated-vasculitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/contribution-of-the-cally-index-at-diagnosis-to-early-prediction-of-all-cause-mortality-in-patients-with-anca-associated-vasculitis/
