Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2470–2503) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a rare autoimmune disease characterized by endothelial dysfunction, self-reactive immune response and progressive systemic fibrosis1. It is well established that bone micro- and macroarchitectural damage is more prevalent in patients (pts) with SSc compared to healthy subjects(HS)2. Moreover, in SSc pts severe microvascular damage exhibit significant alterations in bone health, indicating a strong connection between microvascular dysfunction and muscle/bone impairment3. Consequently, the impaired peripheral microcirculation may contribute to the development of localized hand osteoporosis in SSc. The aim of this study was to assess the hand bone quality in SSc pts in correlation with peripheral microcirculatory status assessed with NVC analysis.
Methods: Hand (left and right) and total BMD and BMC were assessed by DXA and a dedicated software (GE Lunar, USA) in 32 SSc pts (age 61 ± 14 years, 94% women) affected by limited or diffuse cutaneous (dcSSc 47%) according to the 2013 EULAR/ACR criteria and 30 age-matched HS. Progressive peripheral microvascular damage, assessed by validates nailfold capillaroscopy (NVC)4. Statistical analysis was carried out by non-parametric tests and logistic regression analysis was performed to examine the influence of the capillary loss and hand bone status.
Results: Data revealed significantly lower hand BMD and BMC values (mean±SD) in SSc pts and age matched HS (BMD 0.31 ± 0.07vs 0.39 ± 0.06, p < 0.01; BMC 21.27±7.32 vs 30.09 ± 7.8, p< 0,01). The presence of SSc was associated with lower hand BMD compared with HS (adjusted for age, gender, BMI and history of osteoporosis; Beta= -0.2234, p = 0.025). In SSc pts a positive correlation was observed between hand and both spine vertebral bodies values (r(30) = 0.4671, p = 0.007) and femoral bone status (Neck r(30) = 0.3866, p = 0.029; total r(30) = 0,354, p = 0,047). Clinical, laboratory and NVC correlations have been performed (Table I). The regression analysis revealed that reduced capillary count significantly accounted for 38.26% of the variance in BMD values (R² = 0.3826, F = 17.35, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: In conclusion, hand bone status in SSc pts was found significantly lower compared to spine and femor bone and HC as well as associated with disease severity. The hand bone damage seems linked to the microvascular insufficiency. Therefore, care to the bone status should be taken as consequence of the progressive microvasculatory damage/insufficiency in SSc.References: 1) Volkmann, E. R. et al. (2023). Systemic sclerosis. The Lancet, 401(10371), 304–318. 2) Omair, M. A. et al. (2013). Low bone density in systemic sclerosis: A systematic review. The Journal of Rheumatology, 40(11), 1881–1890. 3) Paolino, S. et al. (2021). Body composition and bone status in relation to microvascular damage in systemic sclerosis patients. Journal of Endocrinological Investigation, 44(2), 255–264. 4) Smith, V. et al. (2020). Standardisation of nailfold capillaroscopy for the assessment of patients with Raynaud’s phenomenon and systemic sclerosis. Autoimmunity Reviews, 19(3), 102458.
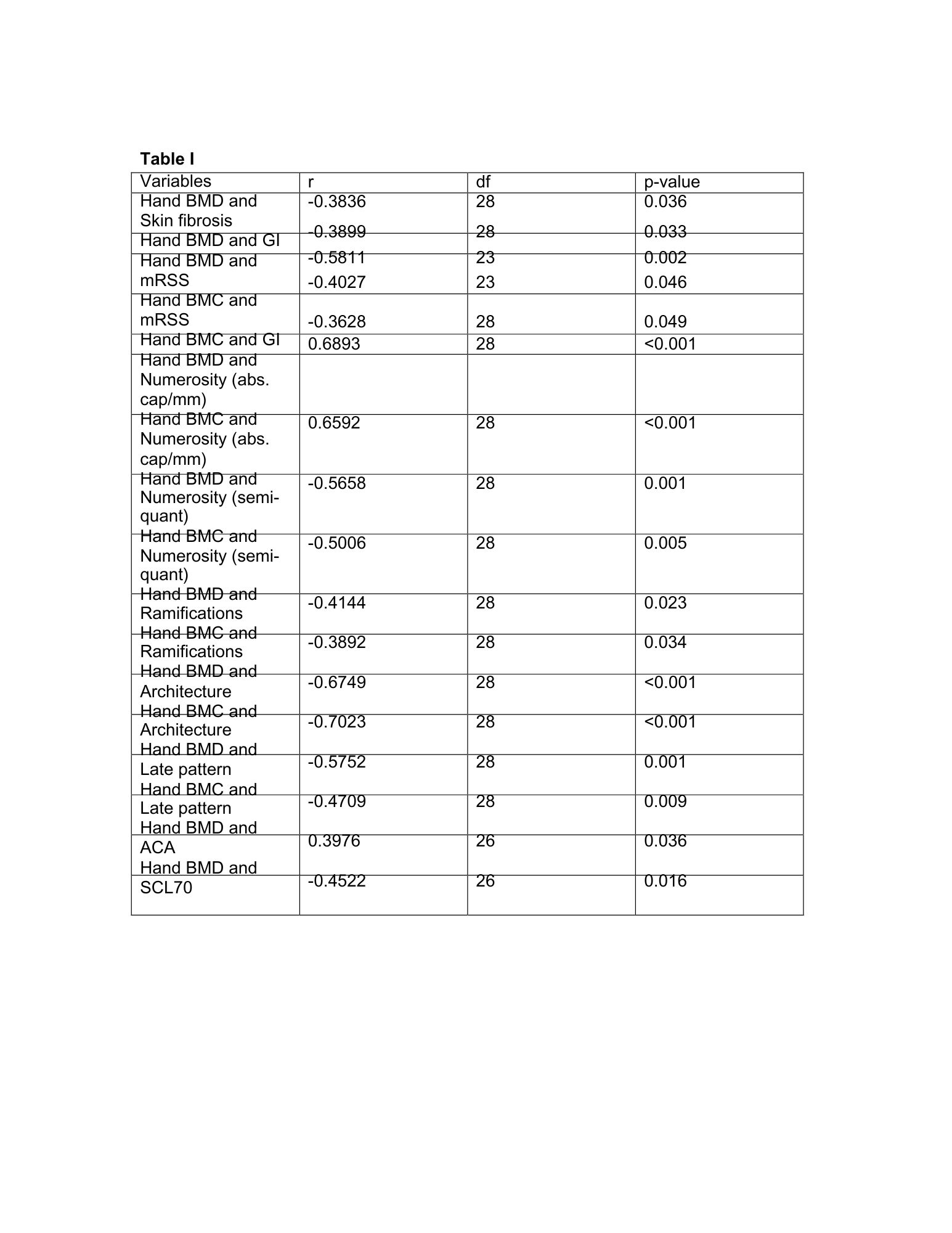 Table I. Statistically significant Spearman correlations between hand BMD and BMC and clinical features, antibody profiles, and NVC parameters in SSc patients.
Table I. Statistically significant Spearman correlations between hand BMD and BMC and clinical features, antibody profiles, and NVC parameters in SSc patients.
Abbreviations: BMD: bone mineral density; BMC: bone mineral content; SSc: systemic sclerosis; GI: gastrointestinal involvement; mRSS: modified Rodnan skin score; NVC: nailfold videocapillaroscopy; ACA: anticentromere antibodies; SCL70: anti-topoisomerase I antibodies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Campitiello R, Paolino S, Casabella A, Davoli G, Caratto E, Gotelli E, Hysa E, Pizzorni C, Smith V, Sulli A, Cutolo M. Microvascular dysfunction contributes to hand bone deterioration in SSc patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/microvascular-dysfunction-contributes-to-hand-bone-deterioration-in-ssc-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/microvascular-dysfunction-contributes-to-hand-bone-deterioration-in-ssc-patients/
