Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (2338–2376) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: We previously reported primary outcomes from a Bayesian series of N-of-1 trials comparing celecoxib, meloxicam, and naproxen in axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA), demonstrating improved ASDAS disease activity with individualized NSAID selection. Here, we present secondary outcomes evaluating function, quality of life, and safety, hypothesizing that the preferred NSAID would also yield superior patient-reported and disease-specific outcomes compared to eliminated NSAIDs.
Methods: This single-center, double-blind, randomized N-of-1 trial enrolled adults with active axSpA (ASDAS ≥2.1). Participants completed two treatment cycles in random sequence, receiving each of three NSAIDs for four weeks. Of 42 enrolled, 30 completed the full trial series and were included in the secondary analysis. Prespecified secondary outcomes included BASDAI, BASFI, BASMI, CRP, Maastricht enthesitis score (MASES), VAS Pain, VAS Global, Standard Gamble (SG), and PROPr utility scores. Bayesian multilevel models estimated both average NSAID-specific effects and within-patient comparisons between preferred and eliminated NSAIDs. Posterior probabilities of benefit (PPB) were calculated to assess clinical meaningfulness.
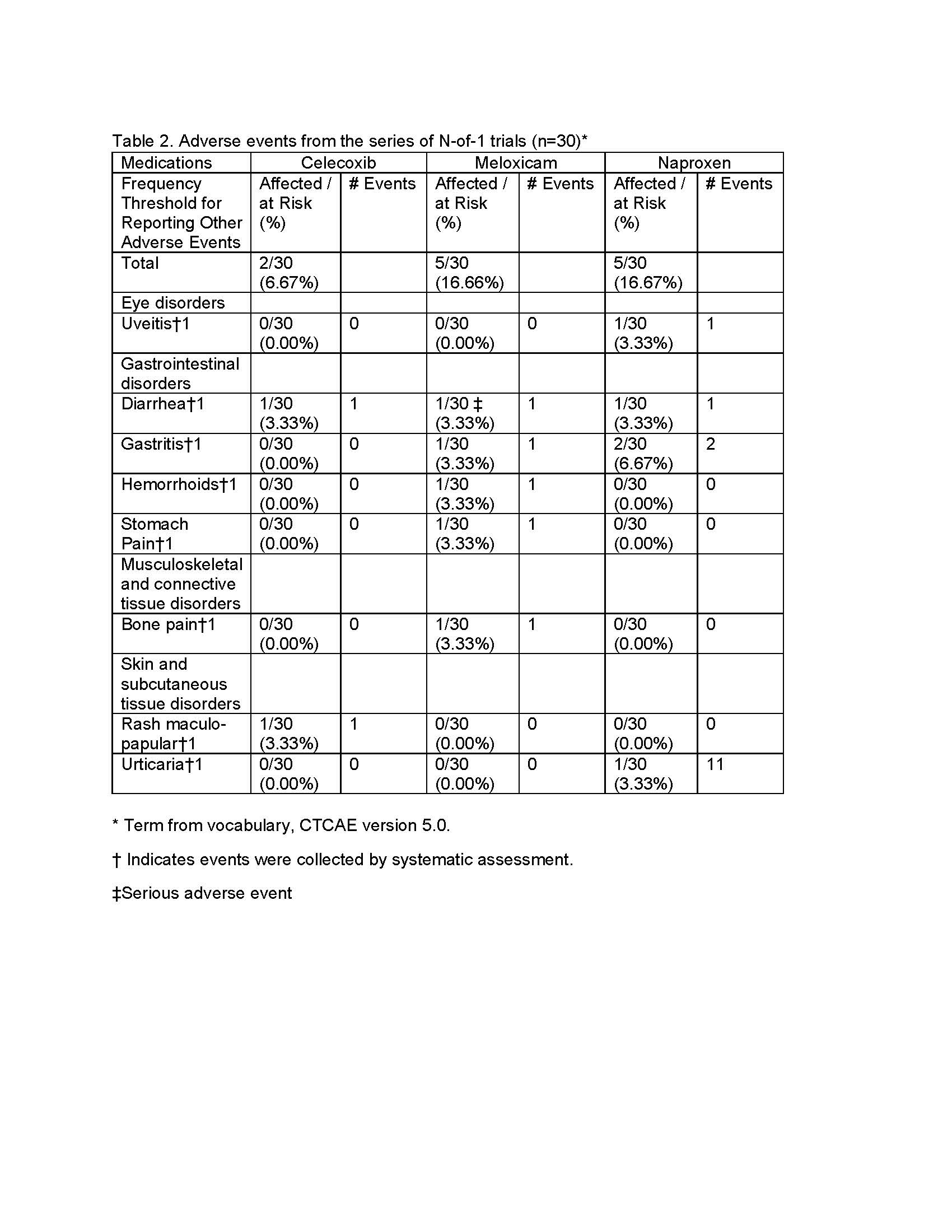
Results: The preferred NSAID was associated with substantial improvements across multiple domains. Mean differences (preferred minus eliminated) included: BASDAI 1.39 (95% credible interval [CrI]: 0.99–1.78; PPB >0.99), BASFI 0.86 (95% CrI: 0.44–1.28; PPB >0.99), BASMI 0.27 (95% CrI: 0.09–0.45; PPB >0.99), and MASES 0.65 (95% CrI: 0.05–1.24; PPB = 0.98). Smaller differences were observed for VAS Pain (1.24; CrI: –0.69 to 3.19; PPB = 0.89) and VAS Global (1.13; CrI: –0.82 to 3.06; PPB = 0.87). Utility improved with PROPr (–0.05; CrI: –0.09 to 0.00; PPB = 0.98), though SG showed nonsignificant trends. Adverse events were infrequent and mild across all NSAIDs, with only one serious adverse event (diarrhea) reported (Table 2). Average differences between NSAIDs across all patients were smaller and less consistent (Table 3).
Conclusion: Bayesian N-of-1 trials not only individualized NSAID selection in axSpA but also identified clinically meaningful improvements in function, pain, and quality of life with preferred medications. These findings support the broader utility of this personalized approach beyond disease activity metrics, offering a feasible strategy to optimize treatment in axSpA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hwang M, Kim S, Assassi S, Samuel J, Green C, Tyson J, Reveille J. Secondary Outcomes from a Series of N-of-1 NSAID Trials in Axial Spondyloarthritis: Functional, Quality-of-Life, and Safety Results from a Bayesian Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secondary-outcomes-from-a-series-of-n-of-1-nsaid-trials-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-functional-quality-of-life-and-safety-results-from-a-bayesian-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/secondary-outcomes-from-a-series-of-n-of-1-nsaid-trials-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-functional-quality-of-life-and-safety-results-from-a-bayesian-analysis/

.jpg)
.jpg)